1Pidherska L.O., 2Tugay
A.V., 2Tugay T.I.
1National University of food technology, Kyiv
2 Institute of Microbiology and Virusology
by D.K.Zabolotnyi NAS of Ukraine, Kyiv
Effect of chronic ionizing radiation on the intensity of lipid
peroxidation in strains of Aspergillus
versicolor
Introduction
Fungi are constant components of
biogeocoenosis and have a number of adaptations to survive in the
conditions with abnormally high radioactive baokground, which up to this time haven’t
been studied yet and taking into
the consideration the growth of technogenic weight on our planet and aline organisms,the
actuality of this theme is increasing [1]. Microscopic fungi play one of the main roles in
the process of transformation of radionuclides
turning them into the dissolving form,which is capable to build in the processes of
migration in soil and trophic chains. It is known,that
negative radioactive damage leads to the stimulation,of free
radical processes. The adaptation of micromycetes takes place with the help of
certain mechanisms, that provide the support of oxidation-reduction
homeostasis in norm.
One of the
important metabolic processes, which play an important part in the formation of
the firm mechanism and adaptation to different kinds of extreme influences and
reflects the degree of given firmness is a lipid peroxidation.
The given process in fungi hasn`t been
studied influence enough. Besides, the knowledge about the of physical facts on
a lipid peroxidation of fungi cells is practically absent [2].
Materials and methods
Two
chiches of lighpigmented microscopic fungi Aspergillus
versicolor 99 and 432 were used in work, which were kept in the collection
of the physiology department and systematization micromycetes of the Institute
of microbiology and virusology by D.K.Zabolotnyi NAS of Ukraine.
Strain Aspergillus versicolor 99, which was
taken out from the building «Shelter», showed the radio adaptational
possibility, and another strain
A. versicolor 432, taken out from the
clean, as to radionuclides, building (control) dosen`t have such capabilities
[1].
The
microorganisms were grown under the temperature 25±2°C on the modificated
environment of Chapek, which contained 20 g/l of glucose along 7, 14 and 21
days, which corresponded to the exponential phase, according to the beginning
and the end of stationary phase.
The growing of
micromycetes in the conditions of chronical radiation was made on the earlier
designed model device (Pic.1). The power of expositive dose on the surface of
model device was 3 mP/hour on the seventh day of growing fungi (extonational
phase the integral absorbed dose was 1,5 Gr., and on the fourteenth day
(stationary phase) was 3 Gr. The source of ionic radiation is the soil form the
5-kilometre zone of alienation [3].
The given device
gives the opportunity to modes the conditions of wide range doses of chronical
radiation, which microscopic fungi were undergone during a long time being in
the zone of ChAE Station.
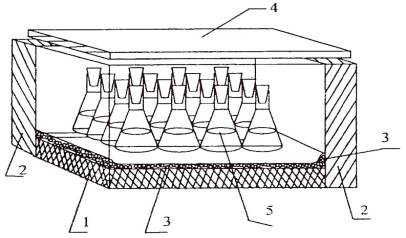
Pic.
1. A model system of the radiation of microscopic fungi with ionic radiation:
1- the layer of radioactive soil; 2 - biological defence, lead – 100 ml; 3 -
pinoplastic box of thermostat; 4 – the lid of the thermostat; 5 - flasks with
environment, showed with microorganisms.
For estimation of
intensiveness lipid peroxidation it is necessary to define the concentration of
one or some products oxygen changes of hydrooxygen lipids in testing
microorganisms; primary (diene conjugates - DC) and intermediate or second
(malonic dialdehyde - MDA).
In researchcd micromycetes we defined diene
conjugates (DC) and malonic dialdehyde (MDA) with the following melhods. The content of diene conjugates
(DC) in the mycelium evaluated for indications of spektorofotometer at λ =
232 nm. And the determination of malonic aldehyde (MDA) was carried out by
reaction with thiobarbituric acid [2].
Results
We have researched the influence of ionic
radiation on the formation of primary and second products of lipid
peroxidationin micromycetes Aspergillus
versicolor 99 and 432 and exactly: DC
and MDA.
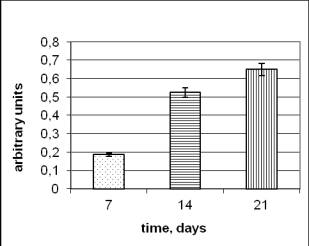
It was proved that the amount of DC in searched
cliches of controland with radioactive ability was raised in the process of
growrng under the change from exponential to permanent phases of growrng, the
maximam level of DC reached at the beginning and at the end of the stationary
phase of growth (Pic.2). The level of DC depends on the existence of adaptational
ability and the period of fungi ontogenesis.
a)
b)
Pic.2 The content of
diene conjugates in the dynamics of growth in the control strain Aspergillus versicolor 432 (a) and Aspergillus versicolor 99 (b) of
radioadaptive properties properties
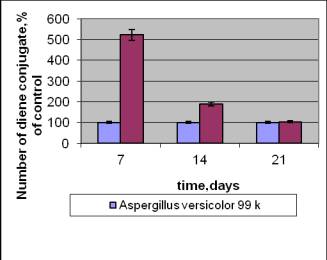
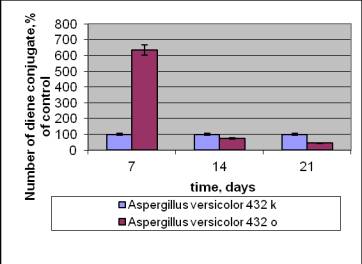 For functions of chronical radiation
in control strain they
noticed a considerable (in 6 times) increase of the level of DC in the
exponational phase of growth and decrease in a stationary one (Pic. 3). They
watched the increase of the level DC in the strain with the radioactive ability along all
the period of cultivation with maximum in the exponational phase. It may
witness that certain mechanisms of adaptation began to form in the cell as to
stressed conditions of surrounding, but oxygen homeostasis didn`t stabilize.
For functions of chronical radiation
in control strain they
noticed a considerable (in 6 times) increase of the level of DC in the
exponational phase of growth and decrease in a stationary one (Pic. 3). They
watched the increase of the level DC in the strain with the radioactive ability along all
the period of cultivation with maximum in the exponational phase. It may
witness that certain mechanisms of adaptation began to form in the cell as to
stressed conditions of surrounding, but oxygen homeostasis didn`t stabilize.
a) b)
Pic.3.
The influencet of chronical radiation on the amount of diene conjugates in
strain Aspergillus versicolor 432 (a)
and Aspergillus versicolor 99 (b)
with respect to the control without irradiation.
Diene conjugates and hydroperoxides can be considered as the primary
products lipid peroxidation. That`s
why we have also conducted the research as for the influence of ionic radiation
on the formation of products lipid peroxidation and exactly MDA.
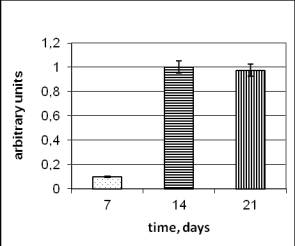
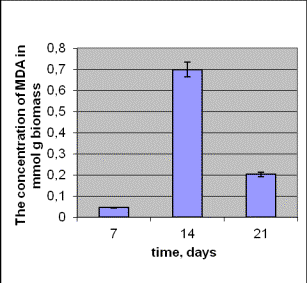
The
level of MDA in the strain with radio adaptational ability and in the control
one is the highest at the beginning of the permanent phase of growth and it
lessens at the end of this phase (Pic.4). It`s necessary to mark, that the
level of the level MDA on the contrary from MDA was the highest at
the end of the permanent phase of growth (Pic. 2).
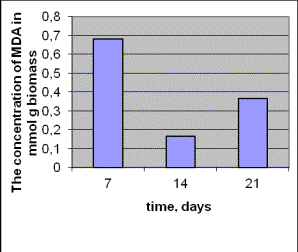
During
the actions of chronical radiation the important changes were in the level of
MDA in the researched stams (Pic.5). In
the control stam the level of MDA
was changing wave-like was increasing
in the exponational phase and lessening at the beginning and raising at the end
of the stationary phase of growth.

a)
b)
Pic.4
The concentration of
MDA in the dynamics of growth in
the control strain Aspergillus versicolor 432(a) and Aspergillus versicolor 99 (b).
One
noticed the raising of the level MDA in the strain with radioadaptation ability
during the whole period of research. The maximum level MDA was noticed in the
exponational phase of growth.
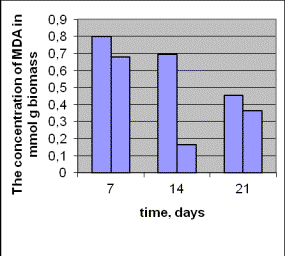
Under the
influence of ionizing radiation the
changes of level second products lipid
peroxidation were found at the
beginning and at the end of the stationary phase of growth in research strain.
The level of MDA
in the research strain A. versicolor 99 in the exponational
phase is much higher in comparison with the control strain, but at the
beginning and at the end of the stationary phase the level of second products
lipid peroxidation is stabilized
according to control, it shows the entering in action a number of mechanisms of
micromycetes
adaptation to a stressed situation, which appeared and the renewal of oxidative
homeostasis of cell.
a)
b)
Pic.5. The concentration of MDA in the dynamics of
growth in the strain Aspergillus
versicolor 432 (a) and Aspergillus
versicolor 99 (b) under the influence of radiation.
In literature we
have a few date as to the influence of chronical radiation on the processes
lipid peroxidation in fungi with radioadaptational abilities.
But there is some
discoveries, that impulsive magnetic field, especially in a shorten period, can
lessen the intensity of the process of lipid peroxidation in micromycetes Trichoderma viride, which gives the reason
to think that the given fact can possess of membranotropic effect [4].
It
was discovered the presence of physical-chemical system of regulation lipid
peroxidation in the cells of gramnegative bacteria, yeast of different toxicant
groups and strains and mycelium tree damaged fungi of different toxicant
groups [5].
The
influence of processes lipid peroxidation on the regulation of the cell metabolism of microorganisms is shown
in the standard and under the damage influence and also in the process of
“communication” of cells with the environment of cultivation. The authors
established the existence of correlation between the parameters of
physical-chemical system of regulation lipid peroxidation on cell and body level in biological systems of different level of
complication.
The correlation
was established between the intensification lipid peroxidation and biodegradation of wood which presents
the interest in the connection of search of ecological clean and less energy
capacious methods of wood decomposition [5].
So,
it was ascertained that micromycetes have a complicated answer in the form
of adaptational accommodation to the
influence of chronical ionized radiation, which depends on the presence or
absence of radioadaptive abilities and the phase of growth. It was found out
that in researched strains A. versicolor,
which had radiadoptive abilities, the level of the first and second products
lipid peroxidation at the beginning and on the end of the permanent phase under
the influence of chronical radiation was stabilized according to the control,
it may be explained the existence of formed adaptative mechanisms which renew
the oxidative homeostasis of cells.
References
1) Tugay T.I. Influence of
ionizing radiation on the synthesis of carotenoids in light pigmented micromycetes Aspergillus
versicolor, isolated from "Shelter"// Ukrainian Food Journal. –
2013. – Vol. 2. – Ð. 154-157.
2) Orel N.M. Biochemistry of membranes: method. certainly appreciate category
laboratory classes for students of the faculty of biology specials. 1-31 01 Biology.- Minsk: BGU, 2010. –
28p.
3)
Baloga V.I., Holosha V.I., Evdin A.N. Chernobyl
disaster 20 years. Sight in the future: The National Report of Ukraine. - K.:
Atika, 2006 - 232 p.
4) Smirnol V.F., Lazareva E.S., Borisova I.V. The influence weak pulsed magnetic field on lipid
peroxidation micromycetes Trichoderma viride // Microbiological journal. – 2009. – ¹4. – P. 31-35.
5) Shishkina: L.M. Peculiarities of function of physical-chemical system of regulation
lipid peroxidation in biological objects of different levels of complication in
the norm and under the influence of damage facts:
Dis. … doctor of science. – Moscow, 2003. – 406 p.