Ñîâðåìåííûå
èíôîðìàöèîííûå òåõíîëîãèè/ 3.Ïðîãðàììíîå îáåñïå÷åíèå
Stradetskyy O., Bilas O.
Lviv Polytechnic National
University,Ukraine
Software
project estimation time error calculating
In programming as
in everyday life, often need to estimate how long it takes to perform a
particular task. It is necessary for the success of the project and is
one of the hallmarks of transparency and understandability of the system. After all, if one cannot describe what you need to do
to achieve the goals of the project, then it may not properly assess the time
it is expected to spend on the task. This estimated time is approximate and in most cases
are not precise. Although, this assessment is often required to make during the
development of software as a programmer that performs tasks on the project and
the project manager is responsible for all software. The customer wants to know the least about how long it
takes for developer to complete the task.
Since managers are often not very
transparent imagine the amount of work before they start, as well as the
rapidly changing requirements of software that practiced methodologies Agile -
there are many risks that cannot be taken into account when assessing planning
time task or project. It is advisable to clearly identify the
stage of planning and risk assessment.
In order to assess as accurately as
possible the planned time to be fully divide the task into smaller parts so
long until you clear understand idea about each of the items. Often in practice the approach when the
task is divided into paragraphs so long until you evaluate it in bounds. But in this case, the person who counts
the scheduled time may not consider some risks as random and periodic. So should propose and investigate
algorithms for error evaluation scheduled time, and develop software to help
calculate this error for certain tasks.
To estimate the error of the planned time
is divided into two basic ways:
·
Estimation
total error
·
Estimation
of error based on earlier experience.
The estimated total error (standard
deviation, designated as ![]() or
or ![]() ) - in probability theory and statistics,
the most common indicator of dispersion of the values of a random
variable with respect to its expected value. In fact, if we applied problems, the
standard deviation - is the most used indicator of variability of the object,
which shows how much the average individual values
) - in probability theory and statistics,
the most common indicator of dispersion of the values of a random
variable with respect to its expected value. In fact, if we applied problems, the
standard deviation - is the most used indicator of variability of the object,
which shows how much the average individual values ![]() deviate signs of their average (
deviate signs of their average (![]() ).
).
That
is in our case, this
assessment will show how much the average current estimate deviates from the
planned time average.
Standard deviation
- is equal to the square root of the variance of the random variable [1]:
![]()
According to the
formula of calculating the variance:
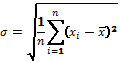
·
With small sample
(n<=40-50) Bessel correction
is [2]:
·
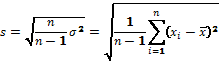
Where: - standard
deviation, constant average score standard deviation of a random variable ![]() relative to its expected value;
relative to its expected value;
![]() — variance;
— variance;
![]() — i-th element of the
sample;
— i-th element of the
sample;
![]() — the arithmetic
mean of the sample:
— the arithmetic
mean of the sample:
![]()
![]() — the volume (size)
of the sample.
— the volume (size)
of the sample.
So, in order to
calculate the standard error, use the following formula [3]:
![]()
where, ![]() – standard error
– standard error
![]() – standard deviation, unchanging rating average deviation of a random variable with respect to its expected value;
– standard deviation, unchanging rating average deviation of a random variable with respect to its expected value;
![]() – the number of elements in the sample;
– the number of elements in the sample;
![]()
![]() – sample standard deviation
– sample standard deviation
![]() — i-th element of the
sample;
— i-th element of the
sample;
![]() — the arithmetic
mean of the sample;
— the arithmetic
mean of the sample;
![]() — the volume (size)
of the sample.
— the volume (size)
of the sample.
Consider the
example calculations, even made 5 guest scheduled time (5, 20,
40, 80, 100)
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Looking standard
error, ![]()
![]()
So we can assume that the error is 18
hours, which means that it is worth to total 245 hours to add 18 and then the
total number of hours would be 263.
However, this method ignores a very
important factor that can significantly affect the performance results and the
experience of the person who will perform these tasks. It is therefore advisable to develop an
algorithm that would also give error estimates for the planned time, but based
on earlier experience.
Method error
estimates based on earlier experience, based on a simple and reliable
principle. Based on indicators obtained during the
preliminary work performed, calculates the coefficient of error, ![]()
![]()
where: ![]() — ³-th element of routine sampling time;
— ³-th element of routine sampling time; ![]() — ³- th element of the sample spent time;
— ³- th element of the sample spent time;
Next, to estimate the error (![]() ) for the
planned time a new task (
) for the
planned time a new task (![]() ), you
must multiply by a factor of (
), you
must multiply by a factor of (![]() ).
).
![]()
where: ![]() - the number of hours, how many rejected
theoretically predictable at times, that costs of its implementation.
- the number of hours, how many rejected
theoretically predictable at times, that costs of its implementation.
|
Planned time, |
5 |
20 |
40 |
80 |
100 |
|
Spent time, |
8 |
16 |
52 |
78 |
125 |
![]()
![]()
This means that
the assessment of the planned time of 48 hours should be increased to 67 hours.
After analyzing
these two algorithms, we can say that they complement each other, although to
some extent and overlap each other. It should be noted that in practice, both
methods should be used to analyze performance of one and another, and even
combine them. This can give good results and reduce the
risk of exceeding the scheduled time.
References
1.
The
Cambridge Dictionary of Statistics, CUP / Everitt,
B.S. – 2003
2.
Kenney J., Keeping E.S. Mathematics of Statistics / van
Nostrand.- 1963.- p. 187
3.
Zwillinger D. Standard Mathematical Tables and Formulae.-
1995