Electronic auctions in
companies as on-line selection process
Ing. Vladislav Bobenič - Ing. Patrícia Slaninová
Ing. Vladislav Bobenič
Specialist of department Procurement Operation & Support
U. S. Steel Košice, s.r.o., Vstupný areál U. S. Steel, 044 54 Košice-Šaca
Ing. Patrícia Slaninová
F BERG Technical University of Košice, Department of Geotourism, B. Němcovej 32,
040 01 Košice
Abstract
Electronic auctions create nowadays
multi-criteria relations between business partners. They are one of the
e-procurement methods in e-sourcing. Electronic auctions bring us cost
reduction at inputs, save time, enable marketing to become more effective
in supplier relations and lead to more objective conditions in commercial
relations.
1. Introduction
Procurement in
large enterprises has one of the major roles as a real source of costs
saving directly at starting point (input) of production process. Purchase
costs, no matter what industry we talk about, represent 30% - 70% of the
company turnover. This ratio is generally growing, because companies always
spend large amount of their financial resources to support the „core business“,
i.e. what they produced before, they now purchase from external suppliers. This
is how the area of Procurement Management earns a more important role,
because every profitable contract brings the company net profit. Another important
factor of competitiveness is the fact that prices of suppliers (e.g.
metallurgic industry) often very similar. This means, that the company may
often create profit due to excellent negotiated purchase. Well realized
purchase ensures significant decrease of input prices, ensures cost reduction
by buying only a needed amount and thereby improves the economic situation of
company.
The awareness about
savings and quick returns of investments using electronic procurement is
increasing year by year. The goal of management, which decides to implement
e-procurement, is in particular cost reduction for operation. Connected with
production systems and the supplier chain, it brings reduction of total costs
and finally helps to achieve higher profit and better competitive position due
to lower prices of products. [3]
Another important
key-factor in this process is selection of suitable suppliers. Feasibility of
supplier is then also considered by the possibilities offered in its electronic
interface. He, who don’t have it at appropriate level is loosing the advantage
of being competitive and simply can not be a supplier of matured
companies. A supplier using electronic tool to process business
activities, a supplier able to create and handle electronic commercial
documents, this supplier has a significant favorable position. This
supplier could be the improvement initiator in area of electronic equipment on
the side of buyer. On the other hand, a strong buyer can force a weak
supplier to communicate in accordance to its own rules. However, the power is
not the correct tool to use in sake of building successful and lasting
supplier/buyer relations. That is why often software is used, which
enables to help the supplier. For instance, small suppliers can be offered an
environment for hosting, in which they can work with electronic catalogues,
accept and confirm orders or to issue invoices. They could dispose with
electronic communication, eventually tools used for direct integration of
supplier WebPages into the e-procurement system of buyer. [4]
Managing the
procurement process is becoming more important to achieve company goals and to
increase competitive position of individual companies. Continually, the
supplier/buyer environment is being changed where both realize the importance
of close cooperation also on the level of salesman / buyer, mutual connection
of logistic chains, proving itself in reduction of purchase costs, increase in
reliability and quality of delivery. In the next chapter, we will clarify basic
fundaments of electronic commerce workflow, i.e. on-line selection process.
Because it concerns the process connected to other transaction mechanisms, we
will focus in the article on the core and not analyze deeply the support
mechanisms.
2. Electronic procurement
Nowadays, the
preference is set to automated procurement activities and external form of
electronic procurement – outsourcing of procurement. In the past, the employees
had much freedom in purchasing, where they could take own initiative by selecting
suppliers. Nowadays, the acceleration of procurement processes leads to
excluding specific activities. Orders are applied electronically what
accelerates the whole ordering process and overcomes some activities of
employees and relieves them for other tasks, e.g. market research or to focus
on supplier/buyer relations. Electronic procurement demands a more active
role of employees.
Opportunity: understanding strategic goals and
intentions of company represents the active role and value of purchasing within
the scope of total customer satisfaction. Focus on customer value-added is
shown in changing the company strategy from „lets do things better“ to „lets do
things in another way – the more effective way“. Supply Chain Management (SCM)
can be nowadays considered as „core“ of company strategies. [1]
Electronic procurement is connected with the
total development of e-business and the development of e-commerce. Electronic
commerce creates an environment of electronic relations between partners:
• supplier – producer
• producer – producer
• producer – merchant
• producer – service provider.
The
benefits of e-procurement – electronic procurement, for each participant can be
characterized as:
• shortening of period of processing an order
• immediate access to information
• orders also after working time
• immediate information about delivery terms and prices
• lower workload of employees by processing of orders
• fast deliveries.
The basis
for processing a commercial documentation is using standard EDI –
Electronic Data Interchange. Company information systems offer this service as
standard. [2]
3. Purchase on-line auctions and their benefits
There are already many articles written about
electronic purchase auctions. Because it is one of the best working mechanisms,
we can state that it is a great source for money making. Despite that most
of the employees did a good job, they had to back down when attacked by
this tool.
The attention given
to purchase processes and to purchase costs is rising yearly. Continually,
there are new trends and concepts created. E-auctions are exactly the trend
tool, which charmed others by simplicity and clarity of performance and which
becomes an indisputable part of extensive procurement concepts. To be
a leader in procurement and not using the e-auction principal of dynamic
price comparison, this would be old-fashion. [5]
3.1 What is e-auction ?
E-auction
(electronic auction) is an internet application or so called e-auction hall,
which enables the buyer to apply in the electronic on-line selection process
and involve specific suppliers in real-time. Based on pre-determined conditions
and specification of an e-auction, the suppliers can enter their introductory
price offer, which can be adjusted during the course of e-auction based on
price offers of other suppliers. Having finished the e-auction, system
automatically compares and evaluates individual price offers. E-auction is
a suitable tool for obtaining materials, goods and services which are easy
to substitute and which can be supplied in same quality, time and volume by
more suppliers. [8]
E-auctions save
money of the enunciator, lead to increase of effectively in marketing and
supplier relations, lead to extraordinary transparency of procurement processes
and are very effective anti-corruption tool. They also enable procurement to
obtain objective prices, shorten transaction times and decrease transaction
costs of procurement process, confirm objectivity of supplier conditions
requested by the enunciator, enable the enunciator to analyze its negotiating
position, accelerate the preparation process and shorten competition time from
weeks to hours.
Purchase on-line
auctions surely offer space for improving the quality of marketing/supplier
relations. In the same time, it enables
evaluation of investments in a sophisticated IT environment, whereby it
supports the competitiveness of companies. [6]
3.2 When to use e-auction ?
Research of various
reputable marketing and consulting companies (Aberdeen Group, IDC, Cartegic Group)
in the area of e-business agree that on-line reverse auctions as part of total
e-Sourcing system, applied in continually increasing number of companies
worldwide, bring real costs saving in average of 10 – 25% of expenses for
purchased materials, goods and services. An important factor influencing
success of an e-auction, as cost reduction tool, is a correct
implementation into the strategy of providing company resources. E-auction
shall not be used in a flat method, same in all areas of acquisition. The
attention should be drawn to question „Where & How to use e-auction?“, i.e.
to specify which types of materials, goods or services shall be obtained using
an e-auction and how to use the results thereof.
Ed Goetting
(Manager of e-commerce and supply chain with Gibson & Associates, Inc.)
formulated basic characteristics of acquisition areas in company, i.e. those
material and goods groups, which are suitable for on-line reverse auctions:
1. Strategic Relationship is Less Important
It is difficult to build a
cooperative relationship with suppliers through an auction and as a result,
auctions should not be used where an ongoing relationship involving mutual cost
reductions, joint design, joint marketing, and open information sharing is
important. Categories where strategic relationships may not be as important
include indirect categories and off-the shelf, near-commodity direct materials.
2. Price is main decision factor
Although factors besides price
can be addressed in an auction format, auctions are built around price. For
this reason, an auction works best for categories in which the main
differentiator between suppliers is price.
3. Many Qualified
Suppliers
Auctions will be most
successful with competition. If you purchase custom electrical components that
only two suppliers in the world can supply, you should not attempt to hold an
auction between those two suppliers. In a situation such as this where
commitment of supply is important, a solid relationship with suppliers is far
more important than any incremental price savings that could be achieved
through an auction.
4. Standard (but not
pure commodity) Product
The less differentiation there
is between each supplier's products, the easier it is to make a true
apples-to-apples comparison and, by extension, the easier it is to auction.
5. Low to Medium Strategic Importance
Your most strategic categories
should not be put through a stand-alone auction. You should not put these
categories through an auction unless you are very comfortable with the auction
format and have tested it on less strategic categories. [10]
6. Present purchase price under the value of market
price
In many cases, company buys
material from current supplier and pays a lower than market price. The reverse auction informs here the
supplier, that there is space for a price increase without risk of loosing
the buyer. In case that the company is not aware of market price and does not
want to risk unexpected reaction of supplier, he can organize a sealed
e-auction.
7. Purchase can be „lotted“
It may be cumbersome to run
individual auctions for each of many line items. Line items can be bundled into “lots” and suppliers will be
required to bid on all the parts in that lot or none. This concept of “lotting” works well with office products. [11]
8. Benchmarks (testing of market)
A final area where reverse
auctions can be an effective tool is in benchmarking. Often a company will be
very happy with their current supplier(s), yet feel they need to test the
market to ensure they are still receiving competitive pricing. Rather than go
through a full-scale sourcing program, companies can use an auction to expedite
the process. The key to a successful auction benchmark is to document your
service, delivery, payment terms and other "non-price" requirements
up-front to ensure that suppliers are bidding on an apples-to-apples basis.
[10]
3.3 Is price the main decision factor by e-auctions?
In accordance with
this working mechanism and in accordance with abovementioned objective
processes, we can state that the price is surely not the main decision factor.
However, if some
trustworthy supplier offers you demanded commodity under same terms, same
quality and guarantees a cheaper delivery, promising that your savings will
cover the costs connected with supplier exchange; you won’t spend much time
with decision. It is healthy when a reliable supplier learns that
a trustworthy competition (surely, others would be not invited) has lower
prices, thereby is pushed to adjust to the new situation and looks for future
savings on own side. [5]
3.4 How can e-auctions bring such high price saving?
The auction hall
often enables your supplier to see first time the real possibilities of other
(potential and relevant) suppliers, interested to win the deal and it is up to
him how he reacts to this fact. This is a clear and correct marketing
approach. Sure, none of the suppliers will go too deep under real costs and
thereby endanger its economy. It is obvious that by using e-auction mechanism,
the price starts loosing some of the „soft negotiating power“. Suddenly,
marvelous arguments of individuals, smooth voice, pretty eyes, worldwide brand,
none of them matter anymore. You match the comparable with comparable, you
negotiate real market price and real supplier conditions. [5]
It is not
a given that if you save in the first round, same happens by other rounds
with same type of assortment. But you can be happy, because if you did not use
the dynamic comparison mechanism, the difference would be much more notable.
4. Process connected with electronic auctions
Within the process
and the within the preparation of e-auction we interfere with term „eSourcing“
(electronic selection process, see Figure 1 below) which can be defined as
usage of tools supporting and optimizing
the benefits within the process of strategic supplier selection by RFx. The
term RFx means "request for something" – description what exactly we
want to purchase, reaction to which the supplier submits its offer. The
proposal for specific RFx template is in the hands best employees of
procurement, using their experiences and best-practices. Mostly three types are
used in praxis:
RFI - request for
information
RFQ – request for
quotes
RFP – request for
proposal
![]()
![]()
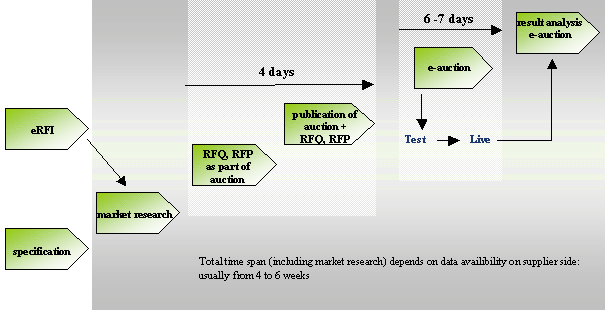

![]()
Figure 1. Phases of eSourcing
process
When evaluations of
all criteria and date of new supplier is finished, selected target group
receives a decision if invited (or not) to participate in testing and to
participate in a real e-auction. The enunciator usually e-mails basic
information about registration, user conditions and rules for placing offers,
fixing the date and time of an e-auction. Testing an e-auction should take
place approximately 2 – 3 days before the real auction. The scope of testing an
auction is to get the suppliers familiar with the environment and possibilities
of the auction system. The offers placed by suppliers during the testing
e-auction are not considered as binding.
Next step is to
start the real auction. This e-auction can be attended only by suppliers who
fulfilled all conditions. E-auction has an allowed time and length where the
suppliers can place their offers in accordance with rules. None of the
suppliers has the information about other invited suppliers or the number of invited
suppliers. The whole e-auction is controlled by an administrator. The
administrator can interfere into the process during the run of e-auction, i.e.
receive comments from suppliers, advice them to add missing data in placed
offer or warn them about a wrongly placed price. Praxis shows that
suppliers are very careful when starting in auction hall. Most of them choose
a strategy to wait, feared to loose their competitive position at early
beginning. The most interesting part of whole e-auction is the end, because
this is the part of real changes, influencing the success of a supplier.
The development and
the course of an auction depends from software, i.e. interface possibilities
where most of the conditions can be set, e.g. duration of auction; method of
ending the auction; enable or disable the supplier to see own position; disable
supplier to know what is the best price; etc.. It is impossible to define exact
model and to state which is the best or most suitable. Everything depends
on demanded materials, goods or services and also from strategy.
Of course, same as
by other processes, there are risks connected with e-auctions. It concerns
mostly closing a contract with an unauthenticated supplier, coming
with lowest price, but not keeping its promise. This risk can be eliminated by
a good audit of suppliers. Another disadvantage is potential technical
problems, which can occur in this process. In such case the administrator must
interfere and extend the time necessary to solve technical problems.
Final step is to
evaluate e-auction, i.e. to nominate the winner. As mentioned in point 3.3,
price does not have to be the main decision factor. The winner does not have to
win the deal. After ending an e-auction, the announcing company shall evaluate
all offers of suppliers in detail, not only price offers, and shall decide on
closing contract with the most suitable supplier.
Conclusion
An on-line
selection is a young tool in the B2B procurement environment, but is an
enforcing element of marketing behaviour. Current trend shows that e-auctions
will become a natural part of selection process within few years,
considered and accepted as procurement standard. They enable to purchase with
minimum transaction costs, within a short time and with objective prices.
Nevertheless, thoughts and creativity can but be bought, but can be stolen
easily.
Literature:
[1] CSIKÓSOVÁ, Adriana - ANTOŠOVÁ, Mária: Elektronický marketing a nová dimenzia šírenia informácií. In: Obchodné podnikanie a marketing v novom európskom hospodárskom priestore : Zborník z medzinárodnej vedeckej konferencie, Mojmírovce, 7.-8. október 2004. Bratislava : EU, 2004. s. 712-717. ISBN 80-225-1904-9
[2] CSIKÓSOVÁ, Adriana - ANTOŠOVÁ, Mária: Súčasné tendencie vývoja priemyselného marketingu na globalizujúcich sa trhoch. In: Marketing a obchod 2006 : Trvalo udržateľný rozvoj - predpoklad hospodárskeho rastu : Zborník z medzinárodnej vedeckej konferencie : Zvolen, november 2006. Zvolen : Národné lesnícke centrum, 2006. s. 23-27. ISBN 80-8093-009-0
[3] DUDINSKÁ, E.: Znalostný manažment a jeho význam pre generovanie konkurenčnej výhody. In.: Podniková revue. PHF EU Košice: roč. III., 2004, č.5, s.31- 41. ISSN 133-9746
[4] HUTNÍKOVÁ, Alica - SEŇOVÁ, Andrea: Efektívne manažérske riadenie krízových situácií v podnikoch. In: Teoretické aspekty prierezových ekonomík 4 : Zborník vedeckých prác : PHF EU BA, Košice, 2007. Bratislava : EKONÓM, 2007. s. 130-135. ISBN 978-80-225-2472-8
[5] Kaplan,
Milan – Zrník, Josef
a kolektiv: Firemní nákup a e-aukce. Jak šetřit čas a peníze. Praha:
Grada Publishing, 2007. ISBN 978-80-247-2002-9
[6] http://www.proe.biz/www/cz/reference170.html
[7]
http://www.proe.biz/www/cz/reference284.html
[10] http://bctim.wustl.edu/topics/topics.cfm?Categories_ID=3
[11]
http://www.fta.dot.gov/documents/BPPM_ch4.doc