Kazakov V.A. Ph.D (in
technics), Vinogradov O.S. Ph.D. (in technics), Vinogradova N.A. Ph.D. (in technics).
Penza Region Centre of Higher
School (Branch) Russia State University of Innovative Technologies and
Business. Penza, Russia.
The problems of electrochemical productions automation
Covering
of metal coating different materials is done in electrochemical shops. The
process of coating by alloys is rather complicated meaning maintaining given
technological data. Such data considered to be temperature, currency` density,
concentration of components, acidity (pH) [1]. Changing
even of one of the components during the job's process might lead to a failure.
Nowadays,
control of the process is has been done periodically by the means of selection
of samples and temperature testing of mixture. Mentioned above control is
usually done not often than once in a shift- time. Rave control leads to
appearance of poor surfaces.
Usage
of automation for control and adjustment and technological process given an
opportunity not only to prevent defect but will let to realize during
production process coating super thin coverings with different alloys. But
realization these projects: coating plural-componential alloys with a given
exact component comes into collision with a problem of maintaining the
concentration initial substances in electrolyte. A solution to this problem
could be solved by a metered constant inputting a needed component into a
solution.
When
coating a surface change of quantity pH or a temperature leads to a change of
component's concentration in an alloy and sometimes to growing electricity
spending needed for the process
realization.
To
control the quantity pH different subsystem realization the following is
suggested (as at pic.1)
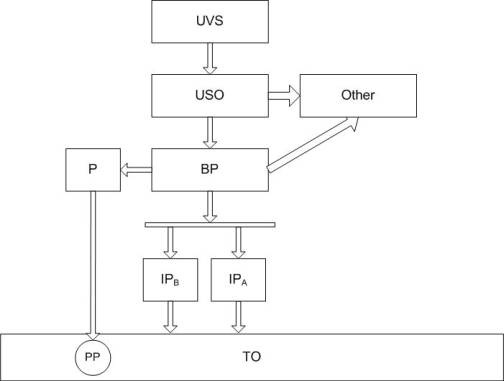
UVS- a universal
computing system
USO – a connecting
UVS device with an object
PP- an initial
transformer\ transmitter (gauge)
P- a transformer
IPa- a performing device for feeding a solution
Other – other
basins
TO- a technological
basin
BP- a shifting
device
Picture 1 – A
system of acidity in electrolysis basin scheme.
A
subsystem realizes a periodic control: compares electrolysis pH meaning de
facto to an optimal one, and also regulates pH electrolysis by input
concentrate solution acid and alkali into an electrolyses basin.
Supply
of acid and alkaline solutions is made by a performing device – a valve with
electromagnetic driving-gear.
Transformer
pH-261 is a device for transforming a
quantity electromotive force reader used for
measuring a pH quantity is analog signals of direct current (d/c) from 0 to 5
mA.
Temperature
maintaining subsystem is for centralized control and two-positioned discrete
regulation of electrolysis temperature in an electrolysis basin.
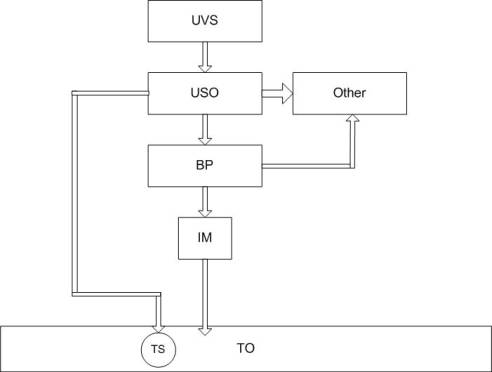
BP- a switching
device for controlled basins
IM- a performing
device
TS- a thermometer
of resistance
Picture 2 – Given a
scheme to it.
Subsystem realizes
periodic measuring of temperature current meanings compares it with admissible
deviations and regulated temperature by switching-in and off a performing
device. A performing device is for control and regulation temperature in
working basins and giving a signal of equipment readiness to work.
A performing
mechanism is a valve with an electromagnetic driving-gear.
When organizing
automated production it is necessary to program auto operator job which makes
transferring parts from position to another one, as if allows to save time of
process and minimize defect.
Usage of mentioned
above subsystems of automated control for feeding technological solutions components
and maintaining temperature of solution gives the possibility to improve
electrochemical production and put it into a better new level of development.
1. Vinogradov O.S.
Automation of electrolysis production Monograph [Avtomatizacia galivanicheckih proizvodstv]. Penza, Penza Branch of
Russia State University of Innovative Technologies and Business Publ.,
2012.162 p.