Технические науки/5. Энергетика
Sadrtdinov A.R., Esmagilova L.M., Galeev Т.H.
Kazan National Research Technological University, Russian Federation
Effect of the preliminary thermo
treatment of a wood waste on gasification process
Environmental and social problems, energy security and fossil fuel
prices lead to increased research and development activities for renewable
bioenergy. This is especially important for biomass gasification technology,
which is actively developing over the last decade and has become the basis for
the production of synthesis gas (raw gas) that can be used directly or can be a
starting raw material in industry for the synthesis of various substances [1-3].
Effect of thermal
pre-treatment of raw materials (wood waste) on the quality of produced
synthesis gas has been studied in the development of the gasification process
improving. The
aim of study was to demonstrate that during the thermal treatment the waste
changes their properties showing more homogeneous appearance and enhancing of
the thermo physical properties [4-5].
Heat treatment of wood waste
is carried out at heating temperatures of 180 - 230 °C at atmospheric pressure
in the absence of oxygen, so that water and volatile components are removed
from waste wood.
The kinetic studies of the
wood waste heat treatment were carried out using thermo-gravimetric analyzer.
The emission, pollution and slags were also identified during gasification of
the treated waste. Calorific value of the syngas obtained from the treated wood
waste was carried out in specialized combustion chamber.
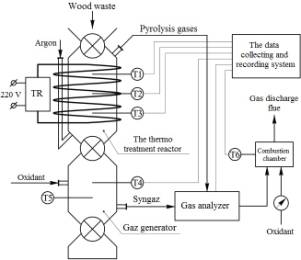
The experimental facility
scheme for comprehensive study of the wood waste thermo pre-treatment and
determination of the produced syngas quality was developed (Fig. 1).
The main unit of the scheme is a cylindrical reactor for the thermal
treatment of wood waste having a height of 500 mm and 100 mm in diameter, in
which for each experiment were placed 300 grams of the studied material. Inert gas, argon, was supplied to prevent combustion of
material in the reactor. Heating of the reactor and argon was carried out using
an electric tape with power of 4 kW. Reactor temperature was monitored at three
levels by thermocouples. Samples of the syngas were taken of at the outlet of
the reactor.
We studied the most frequently encountered wood waste (wood chips,
branches, etc.) which were analyzed as in the wet state as after heat treatment
for 30 minutes at temperatures of 180°C and 230°C, respectively [4].
|
|
|
|
Fig. 1 - Scheme of the
experimental facylity |
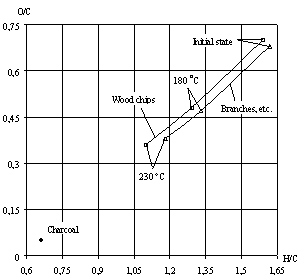
Fig. 2 - Changes in
carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) contents in the studied materials. Elemental
analysis data. The O/C vs. the
H/C ratio |
The elemental composition changes of the wood waste after thermo
treatment processing are presented in Fig. 2. A
comparative analysis of the changes in the interrelations between carbon (C),
hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) was carried out with each treated material using
charcoal as benchmark. All data was calculated (in mole percent) for the dry
and free from cinder part of the sample. Since the carbon in the wood is one of
the basic and significant weight elements we presented the results in the H/C
and O/C ratios, which was also allowed to construct a grid.
In the raw (wet) materials the O/C ratio varies in the range of 0.65 -
0.70, after the thermo treatment at 180°C its value is about 0.5 and after the
thermo treatment at 230°C the O/C ratio varies in the range of 0.3 - 0.4. This decreasing in the O/C ratio values is attributed to
the large removal of water and volatile substances with increasing of thermal
processing temperature, that leads to an increase in the relative amount of
carbon in treating material. According to the data obtained the studied thermal
treatment process is similar to the pyrolysis process, but proceeds at
relatively low temperatures with aim to optimally prepare wood waste for the
further gasification and syngas production with the desired quality.
As a result, oxygen
depletion determines a lower degree of oxidation and leads to an increase in
the heating value. The H/C and O/C values tend to rich value characteristic for
coal with heating, giving make assumptions about the similarity in the
properties of the treated materials and coal at gasification. Summarized data
also confirm that with increasing temperature of the treatment in addition to
removing of the volatile substances relative charring of material occurs.
Kinetics of devolatilization and charring at the thermal treatment was
determined by thermo gravimetric analysis.
|
|
|
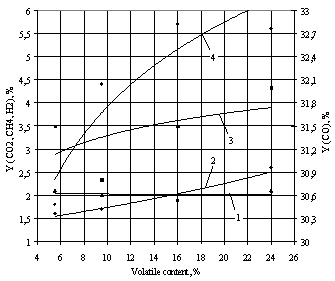
Fig. 3 - Variations in the
composition of the syngas from the gasification of treated wood waste |
It is well known that the composition of the resultant syngas from coal gasification
is most clean and better quality [2]. With this data the best option for gasification
is wood waste treated at 230°C.
The experiments qualifying effect of the volatile processed from the
wood waste on the composition of produced syngas were carried out also. Results
of the treated waste gasification process represented in Fig. 3. The obtained dependences confirm the
legitimacy of the data presented in
Fig. 2.
Currently we are planning studies on the application of the produced
syngas as fuel gas for gas turbines and in the production of heat and
electricity.
The
presented materials are received during the realization of program for the
grant of the President of the Russian Federation under state support of young
Russian scientists. The cypher of the research topic is MK-3434.2015.8
"Development of theoretical foundations, technologies and equipment of
integrated thermochemical processing of waste wood and plant biomass into raw
materials for chemical synthesis and components of motor fuels".
References
1.
Tuntsev
D.V., Filippova F.M., Khismatov R.G., and Timerbaev N.F. 2014 Pyrolyzates:
Products of plant biomass fast pyrolysis. Russian Journal of Applied Chemistry, 87(9): 1367-1370. DOI: 10.1134/S1070427214090304.
2.
Timerbaev
N.F., Safin R.R., Safin R.G. and Ziatdinova D.F. 2014 Modeling of the process
of energy-technological treatment of wood waste by method of direct-flow
gasification Journal of Engineering and
Applied Sciences (EAAS) 9(5):
141-146.
3.
Tuntsev
D.V., Safin R.R., Hismatov R.G., Halitov R.A. and Petrov V.I. (2015, December)
The mathematical model of fast pyrolysis of wood waste. In 2015 Int. Conf. on Mechanical Engineering, Automation and Control
Systems (MEACS) pp 1-4. DOI: 10.1109/MEACS.2015.7414929.
4.
Safin
R.R., Khasanshin R.R., Shaikhutdinova A.R. and Safina A.V. 2014 Research of
heating rate while termo modification of wood World Applied Sciences Journal 30(11):
1618-1621. DOI:10.5829/idosi.wasj.2014.30.11.14223.
5.
Prosvirnikov D.B., Safin R.G., Ziatdinova D.F.,
Timerbaev N.F. and Lashkov V.A. 2016
Multifactorial modelling of high-temperature treatment of timber in the
saturated water steam medium. IOP
Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering 124(1), 012088. IOP Publishing.
DOI:10.1088/1757-899X/124/1/012088.