Assoc.
Prof. V.Yu. Ovsyannikov, graduate student
A.A. Korchinskiy,
student
E.V. Protopopova, student D.S. Lapshina
The
nature of module design of technological systems concentration
of
liquid foods cold
Today the market of control
systems of technological operations of obtaining concentrated liquid media in
food production present a significant contingent of operators, which, of
course, creates a competitive environment for the development of technological
systems and devices of control and organization process. However, there is a
need to create new management methods to the creation of new technology of food
technologies, taking into account the impact of as on the basic technological processes
of processing of raw materials and a local impact on the variation of
technological parameters of functioning of technical system [1-2].
Procedure development system
design involves the development of a set of processing subsystems, aimed at
automation of process of designing of technological complexes, is directly
dependent on the specifics of technological equipment, which operates on the
site of the refrigeration concentration of liquid media by the method of
freezing moisture [3].
In our case, the modeling of
technological processes on the basis of mathematical networks involves the
interaction of events and conditions. The event is an action occurring in the
technological system, and the condition is a logical description of the state
of the technical system.
Many concentrated liquid product denoted as:
![]() (1)
(1)
Many technological complexes will be denoted by:
![]() (2)
(2)
Many types of the main technological equipment denote:
![]() (3)
(3)
Many items of auxiliary equipment denoted as:
![]() (4)
(4)
At each stage of analysis produces many of certain places P1, P2, P3,
P4, P5, P6
and the decision on the choice of variants of technological equipment
complexes, corresponding to the events Q1,
Q2, Q3, Q4,
Q5, Q6.
The special role played by the search order of possible options for the
design of technological systems equipment, which affects the number of options
is too much and thus the duration of the computational operations of a computer
of the computational process.
Initially, the creation of possible variants of the basic hardware in
accordance with hardware performance, referred to as P1. From the database selects all possible variants of
support elements, suitable to the performance of the main equipment.
Next is the creation of possible variants of the basic (already formed
at the previous stage) and auxiliary technological equipment on the basis of
their compliance performance, allowing it to form many places P2.
Then set the ability to use basic technological equipment for the
refrigeration concentration from P3
in accordance with the original properties concentrate a liquid medium is
formed many P4.
Then P4 select only
those options that allow you to handle this technological raw materials.
Then P4 selected
options allow you to get the desired accuracy of functioning of the
technological complex with the formation of many P5.
The final stage involves the selection of P5 set of the sustainability of individual elements of a
coherent technological system refrigerant concentration.
Denoting a gradual impact x1,
x2, …, xi, …, xn – decisions on the choice of any
performance of the main equipment for processing of raw materials for i stage
where i = 1...n; n – the number of stages. The
achievement of the necessary result with i etapower effects still wi . Control x is a set astapovich effects: x = {x1, x2,…, xi,
…, xn}.
In the end, it is required to find such an effect x*, the total effect W will be committed to the maximum:
![]() . (5)
. (5)
In this case x*={x*1, x*2,…, x*i,…, x*n} – the best impact, consisting of a set of
optimal actions.
Thus, for each technology complex Êk it creates
many options for technological subsystems, each of which has at least one unit
of process equipment.
For each subsystem creates a number of possible options of the main
technological equipment with the period between two failures tij. The total period of
equipment operation of each unit of technological equipment is limited to the
period of operation Tij. It
is necessary for many technological subsystems of the many possible variants of
technological equipment Ð6 to create
the best products so that the total processing time of raw materials tΣ was minimal, while the number of replacements of
equipment should be minimal. Impact xi={j, tij
, aij} on i stage means that the subsystem
processing is carried out with j performance of technological equipment
with the period between two failures tij,
with the number of replacements of equipment aij:
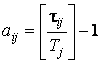 , (6)
, (6)
where τij – total time
permanent work j equipment
after the operation of the first subsystem.
![]() (7)
(7)
The state of the system at each i
the stage is characterized by the vector Si={j, τij}, which
means that prior to operation within i the subsystem was used j grade
manufacturing equipment, and its used resource is equal to τij.
Write the function of optimality for each stage:
![]() . (8)
. (8)
Define a function changing the state of the system in the form:
![]() , (9)
, (9)
which shows how the condition of Si under the impact of xi.
Write the recurrence equation of dynamic programming
![]() , (10)
, (10)
which characterizes the conditional
optimal effect Wi(Si) (since i stage
to the end) through the already known function Wi+1(S′). This
effect corresponds to conditional optimal impact íà i stage xi(Si).
The solution of the problem the procedure starts with optimization of
the last n stage, calculating
the possible variants of technological equipment at this stage, the conditional
optimal effect:
![]() (11)
(11)
and determining the conditional
optimal impact xn(Sn).
In our case, as the last stage defines a subsystem, which can be used by
the least number of different items of process equipment, because otherwise it
is not guaranteed definition of this subsystem because of the probability of
exclusion of appropriate technological equipment in the previous stages.
Further implements conditional optimizations (n–1), (n–2) and the following stages by the formula (10). The result is
to produce unconditional optimization impact, taking into account the
recommendations received at each stage.
On the basis of the proposed method has a possibility of design
simulation technology refrigerant concentration of liquid food and biotechnology
environments [4-5].
Literature
1. Ovsyannikov V.Yu. Concentration of the plasma of the blood of large
livestock by freezing. Meat industry. 2013. ¹ 7. pp. 47-49.
2. Antipov S.T., Ovsyannikov V.Yu., Kondratyeva
Ya.I. Kinetics of the process of concentration by freezing cherry juice. Bulletin
of the
3.
Ovsyannikov V.Yu., Bostynets N.I.,
Denezhnaya A.N., Kraminova Yu.S. Thermophysical special features of
freezing food media. International student scientific bulletin. 2015. ¹ 3-1. pp. 69.
4. Ovsyannikov
V.Yu., Kondratyeva Ya.I., Bostynets N.I.,
Denezhnaya A.N. Investigation of the process of freezing and thawing of fruit
juices. Bulletin of the
5.
Ovsyannikov V.Yu., Bostynets N.I.,
Denezhnaya A.N., Kondratyeva Ya.I. Control of the process of low-temperature
concentration of liquid media by freezing. Automation. Modern technologies.
2016. ¹ 2. pp. 10-13.