Mathematics
/ 5. Mathematical modeling
Kulyk A.J., Krivogubtchenko D.S., Kulyk A.A.
Vinnitsa national technical university, Ukraine
COMBINED ALGORITHM OF NUMERAL INTEGRATION
BY METHOD OF NUTON-KOTES
In tasks, which are related|tied| to the analysis, authentication, estimate of
qualities, simulation of different
devices of automation, control, informatively-measuring technique and electronics, there is the necessity of
calculation of the noted integrals. More frequent in all functions which must
be integrated is set in a tabular kind
with the even step of dyskretization. It at once substantially limits the
variety of the used methods. Practically can be used only method of Nuton-Kotes| with application of different formulas – rectangles,
trapezoids, parabolas and others like that. But their use is related to the row of complications:
: coefficients of Kotes for
plenty of dyskrets are
difficult, that is why the amount of the used points of integration
does not exceed nine;
: opened
formulas for the calculation of the noted integrals by the method of Nuton-Kotes| by the indefinite amount of points for the polynomials
of order more high three, in literature is absent. Its destroying and use in
principle is possible [1],
but difficult
and have badly algorithmization for calculations on the personal
computers;
: amount of initial values of array,
that is subject to integration, must be multiple to the amount of points of integration.
In other case a remain
substantially reduces validity of result. It is related|tied| to the necessity of calculation of integral by
the formulas of rectangles, trapezoids or parabolas, and|but| its exactness is considerably below;
:
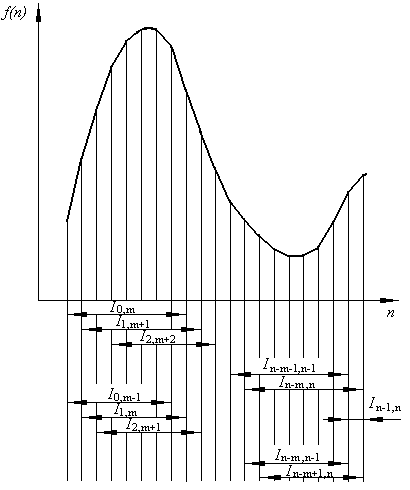 on the interval of integration to the total error most payment is given a report by
constituents at the beginning and at the end of interval. Except for it, determination of integrals on
contiguous intervals
causes the increase of error on limit of
contiguity. It is related
to the loss of control by the dynamics of process.
on the interval of integration to the total error most payment is given a report by
constituents at the beginning and at the end of interval. Except for it, determination of integrals on
contiguous intervals
causes the increase of error on limit of
contiguity. It is related
to the loss of control by the dynamics of process.
Especially these failings
appear
during numeral integration of quickly changeable functions [2]. Coming it from, it is expedient
to build a simple algorithm which
would not be limited by the amount
of integration points. Doing
it by one formula is impossible, that is why it is needed to conduct integration by two
formulas in contiguous intervals,
as it is given on figure.
It will allow to define elementary integrals between two located alongside
points.
|
Principle of numeral
integration by the combined method |
For realization of the principles set forth above, it
is necessary to define for all array [0, n] of initial values partial
integrals after m points in intervals which are blocked:
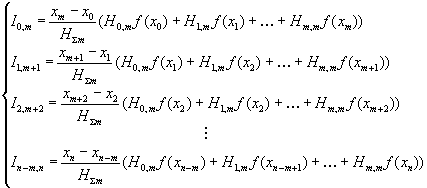 (1)
(1)
where m – amount of points of determination to the integral;
![]() –
Kotes coefficients for m points;
–
Kotes coefficients for m points;
![]() –
value of
partial to the integral on an interval
[i, j].
–
value of
partial to the integral on an interval
[i, j].
Consideration of the system of equation (1) shows
that she can be given in a
kind:
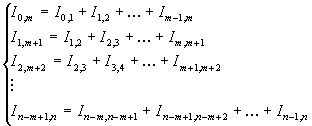 . (2)
. (2)
It is
similarly possible to make the systems of equations for the formes of Nuton-Kotes by
(m – 1) points in intervals|spaces| which are blocked:
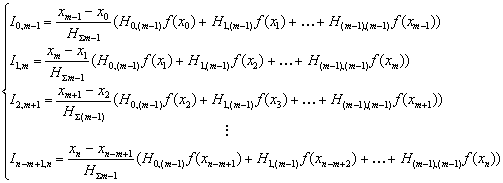
(3)
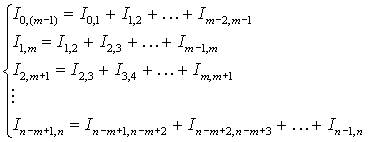 . (4)
. (4)
Compatible decision of the systems of equations
(2) and (4) allows to define the value
of elementary integrals of ²0,1, ²1,2, ²2,3 ..., ²n-1,n for the single intervals of dysketretization:
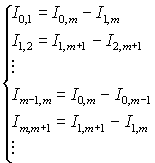 . (5)
. (5)
An
integral on an interval [x0,xn]
is determined as sum of
partial integrals:
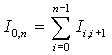 .
(6)
.
(6)
The
developed principle of integration have easily algorithmization and will be realized at software based.
The analysis shows that initial integrations are carried
out independently from each other, that is why the volume of points is practically
unlimited, thus their amount
not necessarily must
be multiple to the used formulas of integration.
As watching dynamics of the controlled
process on all interval
of integration, exactness rises considerably.
The
test of the
developed algorithm was carried out during determination|definition| of effective and practical width of
spectrum of elementary signals at its transmission to the communication line by 50 and 100 points. The
results of calculations confirmed the considerable increase of accuracy (approximately on
30%) exactly due to absence of critical points of joint of integration
intervals.
References.
1. Õåììèíã Ð.Â.
×èñëåííûå ìåòîäû. – Ì.: Íàóêà, 1972, 400 ñ.
2. Áàõâàëîâ Í.Ñ.,
Æèäêîâ Í.Ï., Êîáåëüêîâ Ã.Ì. ×èñëåííûå ìåòîäû. – Ì.: Íàóêà, 1987.