Modern information technology/4. Information
Security
Loza T.Y.
State
higher education institution
"National Mining University"
The use of steganography method for the hidden transmission of messages
in images
In the
age of high technology information is the most important part of our lives. In
view with this problem of information security concerned experts in the field
of computer security as well as many ordinary computer users. This article
discusses a method of protecting information as digital steganography.
The
first records about the use of steganography appeared in ancient Greece. In
this age of information technology science have given fresh impetus to the
development and improvement. Advances in computer technology and multimedia
gave impetus to the development of new methods to ensure the security of
digital data transmission over communication channels. Based on the sampling inaccuracies and redundancy of
the analog signal, these methods allow you to hide secret messages in a file
container. A distinctive feature of the method is to hide the fact of communication.
The
greatest popularity in recent times received a part of the digital
steganography, which is used to conceal confidential messages in images
transmitted over computer networks.
Particular interest
was caused to steganography methods after several countries have imposed
restrictions on the use of cryptosystems. But the problems of protection of
property rights in the digital information caused many works in the field of
watermarking - special labels, insensibly implemented in image or other digital
media in order to control its use.
To encrypt the information that will be integrated
into a container file (graphic image) is formed by a hidden information
transmission channel, called a stenographic system or simply stegosystem. The
scheme of stegosystem work is presented in the figure (Fig. 1).
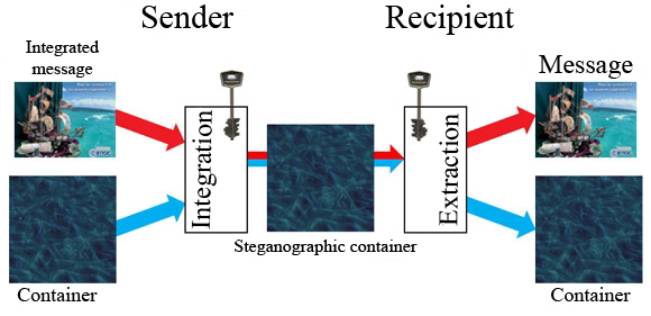
Figure 1. The general model of stegosystem work.
To
improve the reliability of steganographic system necessary to consider the
following points in its construction:
·
The enemy has a full understanding of the steganographic system and
details of its implementation. The only information that remains unknown
potential enemy is the key by which only the holder can establish the fact of
the presence and content of the hidden message;
·
If the enemy somehow finds out about the fact of the existence of hidden
message, it should not allow him to remove such messages to other data as long
as the key is kept secret;
·
A potential enemy should be devoid of any technical or other advantages in
the recognition or disclosure of secret messages.
One of the most popular algorithms for embedding secret information into
a digital signal is a method of replacing the least significant bit (LSB).
We know that
people do not perceive all the information included in the image, and if you
replace less significant bits in the color components of the pixel with
concealed messages, man will not be able to identify this on eye. Consistently
producing such replacement, starting with the pre-specified pixel, can be
implemented message. The idea of the method is simple, but in
such a trivial form it is not highly effective.
Advantages of
the method:
· The size of the container file is not changed;
·
When replacing each of the least significant bit in one pixel changes
are not visually noticeable;
·
The ability to change the number of replaceable bits in accordance with
the size of hidden information.
Disadvantages:
·
Processing of container file leads to an almost complete loss of hidden
data.
The following is an operation principle of algorithm LSB on the example
of 24-bit RGB-image. Each pixel of the image in BMP format is encoded by three
bytes, according to the intensity of one of the three component colors (red -
R, Green - G, and blue – B, Fig. 2).

Figure
2. Representation of the color pixel in the BMP-image.
As a result of mixing of the three channels of pixel becomes necessary
shade. To illustrate the operating principle of the method LSB is necessary to
paint each of three bytes in the form of bits. Least significant bits (in the
figure they are located on the right, Fig. 3) are less noticeable effect on the
final image than the most ones. From this it can be concluded that the
replacement of one or two younger, the least significant bits for other
arbitrary bits so insignificantly distort the shade of pixel that the audience
will not even notice the change.
It is assumed that you want to hide in a pixel of the image six bits:
101100. To achieve the result you need to break them into groups by twos and
then replace the least significant bits of the original image by data (Fig.
3.).
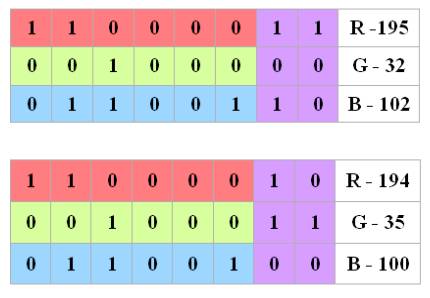
Figure 3. The initial and modified color components
The result will be obtained by a new shade of the pixel that is
virtually indistinguishable from the original (Fig. 4.). These colors will be
difficult to discern even on monotonous fill. As practice shows, the
replacement of two least significant bits rarely perceived by the human eye and
does not affect the quality of the final image.

Figure 4. Pixel color with implemented data
Then you need to calculate the useful volume of the
RGB-container.
Each channel of the eight bits two of them are engaged the hidden
information, which corresponds to 25%. Thus, you can hide useful information of
a quarter of the total size of the image with the confidence that the naked eye
these changes will not be noticeable.
All BMP containers should be divided into two classes: the
"clean" and noisy. In the "clean" image trace a link
between least significant bit, which is changing, and the other 7-bits of
elements of the color, and traced significant dependence of bits to each other.
Implementation of the message in a "clean" image destroys the
existing dependencies, which is very easy to diagnose by passive observer. If
the image is noisy (e.g., obtained from a scanner or a digital camera), then
determine the attachment becomes much more difficult. Thus, for LSB method is
recommended to use the files that were not created on the computer initially as
a container file.
Digital
steganography is the dynamic and rapidly developing science that uses the
methods and achievements of cryptography, digital signal processing,
communication theory and information. Along with the ordinary user
major companies operating in the field of multimedia are also interested in it,
seeking to protect their content from illegal use. It does not attract
attention, as opposed to clean cryptography. Analysis of trends in digital
steganography shows that in the next few years, interest in the development of
its methods will grow more and more.
References:
1.
Computer steganography. Theory and Practice. G.F. Konakhovich
2.
The
foundations of modern cryptography. S.G. Barichev, V.V. Gon-charov, R. E. Serov
3. Gribunin
V.G., Binding J.H., Turintsev I.V. Digital steganography. - Moscow: Solon
Press, 2002. - 272 pp., ill.
4.
Journal
"Information Security " #4, 2007