Биологические науки / 8.
Физиология человека и животных
Peklo A.O., Lych I.V.
National University of Food
Technologies, Ukraine
IMMUNOMODULATORY
PROPERTIES OF THE ABZYMES MILK
Study
of antibodies and immunoglobulins, which have their own catalytic (abzymes)
activity – one of the new trends in immunology and biotechnology [1]. Today has
shown that abzymes can catalyze any type of biochemical reactions. There are
even abzymes that are able to catalyze reactions that are not in the nature of
the enzymes [2]. There is information about some types abzymes activity
directly related to the development immunopathology [1].
Recently,
considerable attention attracted by the modern scientific community that the
performance of catalytic antibodies – abzymes largely due not only to the type
of reactions that need to catalyze and type of pathological processes, but also
with all immune processes that occur in the body. Abzymes are bioactive
components of milk, which play an important role in the implementation of the
functional activity of milk and humoral immunity mukoznoho immunity in general.
Because can argue about the effectiveness abzymes in the prevention of viral,
bacterial and some cancers [3].
Since
the body of healthy people initially abzymes was observed, it was suggested
that their products are closely connected with pathological processes. The
question of the existence of natural abzymes body normally arose after it was
shown that in colostrum and milk of healthy women is secretory immunoglobulin A
(sIgA), are able to catalyze the phosphorylation of casein, they were one of
the first abzymes that were allocated of colostrum [2]. In this study, we aimed
to investigate the effect of a mixture of proteins-abzymes on immunocompetent
cells in experiments in vitro.
Materials and methods
Identification
and study of immunomodulatory properties of catalytically active antibodies –
proteins-abzymes carried out on the basis of experimental data. Abzymes ability
to directly influence the immune defense cells in vitro was determined by
changes in the functional activity lymphocytes (Lph), neutrophil granulocytes
(NG), monocytes (MN), and natural killer cells (NK cells).
A
mixture of proteins obtained from milk and colostrum, which is taken from the
first day of calving cows within 30 days. Purification scheme, which is shown
in fig.1.
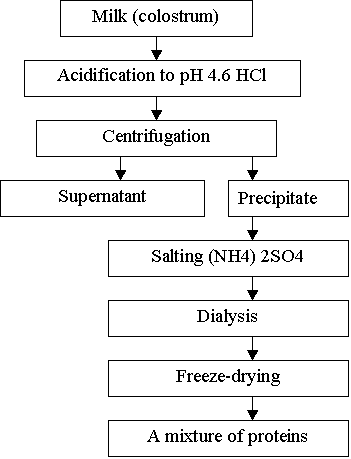
Fig.1. The scheme of obtaining and purification of protein mixtures
abzymes
Lyophilized preparations of proteins dissolved in saline to a
concentration of 1 mg protein/ml. In experiments using mixtures of proteins at
concentrations of 1.0 mg/ml and 0.1 mg/ml.
Catalytic properties argued that abzymes can be prepared for catalysis
almost all chemical reactions. The potential number of chemical transformations
relatively higher than the number of reactions occurring in living systems and
the corresponding catalyzed by enzymes. Using abzymes, creating the possibility
of their use, both in scientific and inpractical purposes.
Evaluation of the direct effects of mixtures proteins-abzymes on
functional activity of immune defense cells in tests performed in vitro. The
functional state of neutrophil granulocytes (NG) and monocytes (MC) blood
characterized by their ability to absorb latex particles (d = 1,0 – 1,3 mm)
with the expectation percentage phagocytosis (PP) – the percentage of
phagocytic cells and phagocytic number (PN) – their average activity [4] and the
intensity of their oxygen-dependent metabolism through NBTR (Nitro Blue
Tetrazolium Reduction) test according to the method [5]. For cytochemical
coefficient (CCC) conducted an assessment of peroxidase activity.
Cytotoxic activity of killer cells was determined by non radiometric
method based on spectrophotometric count of hemoglobin released from the red
blood target cells destroyed by the killers (SE) during their joint incubation [6].
Rosette forming cells (RFC) was defined through the rosette formation
method with application of particles coated with monoclonal antibodies [7].
Results and
discussion
One of the important criteria for assessing the
biological impact of any agent on the immune system is its expression at the
cellular level. Therefore, research imunomodulyuvalnyh properties of a mixture
of protein abzymes conducted under conditions in vitro, using lymphoid blood
cells of healthy donors lymphocytes (LF), neutrophil granulocytes (NG),
monocytes (MC), and natural killer cells (NK cells).
We was interesting to investigate the functional
activity of phagocytes cells as NG and Mc under different concentrations of a
mixture abzymes as a potential immunomodulatory effect on the phagocytic
activity of blood cells is one of the necessary tests navnist immunomodulatory
effect
[8].
To investigate the functional activity of phagocytes
cells in the first phase study conducted absorbance NG using latex test.
Figure 1 presents data on the influence of the mixture
on phagocytosis abzymes NG expressed in the phagocytes percent (PP) (percentage
of cells that have captured the latex particles) (Fig.1a) and phagocytic number (PN) (average number of particles
that were swallowed by the phagocytic cell) (Fig. 1b)
a b
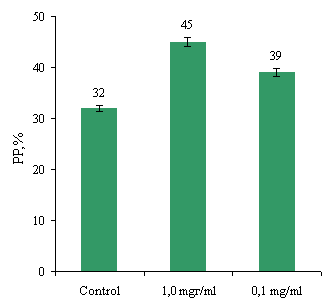
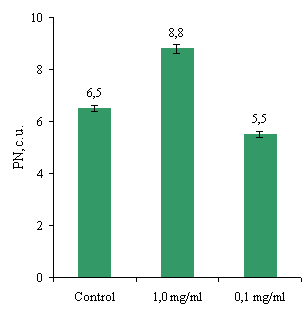
Fig.1. Effect of protein on performance abzymes
phagocytosis NG
As shown in Fig.1, a mixture at a concentration
abzymes 1.0 mg/ml had a marked effect on the level of PP (control – 32% vs.
45%), while the mixture of proteins at a concentration of 0.1 mg / ml slightly
increased the rate of PP (32% vs. 39%). Abzymes mixture at a concentration of
0.1 mg/ml reduced the rate of PN (control – 6.5 USD 5.5 USD against), while a
mixture of proteins at a concentration of 1.0 mg/ml increased the rate of PN
(8.8 against USD 6.5 USD).
Thus, during normal phagocytic activity (32% ± 0,9%)
NG, PP values studied compounds differ from each other. The
percentage of cells that have captured the latex particles during processing of
cells with a mixture of proteins at a concentration of 1.0 mg/ml of white
control and greater relative concentration of 0.1 mg/ml. As for PN, this index
increased significantly also for processing the cells in mixture abzymes
concentration of 1.0 mg/ml.
The second stage of this research was to study the
digestive ability of NG in NBTR-test. Results of change in activity of oxygen
dependent metabolism after interaction of NG with study drugs and comparison
preparations are shown in Fig. 2. Definition of oxygen dependent metabolism of
NG was performed by evaluating the percentage of NBTR-positive cells (Fig. 2a)
and cytochemical coefficient (CCC) (Fig. 2b).
a
b
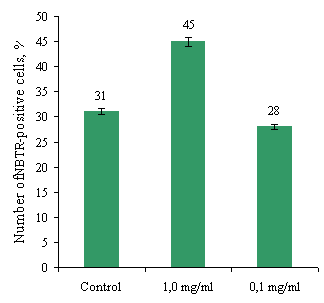
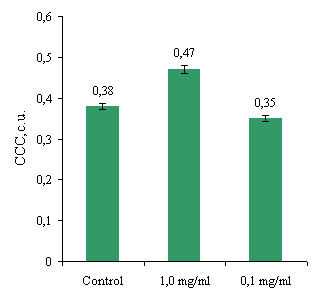
Fig.2. Effect of protein on performance abzymes spontaneous NBTR-test
of NG
Data from this test indicate that the mixture of
proteins at a concentration of 0.1 mg/ml was not significantly influenced not
by the number of NBTR-positive cells than their functional activity (Fig. 2). A
mixture abzymes at a concentration of 1.0 mg/ml had a stimulating effect on NBTR-positive
cells by 31.8% and 20% CCC. This may suggests that this concentration mixture
abzymes positive effect both on the functional activity of NG and on the
activity of oxygen dependent metabolism of NG.
Similar studies of protein-abzymiv impact on
functional activity of phagocytic cells was performed on a model of monocytes
(MC). First, the absorbance capacity of MN was also studied by means of latex
test (Fig. 3).
The data presented in Fig. 3a determine absorption
activity of MN before and after interaction with the studied drugs and show
that MC and rydostyn significantly increase the phagocytic activity of MN both
absorption and digesting one, unlike the NG.
a b
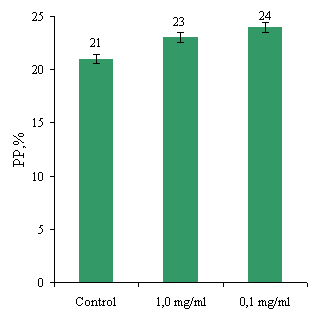
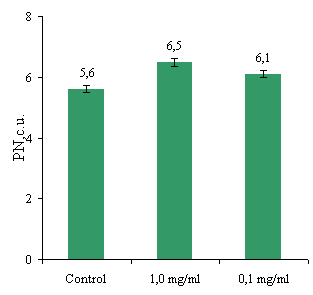
Fig. 3. The impact on performance of
phagocytosis MC
As shown in Fig. 3 none of the studied mixtures in
concentrations abzymiv 1.0 mg/ml and 0.1 mg/ml did not affect the percentage
phagocytosis and phagocytic number. Thus, PP and PN cells monocytes treated
with different concentrations of proteins remained at control.
Thus, cells monocytes were not sensitive to the
activation of the studied mixtures, even when changing the concentration.
Summarizing the results obtained, we can note that proved
a direct impact on abzymes cells and phagocytes Lph. This is confirmed by the
increasing number of fahotsytuvalnyh cells of monocyte-macrophage population increased
cytotoxic activity of PP cells and cells responsible for antibody-dependent
cytotoxic activity.
So abzymy exhibit in vitro
immunomodulatory properties. It shows promise for further study its effects on
the level of microorganism.
References
1. Berger T., Rubner P., Schautzer F. et al.
Antimyelin antibodies as a predictor of clinically definite multiple sclerosis
after a first demyelinating event // N Engl J Med. – 2003. – № 10. – V.
349(2) – P. 139 – 145.
2. Albrechtsen M., Massaro A., Bock E. Enzyme-linked
immunosorbent assay for human glial fibrillary acidic protein using a mouse
monoclonal antibody // J, Neurochem. –
2001. – № 44. – P. 560 – 565.
3. Cuello A.C., Priestley J.V., Milstein C.
Immunocytochemistry with internally labeled monoclonal antibodies // Proc Natl
Acad Sci U S A. 2000 – V. 79(2) – P. 65
– 96.
4.
Унифицированные иммунологические методы обследования больных на стационарном и
амбулаторном этапах лечения: Метод. рекомендации / Киевский НИИ фтизиатрии и
пульмонологии. – К.: 1988. – 18 с.
5. Нарциссов Р.П. Цитохимия ферментов лейкоцитов в педиатрии. Цитохимический
метод. Дисс. Докт. Мед. Наук. М. – 200.
– 378 с.
6. Lotze, Michael T. Natural Killer Cells: Basic
Science and Clinical Application // London: Elsevier. – 2010. – 678 p.
7. Новиков Д.К.,
Новиков П.Д. Метод определения Т- и В- лимфоцитов диагностикумами на основе
моноклональных антител // Иммунол. – 2000. – №2. – С. 31 – 33.
8. Доклінічні
дослідження лікарських засобів: Метод. рекомендації / За ред. О.В. Стефанова.
Вивчення імунотоксичної дії лікарських засобів. – К.: МОЗ України, 2001. С. 102
– 113.