Competitor, Kolcheva D. V.
Donetsk national university of economics and trade named after Mikhail Tugan-Baranovsky,
Ukraine
Use of flame retardants to provide fire
safety of textile materials
Each year huge amount of people die through
the accidental effects of fire. For instance, researching results of European Flame Retardants
Association indicate that every year nearly five thousand people die in fire.
Disastrous fires in the domestic environment and public places, such as
transport, theatres, clubs, hospitals, hotels, hostels, educational establishments,
stadiums, railway stations and so on, regularly make the headlines in the
media. It causes death and injury not only for people but also brings great
financial loss.
The analysis of fire progress shows that on the early ignition
stage, textile
materials are unsafe and can stimulate fire spread over the building and obstruct exit
routes in establishments of the mass gathering of people. The speed and extent of growth of a fire are often
determined by the properties of the materials adjacent to the source. Easily
ignited materials such as curtains, decorations and upholstery can lead to a
rapid and accelerating growth of heat and flames that help to establish the
fire.
It is
possible to complicate the process of flame spreading by special substances for
textile materials – flame retardants, that are not widely used, but nowadays it is getting more practically important because of moderate cost and manufacturing
technology. Textile materials finished by flame retardant can prevent fire from
spreading and ensure that it is kept within its original confines. It is
important to make the distinction that flame retardant treatment of textile
materials will make them less easily ignited and less likely to allow the
spread of fire but it will not make them non-burning.
Actual industry uses phosphates, borates, sulphates, titanium and stibium salts, inorganic and organic nitrogen-containing
and haloid-containing composition as flame retardants. Such flame
retardants show differing effects on different textile substrates.
Nowadays
the most famous flame retardants are manufactured into the following countries:
Russian Federation, Germany, France, Switzerland, the Netherlands, Belgium, Italy,
Spain etc. (figure 1).
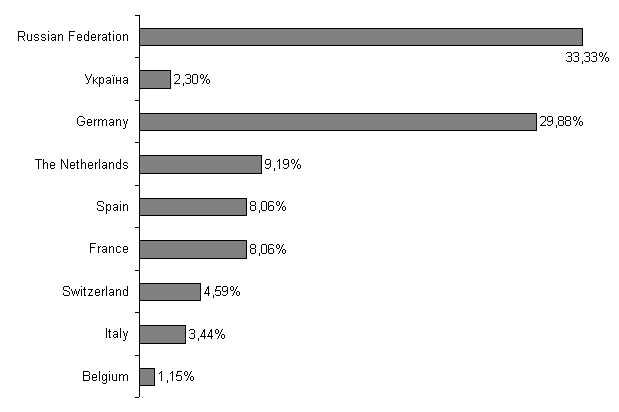
Figure 1 – Structure of flame retardants for textile materials under the
manufacturing countries
In
spite of the complex interplay of the factors that influence fire process, it
is possible to consider different principal methods of effecting flame
retardant products.
Classification
of the principal methods of action of flame retardants:
1.
energy consuming or endothermic reaction (materials that, by their
thermal destruction, use energy without releasing flammable gasses are
effective as flame retardants);
2.
release non-flammable gases (if the endothermic reaction can also lead
to the release of non-flammable gasses then a stronger flame retardant effect
is produced by the dilution of the flammable gasses and the oxygen);
3. flame retardant
effects through barrier formation:
- barrier formation by the dehydration of
cellulose (because of cellulose containing substrates that are special in
having the ability to achieve excellent flame retardant effects using
dehydrating acids. Such reaction involves the release of water as a
non-flammable gas and the formation of a carbonized char that will only ignite
above the temperature given by the burning of the cellulose);
-
barrier formation by chemical intumescence (flame retardant intumescence
systems by an increase in temperature causing the material to expend and form a
heat insulating layer);
-
barrier formation by physical intumescence (chemicals have the ability
at raised temperatures to substantially increase their volume, that’s why the
process consumes energy and leads to an effective barrier layer being formed);
-
barrier formation by Melting (non-flammable chemicals that melt at a sufficiently
low temperature can form a barrier that protects the textile materials form the
flame source).
4.
formation of free radicals (the process of textiles burning has
previously been described as the oxidation of the released flammable gasses in
the presence of oxygen);
5.
changing the melting behavior (melting point of a textile polymer can be
significantly reduced, that has the effect of making textile polymers melt away
from a heat source more rapidly and thus avoid ignition, making them less
easily flammable).
Thus, the necessity of conduct of fireproof treatment of textile
materials is processed by the special substances - flame retardants. Nowadays
we have a wide choice of such treatments available on the market. Flame
retardants can be applied to textile materials using the following methods:
padding, spraying, dipping and coating. We have considered a classification of
principle methods of action of flame retardants, in which main mechanisms of their
influence on textile materials are presented.