assistant
- professor Assel K. Jumasseitova
Kazakh British technical University
Interdependence
of countries in terms of trade
In order to understand
the mechanism of interdependence between countries in terms of trade we have modified a simple model of an open
economy. The model assumes that the two countries related to the flow of
international trade and investment flows. Trade has been divided into exports and imports, because they are
different in their nature to become a national accounts. According to the
modification, import function should depend on the real exchange rate and of
disposable income. Country's exports, in turn, depends on the course and
registration of the partner country.
Very often in the study
of interaction of macroeconomic indicators is necessary to resort to finding
differences in the compared phenomena and processes. Their mathematical
expression allows a clear definition of measures of similarity or dissimilarity
between them. Figures in this case may be the index of dissimilarity (the
variance), calculated by the formula:
![]() (1)
(1)
Where - ![]() - a percantage by the factor X;
- a percantage by the factor X;
![]() - a percentage by the factor Y.
- a percentage by the factor Y.
The index of dissimilarity measure
(variance) is in the range from 0 to 100. ![]() .
.
Table 1 - Trade of Kazakhstan with partner countries, 2009. (Million
dollars).
|
Country
|
Export, $USA (Õ) |
Import,
$ USA (Y) |
|
|
|
|
Russia |
3357,0 |
9352,2 |
20,17221 |
48,99928 |
28,82707 |
|
China |
3279,3 |
5226,7 |
19,70501 |
27,38434 |
7,679329 |
|
Italy |
3144,6 |
874,1 |
18,8959 |
4,579841 |
14,31606 |
|
Germany |
3716,8 |
1999,4 |
22,33407 |
10,47537 |
11,8587 |
|
France
|
2236,5 |
923,4 |
13,43937 |
4,838088 |
8,60128 |
|
USA
|
907,5 |
710,6 |
5,453438 |
3,723073 |
1,730364 |
|
Total |
16641,7 |
19086,4 |
100 |
100 |
73,0128 |
The
index of dissimilarity measure of foreign trade of Kazakhstan with the partners is about 37 units. This indicates a relatively distribution of the volumes of export-import operations in
Kazakhstan with partner countries. "Knocks out" only trade with Russia,
like a the main strategic partner in
foreign economic relations.
By carrying out analysis
of the dissimilarity index in the foreign economic activity in Kazakhstan with
partner countries on an annual basis, we can install the observed trend in this
process and, consequently, determine the strategy of international economic
relations in the future.
First step is to identify
links between exports and imports of goods in Kazakhstan with partner countries. It can be assumed that the export of goods is proportional to
their imports. The
statistical data on exports and imports is represented in Table 2.
Table 2 - Calculation
of the correlation coefficient between exports and imports of Kazakhstan in the
merchandise trade with partner countries, 2009. ($ million dollars).
|
Country
|
Export
mln
$ (Õ) |
Import Mln
$ (Y) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Russia
|
3357,0 |
9352,2 |
583,38 |
6171,13 |
3600127,11 |
340335,14 |
38082800,22 |
|
China |
3279,3 |
5226,7 |
505,63 |
2045,62 |
1034330,10 |
255664,23 |
4184546,18 |
|
Italy
|
3144,6 |
874,1 |
370,98 |
2306,94 |
855833,50 |
137628,02 |
5321961,40 |
|
Germany
|
3716,8 |
1999,4 |
943,15 |
1181,69 |
1114517,34 |
889536,64 |
1396399,92 |
|
France |
2236,5 |
923,4 |
537,08 |
2257,65 |
1212531,76 |
288452,24 |
5096972,99 |
|
USA
|
907,5 |
710,6 |
1866,07 |
2470,46 |
4610064,31 |
3482226,58 |
6103190,73 |
We
used following formula to find the correlation coefficient:
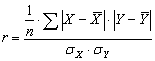 , (2)
, (2)
where ![]() - sum of deviations
from the central column 5;
- sum of deviations
from the central column 5;
n – number of observations;
![]() è
è ![]() - standard deviation
of Õ
and Y
- standard deviation
of Õ
and Y
The correlation
coefficient is 0.69. This suggests that the relationship between the two traits considered
essential. Foreign economic relations of Kazakhstan with partner countries, in
spite of all difficulties, relatively balanced.
From the solution of the linear version of the model obtained
in explicit form, it was possible to establish a positive sign of the
derivative of the national output from the issue of partner country
![]() . Modifying the derivative, we
obtain (3)
. Modifying the derivative, we
obtain (3)
![]() (4) Formula 4 is interdependence deviations editions of the partner countries of their potential value.
(4) Formula 4 is interdependence deviations editions of the partner countries of their potential value.
Modification
of the model was the basis of econometric check for interference - search the
relationship between the release of one country and lagged values of the release of the partner
country (Formula 5):
![]() , (5)
, (5)
where:
![]() - that the equilibrium output in this country
from the potential value
- that the equilibrium output in this country
from the potential value
![]() - changes in exports in
this country
- changes in exports in
this country
![]() - changes the flow of
foreign investment
- changes the flow of
foreign investment
![]() - changes in the output
of the partner country
- changes in the output
of the partner country
![]() - changes in other
factors.
- changes in other
factors.
We used data of
Kazakhstan and Russia for 14 years from 1995 to 2008 in real terms.
The resulting regression
equation is significant at the standard 5% - local level (p = 0.000) and explains 100% of the variation of the
dependent variable with three explanatory variables included in the model.
Y=-207,419+0,357X1+2,436X2+24,384X3 ,
The statistics of the Fisher criteria is
equal to F (3,10) = 541, 56, since p = 0,00000, is less than a = 0.05, then
the hypothesis of significance of the model is rejected.
To test the hypothesis that all serial correlations in the
sequence of residues equal to zero (hypothesis H0) is used the criterion of the
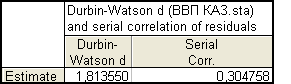
Durbin - Watson (Table 3).
In this case the statistics of the Durbin - Watson d =
1,813550, that more than the table value d2 = 1,75. Thus, the hypothesis H0: all the serial
correlations are zero is accepted at significance level 2 a = 0,1.
Table
3 - Coefficient Durbin – Watson
The constant term is negative (Formula
5), indicating that the advance of the
relative growth of resultant compared
with the relative growth factor
variables.
If exports of goods in Kazakhstan will increase by 1 percent,
then GDP will increase by 0.357 million tenge (Kazakhstani currency). If FDI
will increase by 1 percent, then GDP will increase by 2.436 million tenge, if
Russia's GDP will increase by 1 million rubles, then Kazakhstan's GDP increased
by 24.384 million tenge.
We obtained following regression equation, determining the
economic growth for 8 countries:
Y=-2,353+0,696X1-0,637X2+0,183X3-0,375X4-0,154X5+2,260X6-1,226X7+3,233X8 (6)
where Y – real GDP
per capita of Kazakhstan, %,
X1, X2, X3, X4, X5, X6, X7, X8
respectively real GDP
per capita of Russia, Ukraine, Belarus, Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan,
Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, %
The second most important factor affecting economic
development in transition economies is
inflation. We used data of Kazakhstan and Russia for
17 years from 1992 to 2008 in real terms. The
resulting regression equation (1) is
significant at the standard 5% - local level (p = 0.00030) and explains 100% of
the variation of the dependent variable in the four explanatory variables
included in the model.
To test the hypothesis that all serial correlations in the
sequence of residues equal to zero (hypothesis H0) used the criterion of the
Durbin - Watson .
In this case the statistics of the Durbin - Watson d =
1,423742, that more than the table value d2 = 1,37, consequently, thus the
hypothesis H0: all the serial correlations are zero is accepted at significance
level 2 a = 0,1.
If the population of Kazakhstan will increase by 1 million,
the GDP growth rate to decrease by 8.013%, GDP per capita by 0.110% and the
inflation rate at 0.016%, while foreign direct investment will increase by
0.587%. The character of influence of each of the above factors is different.
Thus, the population and inflation have a negative impact on GDP growth, in
contrast to other model parameters, which leads to the conclusion that an
increase in indicators of negative factors slowing the pace of economic
development of the state. One of the main reasons for the rapid growth of
public debt was a long and significant budget deficit. In our model, has
received confirmation identified on the basis of different theoretical concepts
of non-linear character of the external debt and GDP.
