Ôèçèêà 9. Àñòðîôèçèêà è êîñìè÷åñêèå ëó÷è
T.Kh.Sadykov1,
V.V.Zhukov4,
N.G. Breusov5,
M.K. Mukashev3,
G.Ya. Khachikyan2
N.N.Zastrozhnova1
SeismIC
stations for short-term prediction OF EarthquakeS by means of the cosmic rays
1Institute of
Physics and Technology, Almaty, Kazakhstan
2Institute of
Ionosphere, Almaty, Kazakhstan
3Abai Kazakh National
Pedagogical University, Almaty, Kazakhstan
4Tien-Shan Mountain Cosmic Ray
Station, Almaty, Kazakhstan
5Joint Company
"National Center for Space Research and Technology",
Almaty, Kazakhstan
Abstract. It
is planned to construct two seismic stations on a tectonic fault in the Large
Almaty canyon (Tien-Shan) at the heights of 3340 m and 1700 m above the sea
level. The seismic station prototype is now being built in the vicinity of
Almaty (8 km apart) at the Intermediate Cosmic Ray Station (1700m a.s.l.). We
are going to use the neutron monitor, the Geiger-Muller counters (G-M), sensors
of a magnetic field of the Earth, the radon detector and seismograph for searching
correlation between variation in the cosmic ray particle flux, the magnetic
field of the Earth and perturbation in terrestrial crust in the area under
study.
Introduction. The studies in the area of
prediction of earthquakes and search for its forerunners are very urgent. At
present two identical seismic stations are expected to be built in the Tien-Shan
ranges at the sites of the High Cosmic Ray Station (HCRS) and the Intermediate
Cosmic Ray Station (ICRS) of the Kazakhstan Institute of Physics and
Technology. The stations are located, respectively, at the heights of 3340 and
1700m (a.s.l.) and related to the tectonic fault of the Large Almaty Canyon
(see Fig.1).

Figure 1 -
Locations of seismic stations in the
Zaili Alatau mountains: 1-High cosmic Ray Station
(Tien-Shan) 3340 m a.s.l.; 2-Intermediate Cosmic Ray Station 1700m a.s.l.;
3-Abai Kazakh National Pedagogical University, Almaty 800m a.s.l.
For such seismic area as that of the Almaty megapolis, this problem is
the issue of the day. It is enough to recollect the destructive earthquakes in
the Verny and the Keminy [1], characterized by magnitudes of 7.5 and 8.3 in the
Richter scale. Epicenter of the Keminy 8.3-magnituide earthquake, occurred in
1911, is related to the mountain pass Jusaly Kezen, i.e., in the place where
the HCRS is located at present. Seismic studies are carried out systematically
at the Almaty Institute of Seismology, situated at a height of 850 m. At the
stations to be created the following characteristics are assumed to be
controlled: seismic movements and various components of space radiation:
neutrons, muons, electrons and photons, as well as the Earth magnetic field
intensity and the radon concentration. The essence of the proposed technique
for earthquake forecasting consists of creation of a network of parallel
measuring and on-line processing of several earthquake forerunners at a
mountain level, and the technique key information is correlation between
tectonic processes in the Earth crust, dynamics of the high-energy and
low-energy cosmic ray particles and the Earth magnetic field intensity. Simultaneously,
the concentration of the surface radon will be controlled.
The first indications on the relationship between the high-energy charged particle fluxes in
the Earth radiation belt and the Earth seismic activity were obtained in the
experiment «Maria» on the orbital station Salyut-7. Geomagnetic field was calm,
any signs of enhanced solar activity were absent, but the charged particle
intensity in the radiation belt jumped up three times [2]. It was cleared up
that enhanced seismic activity was observed that day over the globe against
ordinary geophysical calmness of the planet. Similar regularity was found in
experiments on the satellite Meteor-3 [3]. The relationship between the diurnal
solar activity, global number of earthquakes, and the manifested deviations in
the cosmic ray intensity was analyzed. A conclusion was made that the
high-energy particle fluxes are sensitive to seismic activity. Among 36 cases
of an increase in the charged-particle flux intensity, lasting from 1 to 8
minutes, 34 cases were related to the geomagnetic and solar «calm». However,
these cases occurred in the days of the enhanced seismic activity, followed in
the 2.5- to 3-hour intervals by the earthquakes with the magnitude 4.0 in the
Richter scale. It was found that earthquakes were accompanied by the disturbances
of the Earth’s magnetic field, resulting, in turn, in cosmic ray variations.
It’s quite possible that overshoots of the field intensity leas also to
occurrence of optical phenomena in the upper layer of atmosphere: the so-called
«elves», or «sprites», which are studied in the frame of the international
project «Andromeda» with the ISO experiment on the board of the international cosmic
station.
Availability of the prognostic test site will make it possible to make
comparison between synchronized data on optical phenomena in atmosphere and its
potential sources in the Earth crust tectonics. As a result, these optical
phenomena can be included to the network of the earthquake forerunners, in view
of short-term forecasting.
Hardware. In a view of development and implementation of the
techniques for searching of new earthquake forerunners, at the ICRS the seismic
station prototype was created and put into operation. The prototype
incorporated the seismic pavilion provided by seismic receiver (1) and
seismograph (2), the Geiger-Muller counters (G-M) (4) and (6), the lead filter
(5), the Earth magnetic field sensor (8), the neutron monitor (9), the radon
detector (7), the multi-channel analog processor (3), and the PC (10) (see
Figure 2) from [4]. One of two G-M detectors, composed of five G-M counters, is
used to record incident cosmic ray particles. Anorther similar detector,
located under the lead absorber (filter), is used to cut off the low-energy
soft component of cosmic radiation and to record muons. The neutron monitor is
assembled from paraffin blocks with six neutron boron counters CHM-8 in the
center, surrounded by the lead generator 10 cm thick.
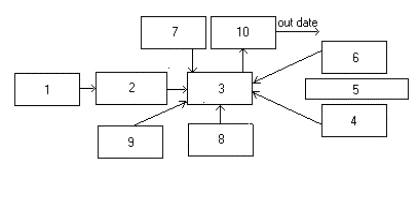
Figure 2 - Layout of the network
for data collecting and processing at
the seismic station prototype
The monitor dimensions are 2.0´.0´0.8 m (see Fig. 3).
Later, the radiowave-range detector of the Earth electromagnetic field is assumed to be
installed.
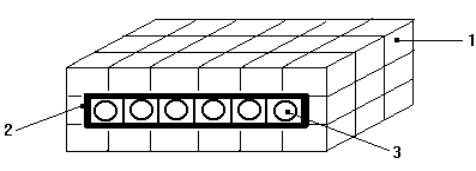
Figure 3 - Neutron monitor NM-06
The seismic station prototype is intended to be used to:
-
study the variable radiowave-range electromagnetic fields, occurring
both in the Earth depths and in atmosphere as a result of electro-kinetics
effects accompanying rock compression;
-
study the effect of the Earth magnetic field to the cosmic ray charged
particle trajectories;
-
study the particle flux intensity versus the Earth magnetic field;
-
implement uninterrupted monitoring of the cosmic ray
neutron/muon/electron-photon components;
-
record the concentration of the surface radon.
The facility incorporates the following detectors:
-
the neutron monitor NM-06, which was
used for studying characteristics of the EAS (Extensive Atmospheric Showers)
hadronic component in the cosmic ray station;
-
the electron-photon component
detector composed of proportional counters, which records the temporal
distributions of the charged particle/photon intensities. It is located above the neutron monitor. The
6-m2 detector consists of three units, each incorporating 20 G-M
counters. The detector will be used later for seismic forecasting also at the
HCRS (3340 m a.s.l.), in view of obtaining of a more clear pattern of tectonic
movements over as large areas as possible;
-
the 1-m2 detector of muon component records temporal
distributions of the muon intensity. The detector is composed of a single unit,
which houses 20 G-M counters. The unit is located under the neutron
monitor.
The whole processor is made in the CAMAC standard. Some of the G.M.
counters operate at high voltage (1060 V), providing a proportional mode of
counter operation. Denial of the Geiger mode has made it possible to get rid of
the long (up to 1000 ms) dead periods, typical for Geiger counters and coming
after registration of each pulse – as a result, the facility dead time has
reduced considerably, and the counter lifetime, respectively, has increased.
Summary. Both
seismic stations will be created with the changes introduced to the prototype
in course of trials of the latter taken into account. At present processing of
the data covers determination of the oscillation amplitudes and correlations
between seismic movements, the magnetometer readings, the cosmic ray intensity
values and the seismic movement duration. The obtained data are, still,
preliminary, and the technique of the data collecting and processing will be
revised in course of seismic station trials.
References
1. G. A. Eiby. Earthquakes. Heinemann, 1981, pp.252-253.
2.
S.A.
Voronov, A. M. Galper, V.G. Kirillov-Ugryumov e.a. – Registration of an
increase in the high-energy particle flux in the vicinity of the Brazil
magnetic anomaly on October 10, 1985. The Moscow Institute of Physical Studies,
Preprint 006-88, Moscow, 1988 (in Russian).
3.
A. M.
Galper, V. V. Dmitrienko, I. V. Nikitina e.a. – Cosmic Studies, v. XXVII, issue
5, 1989, p.789 (in Russian)
4.
The
Kazakhstan Patent N16733, dated 09.27.2005; «The way of Earthquake forecasting
and the device to implement it» (in
Russian).