THE USE OF IMMUNOLOGICAL ANALYSIS TECHNIQUES FOR THE RAPID DETECTION OF
NARCOTIC SUBSTANCES
L.Pulatova, M.Rakhimov, Sh.Tashmukhamedova
Higher military customs Institute
Currently, detection and seizure of
illicit traffic in narcotic drugs, psychotropic substances requires the use of
special technical developments to ensure objectivity, selectivity, fidelity
active component (substance), performance, absence of false results and
therefore completeness of implementation of measures of restraint by law enforcement
authorities against persons engaged in this kind of business.
Solution of issues related to
counteraction to spreading of drug addiction, causes the development of
accessible and reliable methods for identifying facts of abuse of drugs and
their illegal movement across the customs border of the state. In this regard,
the development and production of test - systems for reliable diagnosis of
abuse and violation of various kinds of drugs is one of the urgent tasks in the
field of biotechnology.
Given the above, the objective of this
work was to systematization and generalization of the results of studies on the
selection of the necessary conditions for enzyme immunoassay drugs and other
intoxicating substances.
It should be noted that in modern
practice law enforcement particular practical application is found with
immunoenzyme analysis methods, built on the interaction of antigen and
antibodies and used to define a variety of physiologically active substances
and objects - from low-molecular regulators of metabolism markers to cancer
cells and pathogens. Thus, as diagnostic agents may be used hydrosols:
ultrafine particles of metal oxides side subgroups and complex compounds on the
surface of which certain technology dealt antigens or antibodies. It should be
noted that the quantitative study of physico-chemical regularities of the
reactions of antigens of different nature, are very important for the
understanding of the immune interactions in vivo and to create immunochemical
systems for detection of biologically active compounds. Theoretically EIA is
based on the data of modern immunochemistry and chemical enzymology, knowledge
of physical and chemical regularities of the reactions of antigen - antibody,
as well as on the main principles of analytical chemistry. The sensitivity of
the ELISA and time of the meeting is determined by several key factors:
kinetic, thermodynamic properties of reaction antigen - antibody, the ratio of
reagents, enzyme activity and resolution of the methods of its detection.
Literary sources testify to the fact
that any case of ELISA includes three stages, in particular:
1. Stage of recognition of the tested
compounds specific to him antibody that leads to the formation of immune
complex;
2. The formative stage of the connection
conjugates with an immune complex, or with free places binding;
3. Stage of transformation of the
enzyme label to the registered signal.
Currently it is known that in the
modern practice of forensic medicine, pharmaceutical, toxicological analysis,
including to determine narcotic and toxic substances has developed effective
methods for determination of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay amphetamine and
antibodies to it in the biological liquids of the person, and also optimized
the conditions detection of antibodies to amphetamine in human serum based use immunoenzyme
analysis of new synthetic antigens [1].
In immunoenzymatic methods for
detection reaction Ťantigen - antibodyť as a label (marker) are enzymes that
represent various oxidase-oxidizing bacteria (special chemical substance -
addition of a chromogen substrate) with the formation of colored products,
intensity of colouring which is judged on the presence or absence of narcotic
drugs in the analyzed sample. Technique of execution there are two types of
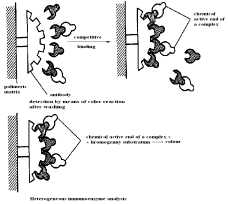
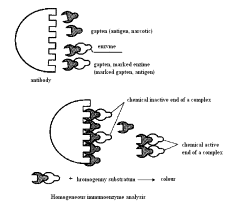
immune-enzyme analysis: homogeneous and heterogeneous.
In the homogeneous ELISA all
components of reaction - antibodies (antiserum), determined by the substance,
labeled determined by the substance (conjugate), the addition of a chromogen substrate
are one aggregate state - solution. As marks are used enzymes such as lysozyme,
glucose - 6 - phosphate dehydrogenase, malate dehydrogenase. When you link
labeled gapten with antibody activity of an enzyme - label in the reaction with
chromogene substrate is reduced through spatial changes of the protein enzyme,
i.e. blocked access substrate to a fermentative centers and comes braking. In
this case colouring of the analyzed solution after addition of the substrate
will be directly proportional to the concentration of which has not entered
into binding of the antibody labeled gapten, i.e. directly proportional to the
concentration of rival drug, which is in the study of biological liquids.
In heterogeneous ELISA provides for
phase separation of reactants - addition of a chromogen substrate is added
after the stage of washing. Holding of incubation of the reaction mixture and
linking gapten (labeled and unlabeled) antibodies on the solid basis ends
removed from the reaction mixture unreacted reagents. The added addition of a chromogen
substrate interacts with the enzyme - labeled associated with antibody
immobilized on the solid medium with education in a particular coloring. If the
concentration of the designated substance in the sample is significantly higher
than the concentration gapten, labeled enzyme, after the removal of the last of
the reaction mixture as a result of cleaning, the addition of a chromogen
substrate will not form color (positive result). As the label in a
heterogeneous method uses such enzymes as peroxidase, glycosidase, alcolin-phosphatase,
at least - acetyl cholinesterase, glucoamylase and glucose oxidase [6].
Today, enzyme-linked immunosorbent
assay is one of the perspective directions of immunochemical determination of
biologically active substances (hormones, enzymes, antibiotics, drugs,
combining the specificity of the immunological recognition and very high
sensitivity detection enzyme labels, which can be applied most active enzymes.
The discovery of the possibility of immobilization of the antigen and the
antibody to the various media with preservation of their binding activity has
allowed expanding the use in various fields of biology and medicine. Thus, as a
solid phase, you can apply different materials, in particular, polystyrene,
polyvinyl chloride, polypropylene and other high-molecular compounds.
In the work [2] it
was noted that a correct description of the interaction of antibodies with
polyvalent antigens, which include oligomeric proteins and synthetic conjugates
Ťgapten - mediať (the drug), is a rather complicated problem due to a lot of
the staging of a process and education of a large number of complexes of
different composition. As artificial polyvalent antigens - liposomes allow
properly characterize the influence of physico - chemical properties and
composition of the antigens on the kinetic and equilibrium parameters of
immunochemical reactions.
Astashkina O.G. developed the method of
enzyme immunoassay for the detection of drugs group of opiates. [3] Research
results, confirmed by standard chemical methods (thin-layer chromatography, gas
chromatography-mass-spectrometry, high-performance chromatography) show that
the method of enzyme immunoassay using diagnostic has high sensitivity and
specificity, and can be recommended in forensic and customs practice to
establish a group of drugs opiates in biological liquids in examination.
Recent advances in molecular biology,
molecular genetics, bioorganic chemistry, and their practical implementation is
allowed to authors of works to conduct studies of the influence of the
properties immune reagents on kinetic and equilibrium parameters of the
reaction Ťantigen - antibodyť. On the basis of the data developed models of
processes of formation of immune complexes are studied structural changes of
protein antigens in the interaction with the antibodies, in particular, the
modulation of the catalytic activity of enzymes antibodies. As model antigens
in the study of immunochemical processes have been used hormones, enzymes,
antibiotics, drugs. For the detection of these compounds proposed new formats
analysis and marker system, designed to improve the sensitivity and
expressiveness the definition. [4]
As already noted, immunochemical
methods for detection of narcotic substances differ necessary sensitivity and
high specificity, resistance to interference factors of biological liquids.
Currently known immunochemical methods of determination of different classes of
drugs are based on the application-labeled analytes, capable of defining the
necessary object or specific antibodies.
Biotechnology industry, the USA, Great
Britain and France to produce the corresponding sets of reagents for radio
prepare, immunofluorescence and enzyme immunoassay various. [5] It
should be noted that the labeled antigen (AG*), when added intoxicants in the
analyzed sample of known concentration, will combine with the antibody to [AG*-At] form
complex.
It
should be noted that currently developed, immunochromatographic analysis
methods, aimed at the determination of the existence of certain concentrations
of substances in biological materials, and is based on immersion test in
physiological fluid that starts migrate along a strip on the principle of
thin-layer chromatography, i.e. the formation of immune complexes between
antibody immobilized on the chromatographic paper, and present in the analyzed
sample free drug proportional to its concentration. Then strip is placed in a
solution containing: a) conjugate (a certain drug - peroxidase); b) glucose; c)
addition of a chromogen substrate (chlorine naphthol). During incubation
conjugate binds with vacant active center of antibodies and interaction with
the immobilized glucose oxidase, there is a consecutive generation of hydrogen
peroxide, which contributes to the substrate oxidation with the formation of
insoluble colored product. The concentration of antigen (defined substances) in
the studied sample is inversely proportional to the intensity developed on a
strip of color, i.e. the concentration of a substance is determined not by the
enzymatic activity of the conjugate, and chromatographic behavior of.
Thus, being an effective method of
diagnosis, rapid tests allow you to visually within a few minutes to determine
and assess the content of the antigens, antibodies, hormones and drugs in
biological fluids. The essential hematocrit, i.e. the ratio of plasma and
formed elements. At high hematocrit reduces the number of plasma with an
antigen, migrating along a strip. Given the above, of particular interest, from
a practical point of view, is the use of marked imminoxyl radical gaptens in
determining the concentration of morphine in biological liquids. For the drug
antibodies were obtained and used in the test system after joining imminoxyl radical.
If in the sample contained detectable drug, then he blocked the active centres
of antibodies. Added as component test system morphine, labeled imminoxyl radical
remained unbound and range of labels coincides with the spectrum of imminoxyl in
the solution. [6]
In the work [1,8] developed effective immunological method of
determination of opiates, kannabiods, barbiturates in urine based on the
reaction latex agglutination with the use of functional polystyrene and polymethylmethacrylate
microspheres. Special practical interest is the development of the ELISA method
of analysis of amphetamine and getting biochemical reagents (antibodies and
antigens), because their qualitative characteristics are the main factors of
analysis, constituting the foundation of the biotechnology development.
Studied solid-phase ELISA method of
determination of amphetamine included immobilization antigen conjugated on
polystyrene tablet; competitive binding of free derivative of amphetamine, present
in the test specimen and adsorbed on solid phase conjugate amphetamine protein
with specific antibodies; identification of the resulting immune complex with anti
species antibody labeled with horseradish peroxidase; measurement of enzymatic
activity in the resulting immune complex.
On the , synthesized sorbents for basis
of the conducted researches in the work [1,9] affine chromatography, conducted selection of
antibodies to amphetamine of biological liquids, optimized conditions of the
analysis of immunoglobulin M and A in biological fluids based on synthetic
antigens.
Given the foregoing, high sensitivity,
combined with the rapidity of analysis, the possibility of simultaneous testing
of a large number of samples and the lack of special need of preliminary
clearance operations and concentration of the analyzed compounds in the sample,
give ELISA advantages over other analytical methods and can be used for
screening diagnostics. In this regard, today IFA is widely used not only in
health care, various sectors such as agriculture, industrial biotechnology, but
in the customs, forensic medical, pharmaceutical and toxicological practice
with the purpose of revealing of drugs, counterfeit drugs, and a variety of
illegally sold their mixtures and modifications.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. Kiseleva R.Yu.
Development of immunoassay method of analysis of amphetamine and antibodies to
it in the biological liquids of the person: Dis ... cand.of chemical sciences .-M,-2012.-
113 p.
2. Gendrikson O.D. The study of
quantitative regularities of interaction of antibodies with low molecular
weight antigens, immobilized on a surface of a studded: Dis... doctor. of chemical.
sciences.-M., 2003.- 220 p.
3. Astashkina O.G. Identification narcotic
substances group of opiates method immunoassay for putrefactive transformation
of the corpse: Dis. cand.of medical sciences.-M.-2004.- 135 p.
4. Panchenko L. F., Starovoitova T.A.,
Vengerov Yu.Yu., Äzantiyev
B.B. Analytical video digital complexes express and screening laboratory
research narcotic control. // Narcology.-2011 No. 12.-64-68 p.
5. Gordon K.V. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent
assay of amino glycoside antibiotics: Dis ... doctor of biol. sciences- St.
Petersburg, Russia., 2004.- 180 p.
6. Samuilov V.D. Enzyme-linked
immunosorbent assay. //The Sorosov journal, Biology.-1999.-š3.-9-15 p.
7. Eremin S.K., Izotov B.N.,
Veselovskaya N.V. Analysis of narcotic drugs.-M: Misl, 2003.- 266 p.
8.
Soloduhina N.M. Analysis opiates, barbiturates and kannabiods latex
agglutination method with the use of functional polymeric microspheres.
Author.... doctor. of chem. sciences.-M.,2012.-18 p.
9. Patent 6534325 USA, 2010ĚĎĘ G 01N 33/546, G
01 N33/533 Roche Diagnostics Gorp. Immunoassay for the detection of
amphetamines, methamphetamines and methylnedioxy designer amphetamines/
Mc.Nally Alan J., Zhao Huiru, Goc - Szkutnika Krystyna (USA).- N09/608524.
10. Demerchyan Sh.A., Petrochenko
S.N., Volozhin A.I. Development of ELISA immunoglobulin class A, linking
derivatives opiates, kannabiods, amphetamines in saliva and blood serum of the
patients with drug addiction.//Biotechnology.-2007.-š2.-91-96 p.