Academic of the RANH, corresponding-member of the IAS
of HS,
Dr.S. (eng.). Professor,
Pil E.A. Russia,
Saint-Petersburg,
THEORY OF THE FINANCIAL CRISES
(PART II)
The
author’s earlier articles demonstrated that in order to describe the processes
taking place within a country’s economy this
economy can be viewed as the volume of the economic shell [1, 2]. This article
considers a country’s GDP as the surface area of the economic shell [3, 4, 5,
6].
GDP can
be calculated by estimating the surface area Ssu, which is affected
by external forces P. To perform the
calculation, we used four variables, i.e. Ssu (GDPsu) = f(Õ1, Õ2, Õ3, Õ4). Here we have Õ1, Õ2, Õ3 and Õ4, the variables
that influence the country’s GDP.
It
should immediately be noted that during calculation and plotting of
construction drawings, the parameters of X1, X2, X3 and X4 could be constant
values, increase or decrease by 10 times. On the basis of the calculations made, 81 graphics were built, which can be divided into
the four following groups:
•
variable values X1, X2, X3 and X4
increase and are constant;
•
variable values X1, X2, X3 and X4 decrease
and are constant;
•
variable values X1, X2, X3 and X4
decrease and increase;
•
variable values X1, X2, X3 and X4
are constant, they decrease and increase.
Figure
1 represents a two-dimensional graph of the dependence Ssu (GDPsu),
where Õ1 = Õ2 = Õ3 = 1 and Õ4 = 0,1…0,99, which shows that the initial values of Ssu
increase gradually from 14,58 to 23,77 in point 9, and then increase
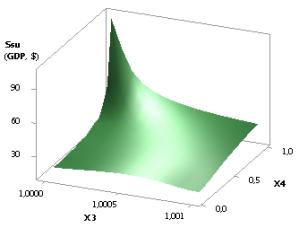
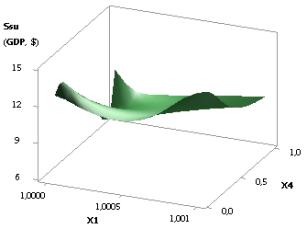
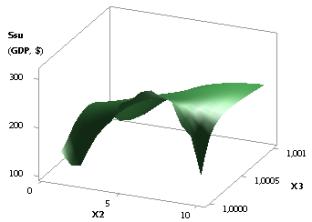
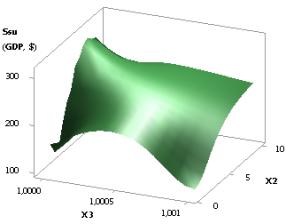
considerably to 102,86, i.e. more than three times 3,22. Figure 2 shows one 3D
graph, which allows us to see the changes of Ssu
more clearly. In this case, it makes sense for us to have the values of the
rightmost points, as at these values the value of Ssu (GDPsu),
i.e. GDP, will be at its maximum. Figure 2 is plotted with the use of variables
X3 and X4, i.e. Ssu (GDPsu) = f(Õ3, Õ4).
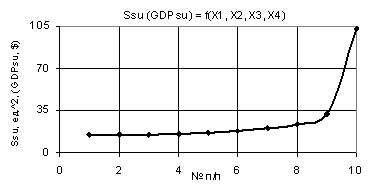
Figure 1. Dependence Ssu (GDPsu) = f(Õ1, Õ2, Õ3, Õ4)
when Õ1 = Õ2 = Õ3 = 1, Õ4 =0,1…0,99
|
|
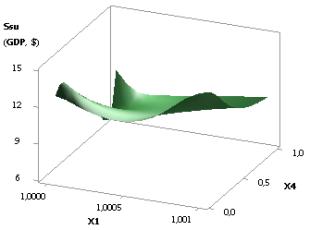
Figure 2. 3D graphic: Ssu (GDPsu)
= f(Õ3, Õ4)
when Õ1 =Õ2 = Õ3 = 1, Õ4 =0,1…0,99
Figure
3. Dependence Ssu (GDPsu) = f(Õ1, Õ2, Õ3, Õ4)
when Õ1 = Õ2 = 1, Õ3 = 1…10,
Õ4
= 0,1…0,99
|
a |
b |
|
c |
d |
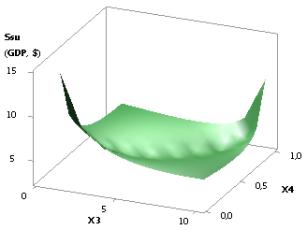
Figure 4. 3D graphics:
a - Ssu (GDPsu) = f(Õ3, Õ4); b - Ssu (GDPsu) = f(Õ2, Õ3);
c - Ssu (GDPsu) = f(Õ3, Õ2); b - Ssu (GDPsu) = f(Õ1, Õ4)
when Õ1 = Õ2 = 1, Õ3 = 1…10, Õ4 = 0,1
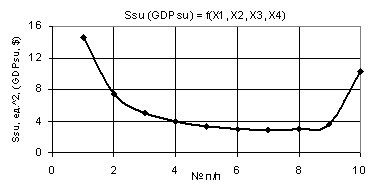
The following Fig. 3 shows that first, at Õ1 = Õ2 = 1, Õ3 = 1…10,
Õ4
= 0, 1 …0,99, the plotted curve Ssu decreases fivefold from 14,58 to the minimum of Ssumin = 2,88 in point 7, and then it
drastically increases 3,4 times to 10,29. Figure
4 demonstrates four forms of this dependence as three-dimensional graphs. Here
we must note that the form of the 3D graph depends on the choice of the applied
axes sequence. For example, in Fig. 4b
and 4c we can see 3D graphs with the
same variables Õ2
and Õ3,
but with different axes sequences. As we can see, these two graphs’ appearances
differ significantly. Based on Fig. 3, it makes sense for us to have the values of the extreme
points, as at these values the value of Ssu (GDPsu)
will be at its maximum.
The
plotted curve in Fig. 5 demonstrates that here the values of Ssu
(GDPsu) at Õ1 = Õ2 = 1…10, Õ3 = 1 and Õ4 = 0,99 are rather high, from 102,86 to 102861,38,
i.e. they have increased more than 1000 times.
Figure 6 shows the plotted 3D graph.
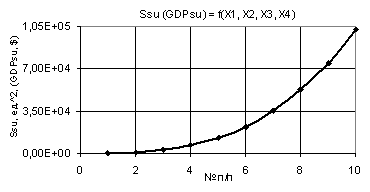
Figure 5. Dependence Ssu (GDPsu) = f(Õ1, Õ2, Õ3, Õ4)
when Õ1 = Õ2 = 1…10, Õ3 = 1, Õ4 = 0,99
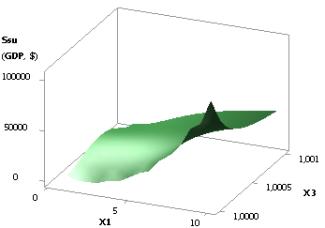
Figure 6. 3D graphic: Ssu (GDPsu) = f(Õ1, Õ3);
when Õ1 = Õ2 = 1…10, Õ3 = 1, Õ4 = 0,99
Figure
7 demonstrates the dependence of Ssu (GDPsu) at Õ1 = 1, Õ2 = Õ3 = 1…0,1 and Õ4 = 0,1…0,99. As we
see from the Figure, at first the values of Ssu (GDPsu) decrease
according to the linear dependence from 14,58 to their minimum of 6,39 at point
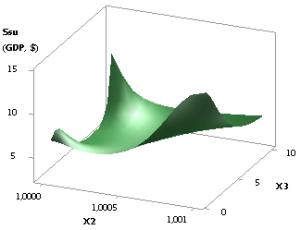
9. Then they increase in steps up to 10,29. Figure 8 shows two 3D graphs Ssu
(GDPsu) = f(Õ2, Õ1) and Ssu (GDPsu) = f(Õ1, Õ4) respectively. At
the given values of the variables, it also makes sense to choose the extreme
point values in Fig. 7, which allows us to have the maximum values of Ssu
(GDPsu).
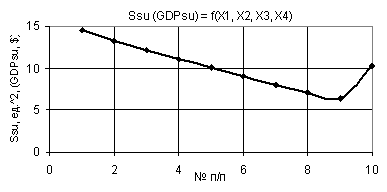
Figure 7. Dependence Ssu (GDPsu)
= f(Õ1, Õ2, Õ3, Õ4)
when Õ1 = 1, Õ2 = Õ3 = 1…0,1, Õ4 = 0,1…0,99
|
a |
b |
Figure 8. 3D graphics:
a - Ssu (GDPsu) = f(Õ2, Õ1); b - Ssu (GDPsu) = f(Õ1, Õ4)
when Õ1 = 1, Õ2 = Õ3 = 1…0,1, Õ4 = 0,1…0,99
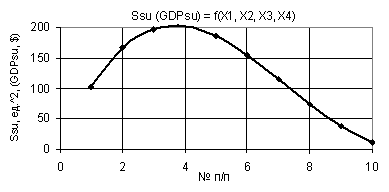
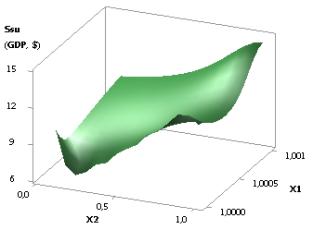
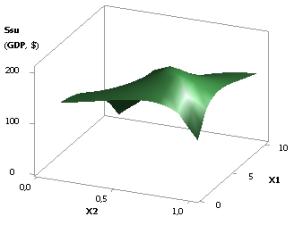
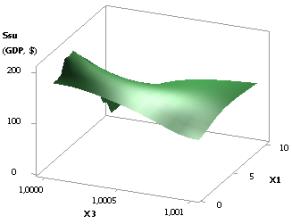
Figure 9. Dependence Ssu (GDPsu)
= f(Õ1, Õ2, Õ3, Õ4)
when Õ1 = 1…10, Õ2 = 1…0,1, Õ3 = 1, Õ4 = 0,99
The following
Fig. 9 shows that first the values of Ssu here increase from 102,86 to
their maximum of 201,64 in point 4, and then they gradually decrease to the
value of 10,29, i.e. go down nineteenfold. Figure 10 represents
three 3D graphs for Ssu (GDPsu) = f(Õ2,
Õ1),
Ssu
(GDPsu) = f(Õ3, Õ1) and Ssu (GDPsu) = f(Õ3, Õ2) respectively.
|
a |
b |
|
c |
|
Figure 10. 3D graphics: a - Ssu (GDPsu) = f(Õ2, Õ1); b - Ssu (GDPsu) = f(Õ3, Õ1);
c - Ssu (GDPsu) = f(Õ3, Õ2)
when Õ1 = 1…10, Õ2 = 1…0,1, Õ3 = 1, Õ4 = 0,99
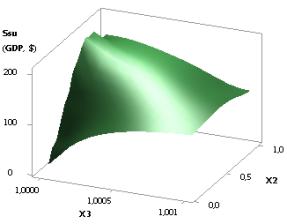
In Fig.
11 we can see that the plotted curve Ssu (GDPsu)
increases gradually from the value of 102,86 to its maximum of Ssumax = 309,72 in point 7, and then
it decreases 2,12 times to the value of 145,82. This Figure was plotted at the
following values of the variables: Õ1 = 1…0,1, Õ2 = 1…10, Õ3 = 1, Õ4 = 0,99…0,1.
For Fig.
9 and 11, it makes sense to choose the values of the variables that are close
to their maximum points.
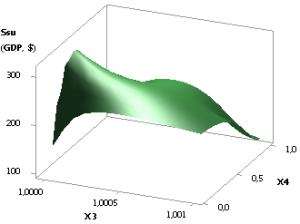
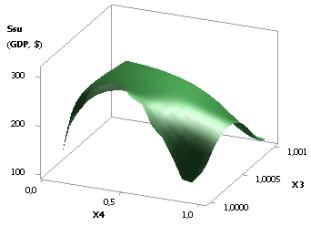
The
last Fig. 12 represents four 3D graphs of Ssu (GDPsu),
and here Figures 12a and 12b, as well as 12c and 12d are plotted
with the axes modified.
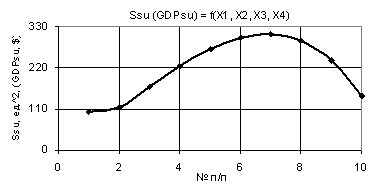
Figure 11. Dependence Ssu (GDPsu)
= f(Õ1, Õ2, Õ3, Õ4)
when Õ1 = 1…0,1, Õ2 = 1…10, Õ3 = 1, Õ4 = 0,99…0,1
After the
calculations were made, their results were gathered into a summary Table, which
contains 95 lines despite the fact that 81 two-dimensional graphs were plotted.
The reason for this is a number of plotted graphs having maximums and minimums.
This
summary Table includes such ratios as:
·
Ssub…Ssuf, where Ssub is the initial value
of the economic shell surface area, units2; Ssuf is
the final value of the economic
shell surface area, units2;
·
Ssuf/Ssub is
the ratio of the final value of the economic shell surface area to the initial
one.
The ratio of the final
value of the economic shell surface area Ssuf to the initial one Ssub shows what fold their values increased (decreased) as affected by
various external forces. Thus, having these data we can choose the values of
the variables Õ1, Õ2, Õ3 and Õ4 at which the economic shell surface area will stay unchanged or even increase under
the influence of external forces. Thus, during the financial crisis, the selected
variable values will allow preserving the country's GDPsu at the
same level, or even increasing it.
|
a |
b |
|
c |
d |
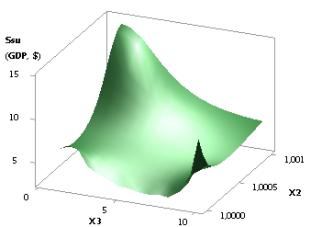
Figure 12. 3D graphics:
a - Ssu (GDPsu) = f(Õ3, Õ4); b - Ssu (GDPsu) = f(Õ4, Õ3);
c - Ssu (GDPsu) = f(Õ2, Õ3); b - Ssu (GDPsu) = f(Õ3, Õ2)
when Õ1 = 1…0,1, Õ2 = 1…10, Õ3 = 1, Õ4 = 0,99…0,1
After the summary Table with 95 lines was plotted, it
was transformed the following way, and only the values where Ssuf/Ssub ≥ 1 were left. On the basis of this transformation, we obtained
the final summary Table, which included 48 lines. Thus, we obtained 48 variants
that allow countries to come out of yet another economic crisis. Below, you can
see Table 1, which includes only a part of the summary Table with 22 lines. Here the ratios Ssuf/Ssub in the last column are
given in descending order.
Table 1 shows that there are two variants at which GDP
of a country will not change in the time of an economic crisis, even if we
change the variables. These lines are 21 and 22, where the ratios Ssuf/Ssub
= 1.
|
Table 1.
Statistics of theoretical relation Ssuf
/Ssub where Ssuf /Ssub ≥ 1 |
||||||
|
No. in sequence |
Õ1, unit |
Õ2, unit |
Õ3, unit |
Õ4, unit |
Ssub
… Ssuf, unit 2 (GDÐsub…GDÐsuf), $ |
Ssuf
/ Ssub (GDÐsuf / GDÐsub) |
|
1.
|
1…10 |
1…10 |
1…0,1 |
0,1…0,99 |
14,58…1,029E+06 |
70539,88 |
|
2.
|
1…10 |
1…10 |
1…0,1 |
0,99 |
102,86…1,03E+06 |
10000,0 |
|
3.
|
1…10 |
1…10 |
1 |
0,1…0,99 |
14,58…1,03E+05 |
7053,99 |
|
4.
|
1 |
1…10 |
1…0,1 |
0,1 …0,99 |
14,58…1,03E+05 |
7053,99 |
|
5.
|
1…10 |
1…10 |
1 |
0,99 |
102,86…1,03E+05 |
1000,0 |
|
6.
|
1 |
1…10 |
1…0,1 |
0,99 |
102,86…1,03E+05 |
1000,0 |
|
7.
|
1 |
1…10 |
1 |
0,1…0,99 |
14,58…10286,14 |
705,4 |
|
8.
|
1…10 |
1 |
1…0,1 |
0,99 |
102,86…10286,14 |
100,0 |
|
9.
|
1 |
1…10 |
1 |
0,99 |
102,86…10286,14 |
100,0 |
|
10.
|
1…10 |
1 |
1 |
0,1…0,99 |
14,58…1028,61 |
70,54 |
|
11.
|
1…0,1 |
1…10 |
1 |
0,1…0,99 |
14,58…1028,61 |
70,54 |
|
12.
|
1…10 |
1 |
1…0,1 |
0,99…0,1 |
71,02…1458,20 |
20,53 |
|
13.
|
1…0,1 |
1…10 |
1 |
0,99 |
102,86…2016,08 |
19,60 |
|
14.
|
1 |
1…10 |
1 |
0,99…0,1 |
102,86…1458,20 |
14,18 |
|
15.
|
1…10 |
1 |
1 |
0,99 |
102,86…1028,61 |
10,0 |
|
16.
|
1 |
1 |
1…0,1 |
0,99 |
102,86…1028,61 |
10,0 |
|
17.
|
1 |
1 |
1 |
0,1…0,99 |
14,58…102,82 |
7,05 |
|
18.
|
1 |
1 |
1…0,1 |
0,99…0,1 |
28,75…145,82 |
5,07 |
|
19.
|
1…10 |
1 |
1 |
0,99…0,1 |
63,92…145,82 |
2,28 |
|
20.
|
1…10 |
1…0,1 |
1 |
0,99 |
102,86…201,61 |
1,96 |
|
21.
|
1…10 |
1 |
1…10 |
0,99 |
102,86…102,86 |
1,0 |
|
22.
|
1…0,1 |
1 |
1…0,1 |
0,99 |
102,86…102,86 |
1,0 |
|
Table
2. The statistics of
constant parameters for Ssuf/Ssub in descending order |
||||||
|
No. in sequence |
Õ1, unit |
Õ2, unit |
Õ3, unit |
Õ4, unit |
Ssub … Ssuf, unit 2 (GDÐsub…GDÐsuf), $ |
Ssuf / Ssub (GDÐsuf / GDÐsub) |
|
1 variable |
||||||
|
1.
|
1…10 |
1…10 |
1…0,1 |
0,99 |
102,86…1,03E+06 |
10000,0 |
|
2.
|
1…10 |
1…10 |
1 |
0,1…0,99 |
14,58…1,03E+05 |
7053,99 |
|
3.
|
1 |
1…10 |
1…0,1 |
0,1
…0,99 |
14,58…1,03E+05 |
7053,99 |
|
2 variables |
||||||
|
4.
|
1…10 |
1…10 |
1 |
0,99 |
102,86…1,03E+05 |
1000,0 |
|
5.
|
1 |
1…10 |
1…0,1 |
0,99 |
102,86…1,03E+05 |
1000,0 |
|
6.
|
1…0,1 |
1…10 |
1 |
0,1…0,99 |
14,58…1028,61 |
70,54 |
|
7.
|
1…10 |
1 |
1…0,1 |
0,99…0,1 |
71,02…1458,20 |
20,53 |
|
8.
|
1 |
1…10 |
1 |
0,1…0,99 |
14,58…10286,14 |
705,4 |
|
9.
|
1…10 |
1 |
1…0,1 |
0,99 |
102,86…10286,14 |
100,0 |
|
10.
|
1…10 |
1 |
1 |
0,1…0,99 |
14,58…1028,61 |
70,54 |
|
11.
|
1…0,1 |
1…10 |
1 |
0,99 |
102,86…2016,08 |
19,60 |
|
12.
|
1 |
1…10 |
1 |
0,99…0,1 |
102,86…1458,20 |
14,18 |
|
13.
|
1 |
1 |
1…0,1 |
0,99…0,1 |
28,75…145,82 |
5,07 |
|
14.
|
1…10 |
1 |
1 |
0,99…0,1 |
63,92…145,82 |
2,28 |
|
15.
|
1…10 |
1…0,1 |
1 |
0,99 |
102,86…201,61 |
1,96 |
|
16.
|
1…10 |
1 |
1…10 |
0,99 |
102,86…102,86 |
1,0 |
|
17.
|
1…0,1 |
1 |
1…0,1 |
0,99 |
102,86…102,86 |
1,0 |
|
3 variables |
||||||
|
18.
|
1 |
1…10 |
1 |
0,99 |
102,86…10286,14 |
100,0 |
|
19.
|
1…10 |
1 |
1 |
0,99 |
102,86…1028,61 |
10,0 |
|
20.
|
1 |
1 |
1…0,1 |
0,99 |
102,86…1028,61 |
10,0 |
|
21.
|
1 |
1 |
1 |
0,1…0,99 |
14,58…102,82 |
7,05 |
|
all the variables |
||||||
|
22.
|
1…10 |
1…10 |
1…0,1 |
0,1…0,99 |
14,58…1,029E+06 |
70539,88 |
The obtained Table 2 gives us a clear idea that it
suffices to change even one variable out of four for the country to
successfully come out of an economic crisis.
Thus, depending on the number of variables applied, Table 2 allows us to
use a different number of variants:
·
with 1 variable (3 variants);
·
with 2 variables (14 variants);
·
with 3 variables (4 variants);
·
all the variables (1 variant).
As we can see, the largest number of variants is available for two
variables. However, if we apply all the variables to come out of an economic
crisis, in this case we will have the strongest economic effect.
Below you can see Table 3, which shows how much the values of Ssu (GDPsu)
change as affected by increase in the number of decimal places for the variable
Õ4. In other words,
this is another variant for a country’s economy to come out of a crisis.
|
Tables 3. The change of
the values of Ssu at the increase in the number of decimal points for
the variable X4 |
|||||
|
No. in sequence |
Õ1,
unit |
Õ2, unit |
Õ3, unit |
Õ4,
unit |
Ssu, unit.2 (GDPsu, $) |
|
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0,9 |
33,29 |
|
2 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0,99 |
102,86 |
|
3 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0,999 |
324,54 |
|
4 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0,9999 |
1026,06 |
|
5 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0,99999 |
3244,63 |
|
6 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0,999999 |
10260,39 |
|
7 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0,9999999 |
32446,20 |
|
8 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0,99999999 |
102603,90 |
|
9 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0,999999999 |
324462,02 |
|
10 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0,9999999999 |
1026038,96 |
REFERENCE
1. Pil E.A. Application of the Shell Theory to Describe
Processes Taking Place in the Economy. The Almanac of Contemporary Science
and Education. 2009. No. 3. P. 137-139.
2. Pil E.A. Theory of the financial crises. International
Scientific and Practical Conference. Topical researches of the world science
(June 20-21, 2015) Vol. IV Dubai, UAE.
– 2015 – Ð. 44-56
3. Pil E.A. Calculation of GDP at Constant, Decreasing
and Increasing Variables. Materialy XII mezinarodni vedecko-practiñka
konference «Veda a technologie: krok do budoucnosti – 2016». 22–28 unora. 2016
roku. Dil 4. Economicke vedy. Administrativa.: Praha. Publishing House
«Education and Science» s.r.o. – 88 stran. – P. 10-12
4. Pil E.A. The Influence of Decreasing and Increasing
Variables on GDP. Materialy XII mezinarodni vedecko-practiñka konference
«Veda a technologie: krok do budoucnosti – 2016» 22–28 unora. 2016 roku.
Dil 4. Economicke vedy. Administrativa.: Praha. Publishing House «Education and
Science» s.r.o. – 88 stran. – P. 12-14
5. Pil E.A. The Influence of Four Variables on GDP. Materials
of the XII International scientific and practical conference, «Modern scientific
potential - 2016», February 28 - March 7, 2016 Volume 5. Economic science. Governance. Sheffield. Science
and education. LTD. UK – 104 ð. – P. 32-35
6. Pil E.A. The Influence of Decreasing and Constant
Variables on GDP. Materials of the XII International scientific and
practical conference, «Modern scientific potential - 2016», February 28 - March 7, 2016 Volume 5. Economic science. Governance. Sheffield.
Science and education. LTD. UK – 104 ð. – P. 30-32