*119873*
Economics
/ 10. Enterprise ekonomiks
Dovga T.M.
Postgraduate
student at economic faculty
of Kiev National
Taras Shevchenko University
Approaches
and implementation issues household waste recycling in Ukraine
Solid
household waste (SHW) treatment is one of the “sharp” nature conservation
problems in Ukraine. Nowadays average index of waste formation is 220-250 kilograms per year on one person and in the big cities
can be even 330-380 kilograms per
year. In general the bulk of this waste is 13 million tons per year and this number is increasing
exponentially. Furthermore, among solid household waste there is a proportion
of waste which is extremely increasing and that is not amenable to rapid
expansion. In fact, it requires considerable space for storage. However, the
number of overloaded landfills is rising, and, unfortunately, some of these
dumps does not meet the standards of environmental safety. Currently, the
number of landfills and dumps in Ukraine is about 4.5 thousand. Ukraine ranks first
in terms of the harmful effects of landfills on the environment among European
countries. In Ukraine about 52 million m3 of solid waste are
produced annually, which is about 13 million tons, which are disposed to 6
thousand dumps and landfills, constituting total area more than 9 thousand
hectares.
Incineration
of waste is extremely dangerous for the environment and has a very negative
impact on health, as it leads to the formation of toxic substances and
compounds that accumulate in the atmosphere. In addition to mentioned aspect,
this method is the most costly way of waste management. That is why today a
fair amount of countries are directing their legislation with the aim of waste
incineration to be banned partially, and some of them prohibit incineration
completely.
To sum
it all up, recycling is the only civilized and safe way of SHW handling (it
must be mentioned that almost all components of solid waste can be reused) and
minimization of waste formation that is connected with environmental awareness
evolution of Ukrainian people.
Thus,
we offer the following definitions made on the basis of critical approaches to
the comprehensive study and generalization of existing views with the aim of
integration into European and world economic systems, establishing effective
national system of household waste treatment:
-
recycling of solid household waste is a special, cost-effective and
environmentally safe solid household waste processing system based on their
household sorting in order to preserve natural resources by reusing recycling
products as secondary raw materials. Complex recycling system comprises
sorting, heat treatment, fermentation and other processes that provide maximum
economic and environmental efficiency;
-
solid household waste
utilization is cost-effective and environmentally safe elimination of
household waste or those of their components, to which cannot be applied
recycling technologies for their destruction. Methods of utilization should be
characterized by complete destruction of waste as the final stage of their
management. To these methods belong exclusively possible waste disposal of
biological origin, characterized by rapid and environmentally friendly
decomposition in the soil and burning as a method of destroying household waste;
-
secondary, waste utilization is elimination of waste component after
allocation from them resource valuable element, which further processing
neither is impossible nor does not carry economic benefits. In fact, this is
the last stage of the destruction of household waste residues. It’s important
to mention that for some waste components of the concepts of recycling and
utilization are of the same meaning, for example glass, which is completely
recycled and does not leave any residues behind.
Currently,
the management and solid waste handling spheres are at the incipience level.
Nevertheless, it must be certainly said that recycling of solid household waste
is the raw material for formation and development of the national secondary
resources market. It has an aim to
reuse sustainable existing raw materials more efficiently as long as possible,
which leads to slowing down the consumption of primary natural ingredients and
minimizing environmental damage. The main problems of solid household waste
(SHW) recycling development can be classified:
![]()



![]()
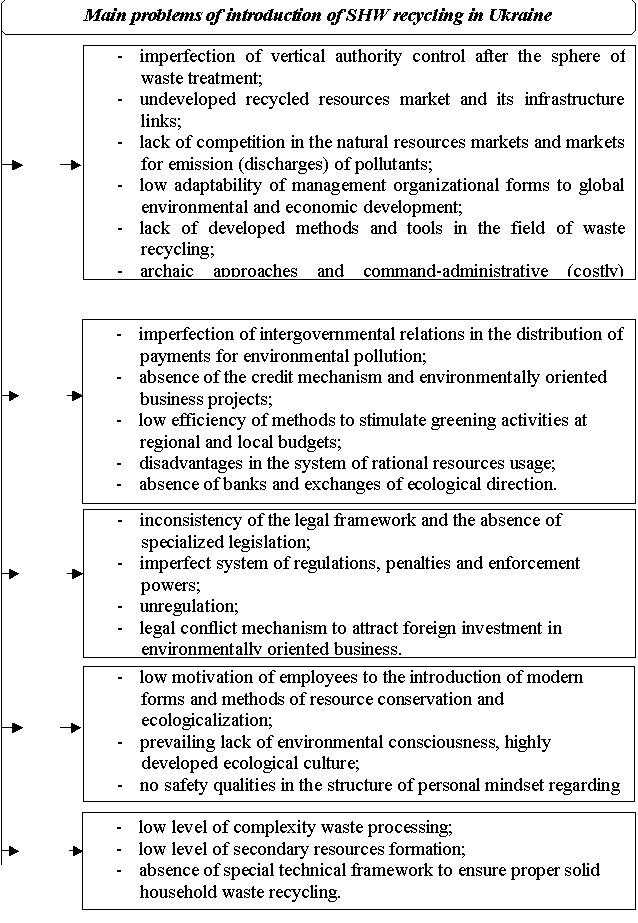
Pic. 1. Problems of
recycling introduction in Ukraine
Implementation
of "circular economy" to be built in future requires a stable
functioning market mechanism of secondary resources. The Law of Ukraine
"On Waste" defines waste as secondary raw materials and provides
regulation of its collection and harvesting. However, there is no determination
of the definition "secondary resources market" in the legislation.
Furthermore, economists had not learned this theme enough. Compared to the
highly developed European space, where the mechanisms of waste recycling have
already established their operating and have been functioning over the years,
the national secondary resources market of Ukraine is being still formed.
Considering this fact, the scientist T. Andreeva gives the following
definition: "Secondary resources market is a combination of economic
relations between legal entities and individuals to buy their products that are
used to replace primary raw materials or partial substitution according to
their functional assignment and should be developed on the basis of
self-regulation and with the state support " [10, с. 188]. These
definitions are correct partly, but still have certain defects and are not
fully convey the essence and purpose of the market. Taking it all into account,
we propose the following definition: "Secondary raw materials (resources)
market is a set of relations of the mechanisms formation and development of
waste recycling products retardation in the system of production - economic
relations with the aim to ensure goods production cycle based on reusing waste
materials on principles of sustainable development through financial
institutions and environmental instruments."
At the
same time, the secondary raw materials market (except for national) has its own
specific characteristics. Dynamics of prices for secondary raw materials is
entirely determined by the state of demand for it from
consumers. Specificity of its collecting and processing does not give an
opportunity to suppliers to respond quickly on changing market conjuncture
conditions. As a result, prices for secondary raw materials move spasmodically.
With growth of demand prices quickly rise, because suppliers cannot increase
the collection and satisfy consumers in the short term. On the other hand,
sharp lowering prices is observed during falling demand, because firms can not immediately reduce the
increased secondary raw revenue recycling and forced to sell goods at low
prices.
Literature:
1. A. Beyond
growth. Economics of sustainable development [text] = Beyond
Growth. The Economics of Sustainable Development / G.Daily, NGO
"Ukraine. Agenda for the XXI Century", Institute
of sustainable solutions. - K.: Intelsfera, 2002. -
298 p.
2. Action
Programme "Agenda for the
XXI Century": Adopted by the United Nations Conference
on Environment and Development in Rio de Janeiro
(Summit "Planet Earth", 1992): Per. from
English. - 2nd ed. - K.: Intelsfera, 2000. -
360 p.
3. Strategy
for Sustainable Development of Ukraine. http://ecolabel.org.ua/index.php?id=253
4. The Law of
Ukraine "On General
Principles (strategy) environmental policy until 2020.
http://www. rada.gov.ua
5. Standard 30772-2001. Resource. Waste
management. Terms and definitions. Interstate standard. http://www.abono.ru/en/product/gost-30772-2001-resursosberezhenie-obrashenie-s-othodami-terminy-i-opredelenija/
6. Skorohod I.S. World
experience of secondary resources / I.S. Skorohod //
International Economic Relations. - 2007. -
№ 12. - P. 229-233.
7. The Law of Ukraine
"On Wastes". http://www. rada.gov.ua/