Lvov A.A., Svetlov M.S., Martynov P.V.
Saratov State Technical University named of
Gagarin Y.A., Russia
Evaluation of effectiveness of the non-binary codecs based on the
dynamic memory device
At
present, especially urgent task is to ensure a high level of the information
reliability of digital information and measurement systems, information and
control systems due to the constant tightening of requirements. For this
purpose, the processing of the signal is carried out while preparing it for the
transmission, generally using coding stages in a sequence (concatenated coding)
by block codes and continuous error-correcting codes including coded modulation
procedure. This allows providing the high rates of noise immunity systems for
the transmission of information in channels with high level of noise. In this
case, a significant gain is obtained by the use of non-binary codes.
Implementing of a reliable synchronous synphased operation of all
transmitter-receiver units of systems that use a synchronous serial interface
is another task that is no less important in terms of ensuring high reliability
of transmission.
Explorations
[1] have shown that the use of codecs (encoding and decoding devices) on the
basis of dynamic memory devices (DMD) allows successful problem solution of the
growth of the information reliability of the digital data transmission systems
in general. The peculiarity of these codecs is to represent each bit of the
code stream transmitted by the pulse sequences - pulse code series. The pulse
code series are formed in the form of tightly linked and fixed by the time
intervals (delays) pulses that are multiples of the value Δt and are infinitely small in duration.
The main blocks of the codecs generating pulse code series are distribution
devices in the form of DMD. Distribution devices based on DMD are universal in
the sense that they can be used in systems with code alphabets of any basis
(valence).
This
work is devoted to optimizing the choice of scheme realization of the
algorithms of coding and decoding of non-binary codes using the n-position distribution devices based on
DMD. Let q be the number of symbols
in the working code alphabet (q≥3),
and p - the number of bits required
writing one q-ary symbol: ![]() (rounded up to the nearest whole number).
(rounded up to the nearest whole number).
The
greatest interest among the developed by the authors variants of embodiments of
codecs based on DMD [1] for q-ary
codes is the analysis of the following variants:
-
Implementation of codecs with two outputs and one DMD, a similar implementation
of it for the binary code (variant 1);
-
Implementation of codecs with two outputs and p DMD (variant 2);
-
Implementation of codecs with 2p
outputs and one DMD (variant 3).
Evaluating
the effectiveness of the algorithms is carried out on the basis of the
criterion proposed by the authors in [2]. In accordance with this criterion,
coefficients of effectiveness ![]() are calculated
for each variant of the decoding algorithm:
are calculated
for each variant of the decoding algorithm:
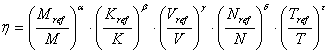 , (1)
, (1)
where M - size of memory required for the implementation of the algorithm;
K - the number of auxiliary variables
in the structure of the algorithm; V
- the number of branches in the structure of the algorithm; N - the number of actions performed in
the course of the algorithm (algorithm complexity); T - algorithm execution time, Mref,
Kref, Vref, Nref,
Tref - reference (the
minimum possible) values of the criterion parameters; α, β, γ, δ, ε - integer
(for the convenience of calculations) positive weight coefficient that take
into account the «weight» (the importance) of the each criterion parameter.
Conducting
the analysis of the algorithms let’s consider the general case where the "weight"
parameter in equation (1) is equal to unit:
![]() . (2)
. (2)
The
input sequence of characters of the m
length can be represented by a polynomial form relative to fictitious variable x:
![]() , (3)
, (3)
where a1, a2,
..., am - elements of the
input sequence (the characters of the using alphabet).
To
enable the implementation of polynomials of the form (3) on the element base
aimed at work with binary codes, q-ary
coefficients can be represented in binary form:
![]() . (4)
. (4)
For
the convenience of the implementation of the q-ary codes polynomial (4) can be represented in the form of system
of p polynomials:
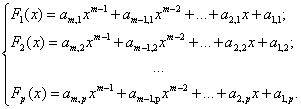 (5)
(5)
2p pulse code series described by
polynomials of code series of binary codes are formed with the implementation
of coding and decoding algorithms by the variant 1:
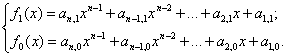 (6)
(6)
The
number of pulse code series transmitted to the channel increases in p times in comparison with variants of
using binary codes.
It
is necessary to use the methods of work with parallel data streams to implement
the algorithm according to the variant 2: encoding and decoding devices include
two outputs but codecs contain p DMD
operate in parallel to each other.
In
the implementing of variant 3 codecs contain one DMD with 2p outputs and form 2p
pulse code series for each of the polynomials of the system (5):
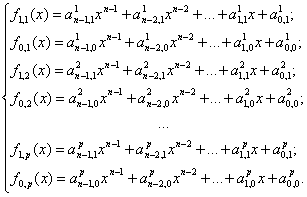 (7)
(7)
|
|
|
Fig. 1. Block-scheme of encoding device with p
outputs on base of DMD for q-ary code
|
|
|
Fig. 2. Block-scheme
of decoding device with p outputs on base
of DMD for q-ary code
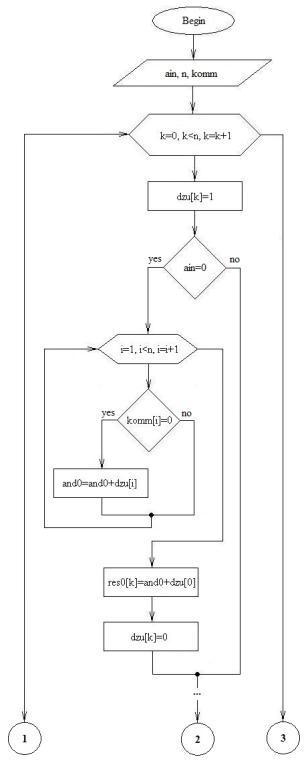
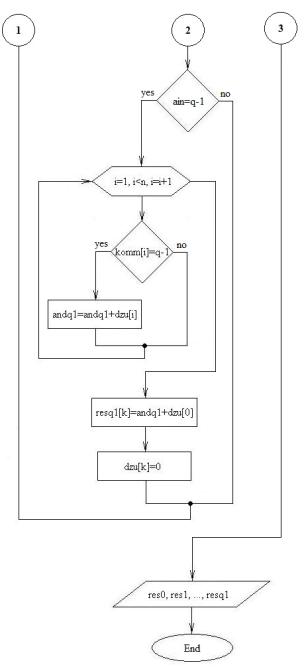
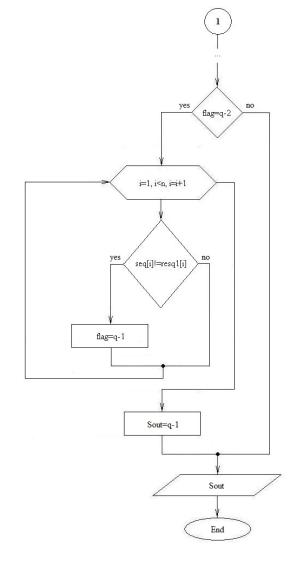
Block-schemes
of encoding and decoding devices for general case are presented on Fig. 1
and 2. The quantity of branches of case operators in the body of generic
algorithm is defined by quantity of symbols in the code alphabet (q). Definitions: ain - input signal, n
– quantity of cells of DMD, komm –
array which defines the commutation of DMD outputs, dzu – array with meanings of bytes in cells of DMD, and0, and1, …, andq1 – meanings
on 0, 1, …, (q-1) output of DMD, res0, res1, …, resq1 – arrays
of code series for “0”, “1”, … “q-1”, aout
- output signal of decoding device.
Let’s
consider the evaluation of the given methods of implementation of DMD for q-ary codes using the proposed
criterion.
Size
of memory is determined by the number of variables and dimensions of arrays
involved in the implementation of the corresponding algorithm. From the
analysis of the generic block-schemes of encoding and decoding devices
(Fig. 1 and 2) it can be calculated as follows:
•
Variant 1 - M1=p(4n+6+3n+4)=p(7n+10). For solving the evaluation task we can accept M1≈7np;
•
Variant 2 - M2=7np;
•
Variant 3 - M3=7n.
The
analysis of the obtained expressions shows that the minimum size of memory is
required to implement the algorithm by the variant 3. We take the given value
of size of memory for reference value and introduce the notation: Mref =M3=7n. Thus,
the values of the efficiency coefficients of the algorithms in terms of size of
memory take the form:
![]()
![]()
![]()
The
number of auxiliary variables required to implement each algorithm is defined
as follows:
·
variant 1 – K1=p(2+n)≈np;
·
variant 2 – K2=p(2+n)≈np;
·
variant 3 – K3=Kref=n+5≈n.
The
values of efficiency coefficients of the algorithms in the number of auxiliary
variables take the form:
![]()
![]()
![]()
The
number of branches from the analysis of the body of each algorithm can be
calculated as follows:
·
variant 1 – V1=10np=Vref;
·
variant 2 – V2=10np=Vref;
·
variant 3 – V3=n2(1+q)+8n+2nq+1≈qn2+2nq+8n≈qn2.
Values
of the effectiveness of the algorithms on the number of branches:
![]()
![]()
![]()
The
number of operations performed in the algorithm:
·
variant 1 – N1=p(7n2+7n+17n+9)≈p(7n2+24n)≈7pn2;
·
variant 2 – N2=p(7n2+7n+17n+9)≈p(7n2+24n)≈7pn2;
·
variant 3 – N3=7n2+28n+nq≈7n2=Nref.
The
values of efficiency coefficients of the algorithms on the complexity take the
form of:
![]()
![]()
![]()
From
the analysis of the structure and complexity of each algorithm it follows that
the minimum time necessary for the performance of the algorithm for variant 2
with the use of parallelizing the operations of coding and decoding of each of
the bits of the binary representation of q-ary
code. We introduce the notation: T2
= Tref = t. Time of execution of the other algorithms
can be defined as follows:
•
Variant 1 - T1 = k1*t, where k1>0
- integer coefficient;
•
Variant 2 - T2 = Tref =t;
•
Variant 3 - T3 = k2*t, where k2>0
- integer coefficient. Due to the fact that the complexity of the algorithm is
lower than complexity of the algorithm by variant 1, the correct relation
is: k2 < k1.
The
values of efficiency coefficients of the algorithms according to the execution
time take the form :
![]()
![]()
![]()
The
values of each criterion of efficiency of the each algorithm according to the
formula (2):
![]()
![]()
![]()
The
value of each of the coefficients belongs to the interval ![]() . If the value is closer to unity, the efficiency of
the algorithm is higher. That’s why if you take the weight coefficient in the
formulae equal to unity, then, based on selected criteria, the most effective
is the algorithm in the variant 3 -implementation of q-ary codes based on one DMD with p outputs.
. If the value is closer to unity, the efficiency of
the algorithm is higher. That’s why if you take the weight coefficient in the
formulae equal to unity, then, based on selected criteria, the most effective
is the algorithm in the variant 3 -implementation of q-ary codes based on one DMD with p outputs.
Literature
1.
Martynov P.V. Increasing of noise immunity in communication data systems with
radio channels / P.V. Martynov, M.S. Svetlov // Bulletin of the Saratov State
Technical University ¹ 1 (64), issue 2, 2012. - P. 328-331.
2.
Martynov P.V. The development of criteria of the effectiveness of the
algorithms of digital information processing / N.A. Lvova, P.V. Martynov //
Collection of scientific papers of the II International Conference
"Problems of control, transmission and processing of information" (ATM-2011),
Vol. 2, Section 2, 2012. - P. 72-74.