*117148*
Ìåäèöèíà/2. Íåâðîëîãèÿ
S.K.Erkebaeva
The international Kazakh-Turkish university named by H.A.Jasavi,
Shymkent
Medical-demographic specificity of
major factors of risk of the early prevention of strokes in the South
Kazakhstan area
To one of the main problems of public health services represents a cerebral
stroke which is the cause of death second for the importance in the developed
countries of the world and the leading reason incapacity of adult population of
the most able-bodied age. The social expenses connected with expenses on
treatment sick stroke in stationary and out-patient conditions, are the main
item of expenses of public health services of many countries [1]. In Kazakhstan
disease of a stroke makes 2,5 – 3,7 cases on 1000 population in year,
death rate from 1 to 1,8 cases on one thousand population a year. The analysis
in different age groups has shown that with increase in age disease sharply
raises. Middle age of patients has made 67 years. Among 29 % who have ill
with a stroke – people of able-bodied age (till 60 years). The general
lethality in the sharp period of a stroke has made 35,2 % (at women of 60,1
%, at men – 39,9 %). In republic, unfortunately, there is a steady
progressing of these diseases while, in economically developed countries there
is a decrease [1].
It is known that development of strokes is preceded often by passing
infringements of brain blood circulation (IBBC) which make about 20-30 % among
patients with IBBC in hospitals and 46 % polyclinics. Among men of 20-54 years
relative density of IBBC makes 25 %.
Thus more than in a quarter of cases IBBC are a debut various latent proceeding
cerebrovascular diseases [2,3,5].
Crucial importance in decrease in death rate and incapacity owing to a
stroke belongs to primary preventive maintenance which is directed on the
prevention of development of the first stroke. Primary preventive maintenance
of cerebrovascular diseases is based on struggle against known risk factors
and possibilities of their correction [4,6]. Various clinical,
biochemical both behavioural and other characteristics concern risk factors of
a stroke peculiar to the separate person and separate populations, and also the
external influences which presence specifies in the raised probability of
development of a stroke. Therefore, the purpose of our research was studying of medical-demographic
specificity and features of major factors of risk for the early prevention of
strokes at the population of the South Kazakhstan area.
Materials and research methods: in a context of complex sociological research questioning of the
population of the South Kazakhstan area made on the basis of chair of nervous
illnesses of IKTU was spent. Sociological research included poll.
The general investigated sample of poll has made 2000 respondents
(as healthy and patients of neurologic, cardiological branches of city and
regional medical institutions of Kentau, Ordabasy,
Aryss and Sajram regions of area).
Results and discussion: Socially-demographic
characteristics of respondents of poll have shown that at the gender
characteristic interrogated, men were made by 45,5 %, and women –
46,7 %. Educational level in most cases at 43,2 % of
patients has made secondary education. Laws of presence the risk factors of stroke developments – hypertensive illness, cardial pathologies, a diabetes,
obesity from the social status of the patient are revealed.
The analysis of the
given age characteristics has shown that the quantity of respondents –
patients with diseases previous a stroke on the average from 16 till 42 years
inclusive has made more than 67 % that proves an existing tendency of a stroke
to "rejuvenation". An ethnic accessory of respondents of
poll 75,5 % of Kazakhs have made, Uzbeks – 19,0 % and 12,5 % -
Russian. Constant place
of habitation of respondents in
a city were made by 52,2 %, in areas SKA – 34,7 %. From 100 % of respondents of 74,5 % -
aboriginals of region, and 15,5 % (310) immigrants have the status «oralman».
The emotional
nervous tension or stresses are one of the factors influencing display of a
stroke. If 43,7 % of respondents of poll notice that the sort of their labor
activity isn't connected in any way with stresses 18,8 % consider that
stressful situations take place off and on, 37,5 % the person mark high frequency
of stresses on a workplace. Among investigated, also mentioned death or illness of the loved one – 37,2 % the
person, dismissal from work – 27 %, divorce – 16,1 % of patients, moving –
19,7 %. More than 30,3 % interrogated keep to a diet in an everyday life,
however, concept of "a dietary food» differentially at various social
strata of the population: or it is the rigid diets excluding the most part of
necessary products, or soft where enter genemodificated (GMO) products, the semifinished products containing harmful
components. More than half interrogated (69,7 %) don't supervise food in
the daily diet, don't keep to a diet from them of 59,3 % of respondents consume
basically fat meat and fried food, 10,4 % interrogated prefer sharp and salted food. Thus, the
culture of a food of the population, being in high group of risk on a
stroke is low. Probably, it is connected with mentality of traditional
southern, Kazakh and east food as a whole, however, considering presence in region of statistically significant
level of socially vulnerable levels of population, it is necessary to take into
consideration and the fact of high consumption GMO products because of their low
consumer cost. As one of significant risk factors of a stroke – the
overestimated norm of weight is marked by 45,5 % (910) interrogated, 54,5 %
(1090) respondents consider the weight within norm. Only 18 % (360) interrogated actively go in for
sports, sports exercises for maintenance of the health. Overwhelming number of
questioned, 82 % from them of 27,4 % seldom do sports exercises, 15,5
% the person can't because of illness, 39,1 % - absence of habits to sports loadings, stereotypes, laziness. The interrelation of state of
health with weather change, i.e. meteosensitivity were marked – "sometimes"
at 55,2 % of respondents, is frequent" at 19,6 % the person
and is constant" at 25,2 % questioned. A genetic heredity of an
arterial hypertensia and an atherosclerosis from parents have no 60 %
interrogated. At 40 % questioned, presence of the given diseases have made
at: the father – 37,8 %, mothers – 30 %, both parents – 32,2 %.
In the spent research of disease of heart have been diagnosed in 37,2 %
(745) cases. Thus, patients who
are registrated in a dispensary at
the cardiologist are revealed 46,2 % the person who
are not registrated in a dispensary of 32,9 % and transferred, a heart attack of
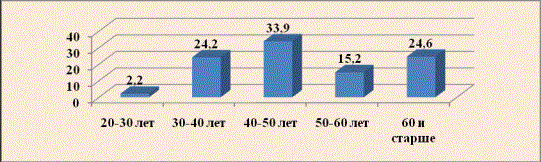
a myocardium of 20,9 % questioned. The first symptoms of an arterial hypertensia have
arisen on the average in age categories from 40-50 years at 33,9 % of the
questioned respondents (drawing 1).
Fig. 1. Quantity indicators of questionad, on the first symptoms of an arterial
hypertensia
Frequency of the maximum borders of indicators of an arterial
hypertensia on the average meets at 46,2 % of patients to
140/90 mm.mr.cl., to 160/100 mm.mr.cl at 35,4 % interrogated, to 180/110
mm.mr.cl at 13,1 %, above 180/110 mm.mr.cl at 5,3 % of respondents.
More than half, interrogated (56,2 %) consider that preparations for
correction of an arterial hypertensia render a positive effect. However, the
others of 6,9 % of respondents notice that pressure isn't always
stabilized, 11,8 % mark the big dynamics of pressure jumps, 14,5 %
the person have refused drug intake and 10,6 % don't follow instructions
of the doctor. Hence, patients with an arterial hypertensia not constantly are
under supervision of the therapist, or it is available the fact of
"self-treatment", use of folk remedies of medicine that doesn't
influence a positive course of disease or full treatment. The diabetes has been revealed in 20,5 % (410) cases,
the others of 79,5 % of respondents didn't suffer a diabetes. From patients
with a diabetes, who are
registrated in a dispensary at
endocrinologist – 34,6 %, who were not registrated in a dispensary of 30 % and at 35,4 % of patients -
insulin - a dependent diabetes.
Frequency of symptoms of display of feeling dumbness, weaknesses in one
half of body (a hand, a foot, language, the person)
among questioned, has made once a month at 44,5 %, once in
3 months at 32,3 % and once in half a year of 23,2 % the person.
More than half of respondents of poll (64,7 %) don't connect symptoms of
dumbness and weaknesses in one half of body with differences of arterial
pressure (sharp increase or decrease in arterial pressure) carrying these
factors to «instantaneous» reactions of an organism to a cold or weather
conditions, 35,2 % sensitively watch displays of dumbness. It is
necessary to organize offices of the psychological help (the office
of the psychologist or the psychotherapist) in polyclinics consider 61,0 %
of respondents of poll, 16,3 % have answered negatively, 22,7 % aren't informed
on the importance for patients.
Thus, considering
the data of sociological poll, it is possible to notice that prevalence of a stroke in SKA depends basically on features of a way of life and the risk factors
connected with it. Updating of a way of life and decrease in levels of risk
factors can prevent development of diseases. By consideration of questions of a migratory gain
it is necessary to consider the genetic status of migrants, a condition of
their health, feature of epidemiological, geographical conditions in the
country, where they have arrived from. Presentation level in region of socially vulnerable levels of population influences
dynamics of a stroke. Culture of a food and social (quality and a diet, hypodinamia,
absence of practice of playing sports) population factors in a
context of traditional cultural stereotypes
of SKA render one of significant influences on stroke occurrence even in
such socially safe environment of a society (the teacher, bank workers,
state employees).
Probably, creation of School of a stroke, an office of the
psychologist or the psychotherapist in polyclinics, family-medical
ambulance stations of a city and area, and also the analysis of a database of
the Register of the strokes, adequate therapy from cardiologists and
therapists, sanitary-educational work will reduce and will
reduce risk of occurrence of strokes on the scale of SKA.
The literature:
1. Djusupova A.S. Stroke – a global problem of domestic neurology//Mag. The person and the Medicine – Kazakhstan. – 2011.
– Iss. 3, ¹3. – from. 6-9.
2. Gusev E.I., Skvortsova
V. I "Modern representations about treatment of a sharp cerebral
stroke". Consilium Medicum: volume 2. ¹2 2002, from.1-18
3. Gusev Å. I, Konovalov A. N, Burd G. S. Neurology and
neurosurgery. Ì: Medicine, 2000,
from. 14-15
4. Suslina Z.A. "Treatment of an ischemic stroke".
Magazine "Treatment of nervous illnesses" ¹1.2001ã, from.3-7.
5. Greydy
B.O. Development and realization of complex system of the help at a stroke//Mag. Neurology and psychiatry. –
2007. – Special Release. – From. 133-136.
6. Khakim A.M. Change in help system at a stroke: the
Canadian experience//Mag. Neurology
and psychiatry. – 2007. – Special Release.
– from. 129-132.