Экономические науки/ Банки
и банковская система
Arunyants G.G., doctor
of technical sciences, professor
Badeyan
A.R. PhD student
Kaliningrad State
Technical University
Analysis
of the commercial banks risks and ways of their management
New level of banking
system development in the Russian Federation is accompanied by the severe
competition and instability of environment. Growth of the bank competition forces
the commercial banks to lead more risk policy on the main activities that
conduct to decrease liquid positions.
To maintaining position in the market, commercial
banks are forced to use innovative banking technologies. As a result, the
problem of credit risk management is actualizing, and the solution to any
economic problem should be based on a proper understanding of its nature and
mechanism of the study.
The concept of risk
covers all stages of the formation and operation of a commercial bank.
Gradually changing the growth rate of banking, there is a need for change, the time
making good decisions about the future development [1].
Banking risk is a situational
characteristic of any bank, reflecting uncertainty about the occurrence of an
event that occurs under the influence of internal and external factors that
affect on income or capital of the bank.
The credit risk could
be considered as the largest, inherent in banking activity. According to the
majority of authors [2], it is risk of unrecoverable loan and interest of
credit.
In the range of the banking risks of Russian
Federation, the leading place on the origin frequency (about 60%) and amount of
losses (more than 80%) are the credit and liquidity risks. Accounting liquidity
risks and lending risks in banks is an obligatory informational basis of
decision-making process for the development of practical measures on increasing
the portfolio of loans, the safety of specific banking operations and transactions
[3]. It substantially determines an originality of methodology of credit risk
management, and emergence of new conditions of managing, application of
financial technologies, modern financial instruments and other innovative
factors caused emergence of new types of risks.
The credit risk
conducts to emergence of all chain of banking risks. Therefore the quality
assurance of a credit portfolio and credit process depend on level of the
organization of credit risk management, and credit risks management is
necessary part of strategy and survival tactics and development of any credit
organization which deserves special attention because the success depends on
quality [4]. By the way, the questions connected with methods of minimization
of credit risks are insufficiently developed in economic literature. The task
of generalization and systematization of all knowledge of an essence and
content of credit risk at the present stage of development of the credit
market, and also development of practical recommendations of minimization and
neutralization of risks is an important task.
In the process of
performing the functions of a financial intermediary banks are facing a lot of
possible risks, which optimization is an indispensable condition for the
stability of individual bank and whole banking system as well as.
Optimization of
banking risks is a process of determining the ratio of certain types of banking
risks, which provide the optimal proportions between the level of profitability
and the level of financial stability of the bank. Maximum effectiveness and
efficiency of the optimization process of banking risks could be achieved only if we use system approach,
when the object of analysis are becoming part of the bank, all transactions
considered in the relationship and interdependence.
The system
of optimization of bank risks assumes [5]:
• formation
of the classification of banking risks, providing the specific application by
the bank operations and services;
• identification
of the indicators of the individual types of banking risks;
• determination
of the overall level of risk, reflecting the highest possible degree of risk to
the bank;
•
simplifying the interpretation of digital information of the bank in order to
take timely and correct decisions.
With this systematic
approach, the problems associated with the functioning of the system components
to optimize banking risks are discussed in the context of the problems of the
whole system, which provides a holistic approach to their solution, and the
higher the validity of the recommendations.
The optimization system of banking risks is an integral part of risk
management and serves as the basis for planning the banking, cash flow
management and banking risk [6,7]. The purpose of risk management is to
maximize profit at the optimal (acceptable) ratio of the value of those profits
and business risks.
There are different approaches [8,9,10] to the assessment and management of risks
such as: statistical method, an approach based on expert judgment and
evaluation of subjective probability, probabilistic and statistical approach,
theoretical-probabilistic method, the method of calculation and risk management
with the use of utility theory . The principal difficulty of conducting such an
analysis of risk for modern systems is that it is often quite difficult to
assess the reliability of the result. A key drawback of most methods of risk
management is that they have essentially two conflicting properties [11]:
The pronounced qualitative and subjective
approach to risk analysis, which leads to weakly formalized, and the difficulty
of creating automated analysis tools and risk management on the basis of the
developed technique.
Rigidly formalized approach to risk analysis.
Sophisticated formal methods is difficult to apply in the absence of
mathematical models of processes occurring in the system, or when insufficient
statistical data [9,11].
This contradiction is extremely relevant is to
build an effective method of choice of the optimal measure of risk for the
studied system as a whole, taking into account the light of all the system
processes that are fundamentally different nature [12].
The justification of the risk measures devoted
many studies [8,9,10,13,14]. A common economic methodology uses the concept of
risk as possible [9]. When considering the risk assessment and management, in
some cases, an approach that allows taking into accounts individual characteristics
of the control subject. This is due to the subjective approach in risk
assessment and the need to take into account the particular purpose for which
the operating control system [8,15,9,11].
The problem of determining the overall risk for
the population of a complex interaction of various risks at this stage is not
fully resolved. [11] Existing methods produce a comprehensive risk assessment
of the system only at a qualitative level.
Due to the structural complexity of commercial
bank lending to the problem being solved in terms of potential risks [12] there
is a problem of adequate identification and assessment of risks posed by the
operation of individual elements of such a system. An important consideration
is the possibility of a risk analysis on the basis of their classification.
Considering
the management of both the impact of credit risk management in the bank can be
defined as an organized entity exposure control (bank employees involved in
activities on the borrowers credit and senior staff) for facility management
(credit risk and the activities of the employees involved in credit operations)
in order to reduce maintenance acceptable level of credit risk indicators of
the bank [15,16].
At present,
commercial banks and other credit institutions may use a wide range of
techniques and methods of risk management: remote monitoring, rated, early
intervention, comprehensive assessment of the risks of credit activity.
However, copying models of assessment of banking risks, successfully applied
abroad, is not acceptable for the Russian banking sector. [12] Implementation
and testing of foreign experience is not possible without considering the
peculiarities of the domestic market.
The main problem of
credit risk management in today's environment is the lack of a comprehensive
and in-depth analysis of the credit process, the methodological and procedural
framework and making wrong management decisions with incomplete information.
Credit risk
management involves the creation of a mechanism to identify risk factors,
analyze and calculate values, monitoring of current open positions.
Effective implementation of these functions is not possible without the use of
formal decision-support systems. Under these conditions, the system of great
interest to research aimed at developing new methods of risk assessment and
management. Credit risk exposure depends on a number of factors that need to be
taken into account in lending and risk management organization.
Structuring of credit
risk factors enables the implementation of risk analysis at different levels -
at the level of each individual loan transaction and the level of loan
portfolio credit institution (commercial bank) as a whole. System analysis in
the framework of development specific measures are minimizing the risks and to
establish appropriate risk management system.
Because the loans are
the main source of income of the bank and at the same time the main cause of
risk, the structure and quality of the loan portfolio depends on its stability
and development prospects.
Liquidity risk
management includes control of how the value of assets and liabilities. Hence
his feature consists in the fact that it is limited, on the one hand, liquidity
and asset price competition in the banking market, on the other, the desire to
get the maximum profit from each possible direction of the bank. [17]
In general, the management of risk a
multi-stage process, which aims to reduce or compensate for the object upon the
occurrence of adverse events [12]. It is important to understand that minimize
damage and reduce the risk inadequate concepts. The second means either
reducing possible damage, or a decline in the probability of occurrence of
adverse events.
The main stages of the risk management process
in general include [18]: the risk analysis, the choice of methods to influence
the risk of assessing their relative effectiveness, decision-making, a direct
impact on the risk, control and adjustment of the results management process.
Risk analysis is the initial stage with the necessary information about the
structure, properties and existing risks. The information collected should be
sufficient to make appropriate decisions at subsequent stages. The analysis
consists of risk identification and assessment. When identifying risks (qualitative
component) we defines all the risks
inherent in the system. Here the main thing is not missing important
points and to describe in detail all the risks. Assessment is a
quantitative description of the risks identification, the definition of probability
and potential damage. At this time the development of scenarios of adverse
situations and for different risks can be constructed distribution function of
the probability of damage, depending on size.
Identification and assessment are closely linked, and
it is not possible to divide them into separate parts of the process. Moreover,
the analysis often goes in two opposite directions from assessment to identify and vice versa. In the first case,
there are already recorde losses and to identify the causes. In the second
case, on the basis of analysis of the system revealed the risks
The choice of method is exposure to risks in order to
minimize damage in the future. Typically, each type of risk allows two or three
traditional ways of reducing it. Therefore the problem the comparative
effectiveness of the methods impact risk for selecting the best one. The
comparison can be based on various criteria, including economic.
The next stage of the decision-making determines required financial and human resources, is
setting and the allocation of tasks, carried out an analysis of the market of
relevant services, consultations with specialists. The
The process of direct exposure to the risk represented
by the three main ways: reduction, preservation and transfer of risk.
Reducing the risk involves reducing the size or
possible damage, or the likelihood of adverse events. Most often, it is
achieved by the implementation of preventive organizational and technical
measures.
Persistence of risk at the current level does not
always mean the rejection of any action for remediation, although this is
available. It is possible to create special reserve funds (funds or
self-insurance risk fund) of which will be compensation for losses upon the
occurrence of adverse situations.
The transfer of risk refers to the transfer of
responsibility for it to third parties, while maintaining the existing level of
risk. These include insurance, which is the transfer of risk the insurance
company for a fee, as well as various types of financial guarantees, etc.
And finally, the final stage of risk management is to
control and adjust the results of the implementation of the selected strategy
in the light of new information. Control is to obtain information from the
managers of the loss occurred and the measures taken to minimize them.
Successful operation of credit institutions in terms
of risk possible the development of a special decision-making mechanism, which
allows to determine the magnitude of potential loss that a credit institution
may itself take, as well as to assess whether the expected return justifies the
risk. Consequently, we need to develop specific activities reducing the impact
of risk factors. This is achieved through the establishment of a risk
management system that would allow the bank management to identify, locate,
measure and control a particular risk and thereby minimize its impact. [19]
The basic principles
of decision-making in risk management are following:
The principle of an
acceptable level.
The basis of practical
measures for risk assessment is often based on the concept of acceptable
levels. In accordance with this management process used thresholds, are deemed
acceptable. In this case, the aim is to control the management of risk to such
levels. Thus, the level of risk should satisfy the following condition:
![]() .
.
The main difficulty
when using this principle arises in defining this threshold value [9].
The principle of
economic feasibility is to apply the criterion of "cost - benefit - risk."
It is that decision-making on operations related to potentially dangerous
objects should be based [9]:
![]() ,
,
where B - the
benefits of the transaction, C - cost (investment), and the R - value
characterizing risk.
Obviously, that is
economically viable solution for which the value of V> 0, and then takes the
maximum value on the entire set of possible solutions. If V <0 for all
solutions, the adoption of any management decisions unreasonably, that is, in
this case, you must use the strategy of avoiding or ignoring the risks [9,11].
The adoption of sound
on this criterion management solutions managed by random processes is also
associated with risk. This risk is due to the emergence of errors of the first
and second kind. First type error is making an informed decision and then gets
a negative result. Second type error is failure to take a decision that was
considered unreasonable, but later is able to provide the maximum benefit.
The principle of
optimization.
On condition of
limited resources it is important to carry out only the actions leading to an
economic profit, the realization of which are lack of resources [9].
For each i element of
the set of managerial decisions, with a cost Ci and decrease the effectiveness
of risk can be calculated:
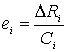 .
.
It is necessary to
consider that within the allocated resources СB there is
the following restriction for a set from k of the chosen operating actions:
![]() .
.
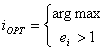 .
.
Then, the problem of
choice of management solutions is reduced to an optimization problem in terms
of restrictions. To find the optimal solutions can be used classical
optimization methods, such as methods of mathematical programming or finding
Pareto-optimal solutions [9].
In economic theory,
there are a few classic criteria for the selection of optimal solutions in the
face of uncertainty. These criteria are the criteria of Laplace, Wald, Savage
and Hurwitz [8, 9,13].
Assessment of risk on
the basis of statistical data for a sufficiently broad class of threats shows a
significant dependence on the time of its values. For such threats is
very important to account for the temporal characteristics of the assessment
and management. Dynamics of changes in risk may be due to natural environmental
factors [11]. Hence, at any given time interval risk assessment should be carried
out according to the law of probability distribution of damage that is relevant
in the current period. This suggests that a description of this law is
necessary to introduce a parameter of time that is to consider the appearance
of damage to the system as a stochastic process.
Based on the
definition of a random process [20], of a random variable that represents the
damage and has a probability density, you can go to a random process. Then the
probability density for each of its sections depends on the time. It is
important that the - time - is used to specify any external influence on the
system by a certain factor.
To monitor the
dynamics of risk in the system under study is important, how the value-at-risk.
In the case where the appearance of damage to the system can be formalized by a
random process, the value as a measure of risk depends on time: ![]()
Of existing risk
measures, which are calculated for the amount of damages provided by a random
variable, you can go to the expressions for the occurrence of the damage, given
a random process.
Often, a measure of
risk is the expectation:
![]()
For a discrete random
distribution law of the appearance of compromising the function defining the
risk of dependence on time will be as follows:
![]() ,
,
for a continuous
probability distribution - respectively:
![]()
Another measure of
risk for the damage represented by a random variable can be given for the
variance of the distribution of the probability of a random variable. When the
change of the damage is a random process, then the following expression for the
risk measures:
![]() .
.
By analogy to a mixed
measure of risk in changing over time, the law of probability distribution
function becomes:
![]() ,
,
where ![]() - the weighting factor.
- the weighting factor.
For the analysis of
changes in the level of risk in the system for a time, you can introduce a
characteristic of its dynamics as a function of differential sensitivity:
![]()
The analysis of the
dynamics of risk can be applied in one form or another for the organization of
credit risk monitoring organization.
The whole
system of risk management of the credit institution belongs to the purposeful
systems that implement certain interests. According to [21] the desire to
promote the interests creates a problem of management. Implementation of
interests requires certain actions that formally is some control associated
with some best result [20]. To formalize the criteria of quality control
results must use appropriate methods.
In the
case of the risk management system as a criterion for the best results should
be given criterion based on risk analysis. It should reflect the interests of the
decision maker, in the framework of the applied method of control. If this
criterion is defined, it can act as targets for the realization of interests.
It can be formulated on the basis of a mathematical formalization. If this goal
is formulated, the set used for its determination of assumptions, demands,
formal objects and structures will be some type of control [21]. Obviously, in
the framework of the control to be used some criteria functions that describe
the quality of management actions and decisions. To enable the practical use of
the model management criteria should be explicitly defined. [21]
Thus,
based on the methodology of risk management of credit institutions is a model
of risk management, including formal decision-making criteria in the model.
In accordance with the model system is a set of entities that produce
certain operations on its resources. System resources are a set of objects.
The subjects can
exercise influence on objects by processes occurring in the system. Effects on
objects are carried out depending on the purpose of effects that belong to the
set goals of exposure.
The decision-maker
(DM) can carry out the following types of control actions:
1. The correction
purposes of influence is the control action in which the effects of changing
target entities in the system, such as the use of risk management arrangements.
Selection of the desired target is the set of system goals impact.
2. The
correction means to implement actions - control action, performing process
changes impact the subjects to objects. Variety of implementation impacts
consists of various options for changing the characteristics of the processes
occurring in the system.
In
consideration of cyclical nature of the process of risks governance decision
maker chooses option of further actions in iteration of the cycle.
The
decision will to carry out a risk assessment before the start of each step. So,
in other words, we need to assess the effects of changes in the effects of the
set of subjects to objects of the system after the adoption of this decision.
In this regard, the risk management model introduced many useful criteria to
assess the situation in the system
The
situation in this case is a comprehensive assessment of the state of the
system, which takes into account characteristics of the subjects, objects and
processes taking place in it. On the basis of this assessment, the decision on
the initiation of any effects on the system of the decision maker, that is
carried out situational risk management based on the interests of (the utility
function).
Every
system consists of operating elements. To perform a risk assessment should take
into account the characteristics of each of these elements. This often involves
time-consuming calculations and sometimes not feasible because of the inability
to obtain objective information about each item. Often when making quality
management solutions do not need to know the exact numerical value of the
specific characteristics of the parameters of the elements of the system, and the
class to which it belongs. Class concept in this case means a set of components
that are similar to the selected characteristics. A set of such characteristics
is called a classifier set. The choice of these features depends on the task at
hand. The difference of this classification of the traditional circuits is that
its implementation must disengage the control type system. That is,
theoretically, in the same class may be different technical elements.
The
effectiveness of different management systems is largely determined by the
results of their classification.
To carry out such a
classification suitable cluster analysis, widely used in predicting the
behavior of an object on a set of features that define its behavior [21]. In
solving such problems, researchers are faced with essentially the same problem:
the allocation of the object considered set to a particular class on a set of
features.
To formalize the above risk management model many subjects
involved in the processes of influence we denote ![]() . Each element
. Each element ![]() of set is a subject that has an impact on the system. The
subject may be external or internal and can have different effects on the
system features. Multiple processes realizing impact objects denoted as
of set is a subject that has an impact on the system. The
subject may be external or internal and can have different effects on the
system features. Multiple processes realizing impact objects denoted as ![]() . Each element
. Each element ![]() of sets is a process
that occurs within a system or process impact on the system from the outside. A
set of objects exposed to influence, we denote as
of sets is a process
that occurs within a system or process impact on the system from the outside. A
set of objects exposed to influence, we denote as![]() . Each element of set
. Each element of set ![]() is an object of
the system. Objects are the resources of the system.
is an object of
the system. Objects are the resources of the system.
For each decision maker, there are many purposes of
impact ![]() . The purpose of exposure may be, for example,
reaching a certain level of risk values. Then, to assess the
state of the system is to be used function defined on the set
. The purpose of exposure may be, for example,
reaching a certain level of risk values. Then, to assess the
state of the system is to be used function defined on the set ![]() . That is, depending on the specific elements included
in these sets is determined by the current state of the system. We denote this
function (utility function) as follows:
. That is, depending on the specific elements included
in these sets is determined by the current state of the system. We denote this
function (utility function) as follows:
![]() .
.
Function allows evaluating the success of the control
inputs to the system. In comparison, the value of this function with some
values entered
multiple criteria utility ![]() . Each element of set
. Each element of set ![]() represents a certain level of risk (the risk) for the
system.
represents a certain level of risk (the risk) for the
system.
Depending on the
value of the function, which characterizes the state of the system is given a
set of possible management solutions. This lot should be divided into two
subsets: the set of control actions for the purposes of correcting exposure, as
well as by means of the correction actions. We denote these sets,
correspondingly, ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
Then, a formal model of management would be:
![]() .
.
Risk management procedure has the shape of a cyclic
process in which on the basis of evaluation of the sets of subjects (![]() ) objects (
) objects (![]() ),
processes (
),
processes (![]() ) and the current values of the set
) and the current values of the set ![]() which formed decisions
which formed decisions
![]() . For each of these decisions, the value of the
function
. For each of these decisions, the value of the
function ![]() is predicted and compared with the criterion of
usefulness, belonging to the set
is predicted and compared with the criterion of
usefulness, belonging to the set ![]() . In this
stage, the choice of the optimal solutions. Implementation of these activities
is based on the set
. In this
stage, the choice of the optimal solutions. Implementation of these activities
is based on the set ![]() , giving the management objectives for the
decision-maker.
, giving the management objectives for the
decision-maker.
The practical
application of management models requires the development of algorithms that
allow a clear and detailed to determine the course of action. These algorithms
should be focused on risk management actions.
Conclusion:
Bank risk has a dual
content (probability of loss, as well as the background and source of income by
the credit institution). The main purpose of risk management is not only an
estimate and neutralization of potential losses, but also uses it as an
effective tool for generating income. Risk management system covers the
strategic management level, the level of organizational units and their
interaction in the case of a complex operation. A system approach to risk management
is necessary for the activities of risk management involve all relevant
relationships and connections of any credit institution (bank) [12].
Advantages of system
approach lies in the fact that it is possible to see the critical variables and
constraints, as well as their interaction with each other. You can not consider
any one element, a phenomenon or problem without further interaction with other
elements.
The effectiveness of
the risk management system is inseparable from the performance of the entire
system of management of the credit institution, and therefore can be measured
by the degree of achievement of the objectives, speed decision making, etc. At
the same time the efficiency of the system is evaluated according to specific
criteria: Income (loss) from operations risk, quantitative indicators of risk, and
the feasibility of using the mechanisms of regulation of the host organization
at risk.
In general we can say
that the effective management of the credit institution (commercial bank) is
not possible without the use of specialized automated control systems with the
use of risk management strategies in constantly acting perturbations of the
system and imposed restrictions.
Bibliography:
1. Банки и банковские операции: Учебник для
вузов по специальности «Финансы и кредит» / Под. ред. Е.Ф. Жукова; Всерос.
заоч. фин.- экон. ин-т. – М.: Банки и биржи: ЮНИТИ, 2005. – 471 с.
2. Банковское дело: Учебник для вузов / Под.
ред. В.И. Колесникова, Л.П. Кроливецкой. – М.: Финансы и статистика, 2005. –
476 с.
3. Белоглазова Б.Н., Толоконцева Г.В. Денежное
обращение и банки. – М.: Финансы и статистика, 2006. – 355 с.
4. Винокуров М.А., Суходолов А.П. Банковское
кредитование: в 3 т. Иркутск, 2005. т. 3 С. 432.
5. Уварычева Е.С. Особенности управления
банковскими рисками. / Труды Международной научн.-практ.
конференции…«Современные проблемы управления риском», 20 октября, 2010 г.,
Пермь
6. Грюнинг Х. ван, Брайович Братанович С. Анализ
банковских рисков. Система оценки
корпоративного управления и управления финансовым риском / Пер. с
англ.;вступ.сл.д.э.н. К.Р. Тагирбекова . М.: Издательство «Весь Мир», 2007. 334
с.
7. Синки Дж. Финансовый менеджмент в
коммерческом банке и индустрии финансовых услуг/ Джозеф Синки-мл.; Пер. с
англ. М.: Альпина Бизнес Букс, 2007.
1018 с.
8. Балдин К.В. Управление рисками и выбор стратегии //
Высшее образование сегодня. – Реферируемое издание ВАК России. – Б.м. – 2005.–
№ 11. – С. 36-38.
9. Вишняков Я.Д., Радаев Н.Н. Общая теория
рисков: учеб. пособие для студ. высш. учеб. заведений. – М.: Издательский центр
«Академия», 2007. – 368 с.
10. Гранатуров В.М. Экономический риск: сущность, методы измерения, пути снижения : Учеб.
пособие. – 2-е изд., перераб. и доп. – М.: Дело и Сервис, 2002 . – 159 с.
11.
Остапенко О.А., Карпеев Д.О., Асеев В.Н.,
Морев Д.Е., Щербаков В.Б. Риски
систем: оценка и управление / под. ред. Ю. Н. Лаврухина, А. Г. Остапенко. –
Воронеж: Междунар. ин-т компьют. технологий, 2007.–261 с.
12. Г.Г.
Арунянц, А.Г. Мнацаканян. Распределение ресурсов банка с использованием
оптимальной стратегии управления рисками при кредитовании. Монография. –
Калининград. БИЭФ. 2009. – 167 с.
13. Балдин К.В., Воробьев С.Н. Риск-менеджмент: Учебное пособие. – М.:
Гардарики, 2005. – 285 с: ил.
14. Бартон Т.Л., Шенкир У.Г., Уокер
П.Л. Риск-менеджмент: практика ведущих
компаний. – М.: Вильямс, 2008 . – 207 с.
15. Баранов В.В. Процессы принятия управляющих решений, мотивированных
интересами. – М.: ФИЗМАТЛИТ, 2005. – 296 с.
16. Гамидов Г. Н. Банковское и кредитное дело. - Москва: ЮНИТИ, Банки
и биржи, 2005. - 315 с.
17. Бэррел, Т. Банковское дело: стратегическое руководство. - М.:
Консалтбанкир, 2006. - 367 с.
18. Хохлов Н.В. Управление риском [Текст]: учеб. пособие для вузов
Н.В. Хохлов. – М.: ЮНИТИ-ДАНА, 1999. – 239 с.
19. Арунянц Г.Г. Стратегия управления риском коммерческого банка
[Текст]/ Г.Г. Арунянц, К.Г. Дзестелова
/ В кн. "Труды Междунар. форума по проблемам науки, техники и образования:
III тысячелетие – новый
мир". - М., 2004. - С. 10-13.
20. Вентцель Е.С., Овчаров Л.А. Теория случайных процессов и ее
инженерные приложения. – Учеб. пособие для втузов. – 2-е изд., стер. – М.:
Высш. шк., 2000. – 383 с: ил.
21. Баранов В.В. Процессы принятия управляющих решений, мотивированных
интересами. – М.: ФИЗМАТЛИТ, 2005. – 296 с.