Сельское хозяйство/4.Технологии хранения и переработки сельскохозяйственной продукции
D.t.s. Kolpakova V.V., c.t.s. Studennikova O.J.
All-Russian Research Institute for
Starch Products, Russia
C.b.s.
Chumikina L.V.
A.N.
Bach Institute оf Biochemistry of Russian
Academy оf Sciences,
Russia
Influence of anionic polysaccharides on
the viscosity and solubility of wheat gluten
Dry wheat gluten (DWG) is produced on an industrial scale as an inexpensive source of vegetable protein, and it is used in the production of flour at a mill and bakery DWG has the potential techno-functional properties and is used as an ingredient in food products capable of binding free moisture and stabilize foams, emulsion and form texture products.
The main factor,
limiting the use of DWG in other sectors of the food industry, is the low
solubility due to the large molecular size and the presence of large amounts of
hydrophobic groups. One of the methods of
regulation of the functional properties of proteins is the effect on them of polysaccharides. Despite the fact that the study of the
interactions of these two classes of polymers continued for many years, some
issues still remain unexplored. Well studied the behavior
of gelatin, milk, whey and soy protein in the presence of anionic polysaccharides,
whereas such data to the DWG is not enough. Therefore, the aim of this study was to investigate the
effect of anionic polysaccharides as a structure-forming agents on the
viscosity and solubility of DWG and its mixture with albumin for use in the manufacture of
products Pastila.
Charged polysaccharides by reaction with proteins under certain conditions, form complexes differing in properties from the starting materials, so study we selected ionised highly esterified pectin, sodium alginate and k-carrageenan.
Viscosity evaluated gelling ability of wheat gluten with polysaccharides. Viscosity was measured in mixtures of gluten in
three treatment regimens: joint swelling polymers for 2 and 4 hours as well as
after swelling polymer for 4 hours, followed by heat treatment. To increase the reproducibility of the viscosity
measured on a Brookfield viscometer after centrifuging the suspensions at 7000
rev / min.
It is found that for the same mass fraction of polysaccharide to protein
mass, the viscosity of DWG - sodium alginate was higher than the viscosity of
DWG - highly esterified pectin, but a strong gel was formed only in the DWG – k-carrageenan heat-treated.
Thermal processing systems DWG – highly esterified and DWG - of sodium alginate
reduce the viscosity, as compared to samples without heat treatment. Gel systems with sodium alginate and highly
esterified pectin not formed, probably due to the absence of calcium ions for
sodium alginate, sugars and acids - pectin.
Changing the viscosity of the suspension under the influence of
hydrocolloids DWG was compared with the results of protein solubility.
The protein content was determined
in the supernatant - centrifugate obtained after joint swelling polymers for 2
hours, 4 hours and 4 hours, followed by heat treatment for 45 minutes at 100 °
C (modes I, II and III,
respectively). Solubility of the protein was expressed as a percentage of the
total in its rigging.
From the results shown in the figure can be seen that all polysaccharides solubility enhancing DWG that may have been caused by the formation of protein-polysaccharide complexes with more hydrophilic properties than the original protein molecule.
Maximum increase in solubility by DWG achieved in the presence of 80% highly esterified pectin, min - 5% k-carrageenan.
Sodium
alginate, at the same dosage as
pectin, considerably less effective in increasing the solubility. A slight
increase in the solubility of the DWG in the presence of k - carrageenan may be due to
its low dosage (5% of the weight of protein), but at higher concentrations of
the hydrocolloid very thick gel formed.
![]()
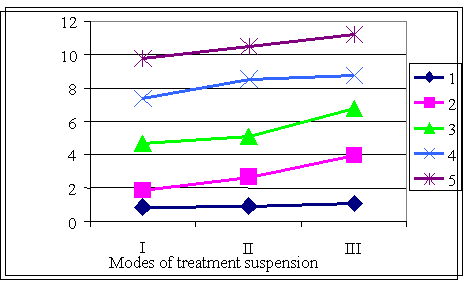

Figure - The solubility of wheat gluten 1 - control DWG; Hydrocolloids,% of
protein weight: 2 - 5% κ-carrageenan; 3 - 40% sodium alginate; 4 - 40% highly esterified pectin; 5 - 80% highly esterified pectin. Modes of treatment suspension: I - 2 hour, II - 4 hour, III - 4 hour heat treatment
From the data
of changes of solubility in the presence of hydrocolloids, it is concluded that
the intensity of interaction with proteins DWG number of polysaccharides as
follows:
highly esterified pectin > k-carrageenan > sodium alginate
Therefore,
for use of polysaccharides as stabilizers of gluten proteins in Pastila
products with gel structure appropriate to use highly esterified pectin or
k-carrageenan, so as pectin largely increases the solubility of DWG, and k-carrageenan - viscosity
of the suspension DWG.
References
1. Stephen A.M. Food
polysaccharides and their application: Marcel Dekker.- 1995. - 654 p.
2. Tomasik P. Chemical
and functional properties of food saccharides: CRC Press. - 2003. - 426 p.
3. Takayuki N.,
Masayuki T. Stripe pattern formation in kappa-carrageenan gel. Trans. Mater.
Res. Soc. Jpn. 2006. Vol. 31. No. 3. P. 827-830.
Сухая пшеничная клейковина (СПК) производится в промышленных масштабах как недорогой источник растительных белков и применяется она при производстве муки на мельничных
комбинатах и в хлебопечении. СПК обладает потенциалом техно-функциональных
свойств и используется в качестве ингредиента, способного в пищевых продуктах
связывать свободную влагу, стабилизировать пены, эмульсии и формировать текстуру
изделий. Основным фактором, ограничивающим использование СПК в других отраслях
пищевой промышленности, является низкая растворимость, обусловленная большим
размером молекул и наличием большого количества гидрофобных групп. Одним из
приемов регулирования функциональных свойств белков является действие на них полисахаридов.
Несмотря на то, что изучение взаимодействий двух этих классов полимеров
продолжается много лет, некоторые вопросы до настоящего времени остаются не
изученными. Сравнительно хорошо изучено поведение желатина, молочных,
сывороточных и соевых белков в присутствии анионных полисахаридов, тогда как подобных
данных для СПК недостаточно. Поэтому целью данного исследования явилось изучение влияния анионных
полисахаридов как структурообразующих агентов на растворимость и вязкость одной
СПК и в смеси ее с альбумином для применения
при производстве пастильных изделий.
Заряженные
полисахариды при взаимодействии с белками при определенных условиях образуют
комплексы, отличающиеся по свойствам от исходных веществ, поэтому для исследования
нами отобраны ионизированные высокоэтерифицированный пектин, альгинат натрия и
каррагинан. По вязкости оценивали гелеобразующую способность пшеничной
клейовины с полисахаридами. Вязкость определяли в смесях клейковины при трех
режимах обработки: совместное набухание полимеров в течение 2 и 4 часов, а
также после набухания полимеров в течение 4 часов с последующей термической
обработкой. Для повышения сходимости результатов вязкость измерялась на
вискозиметре Брукфильда после
центрифугирования суспензий при 7000 об/мин.
Установлено,
что при одинаковой массовой доле полисахаридов к массе белка, вязкость системы
СПК - альгинат натрия была выше, чем вязкость системы СПК -
высокоэтерифицированный пектин, однако прочный гель образовался только в системе СПК - каррагинан,
подвергнутой термической обработке. Термическая обработка систем СПК -
высокоэтерифицированный пектин и СПК - альгинат натрия понижала вязкость, по
сравнению с образцами без термической обработки. Гель в системах с альгинатом
натрия и высокоэтерифицированным пектином не образовывался, вероятно, из-за
отсутствия ионов кальция для альгината натрия, сахара и кислоты - для пектина.
Одновременно с определением вязкости
проводилось определение растворимости белков СПК в присутствии полисахаридов
при различных режимах подготовки. Как показали результаты, присутствие любого
из отобранных для эксперимента полисахаридов позволило увеличить растворимость
СПК. Полученный эффект, вероятнее всего обусловлен ассоциативным
взаимодействием полисахарид-протеин с образованием комплексов, более
гидрофильных, чем исходные молекулы белка.
При одинаковых массовых долях полисахарида
в исследуемых системах больший эффект по увеличению растворимости был достигнут
для высокоэтерифицированного пектина, по сравнению с альгинатом натрия (рисунок).
Сравнить свойства трех видов
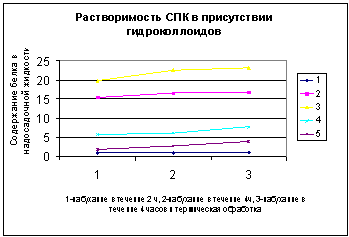
Рисунок. Растворимость СПК в
присутствии гидроколлоидов
1 - 2, - 3 -
полисахаридов не представлялось возможным
из-за образования геля в системе СПК – каррагинан. Термическая обработка систем
способствовала, хотя и незначительному, но увеличению растворимости для всех
полисахаридов в сравнении с системами, не подвергавшимися термической
обработке.
Таким образом, полученные результаты
подтвердили возможность применения анионных полисахаридов для изменения
функциональных свойств СПК и, следовательно, появилась основа для дальнейшего
изучения поведения систем СПК - полисахарид в присутствии традиционных
компонентов рецептуры при протекании процессов, предусмотренных технологией
производства пастильных изделий.