Economics/4.
Investment activity and stock markets.
dr. of sci.
Pistunov I.M.
HEI “National Mining University”, Ukraine
Model of investment
portfolio optimization
Many researchers and practitioners traders investigate the problem of
optimal portfolios formation. This method is an effective tool for filtering
incoming data on securities volatility. As for research works relevant for CIS
countries, a significant contribution to the theory of optimal investment
portfolio.
Despite the existing variety of scientific and practical approaches to
formation of investment strategy and risk management, classical Markowitz and
Sharpe models are widely applied for direct distribution of funds among the
assets.
The aim of this study is to improve the investment portfolio optimization model by combining existing Markowitz and Sharpe models.
Pistunov-Sitnikov
risk-revenue model.
The model was created as a solution to multicriteria optimization task ensuring
risk minimum and profit maximum. As a result convolution of two Markowitz
criterion was formed. Whereby the criterion of "minimum" was placed
in the numerator and the criterion of "maximum" - the denominator.
Also, the numerator was added to the weighted average variance portfolio. The
main idea of this model was to unite the Markowitz model with maximum rate of
return and minimum risk.
Its advantage over the previously described models is that there is no
need to determine the acceptable level of risk and income. This model requires
the same statistical calculations as Markowitz model. This model works great
with small number of assets and with relatively volatile stock market (1).
Integrated
Pistunov-Sitnikov-Sharpe model.
We use the Pistunov-Sitnikov approach, that allows assembling two Markowitz models into one
by putting the rate of return into numerator and the risk into the denominator.
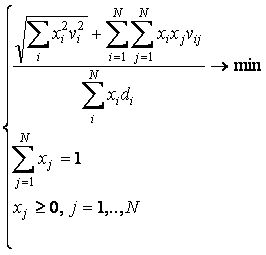 (1)
(1)
where di – average rate of return of asset i, vi– variation
(standard deviation) rate
of return on asset i, vij
– covariance of profitability of
assets
j and i, ![]() xi,j – the share of capital spent on the purchase of
securities i and j.
xi,j – the share of capital spent on the purchase of
securities i and j.
Considering the Sharpe model we have Rf
– rate of return on the risk-free asset. Elimination of this parameter provides
us with portfolio level of profitability i.e.
maximum aiming function.
But there is a rate of return index in the denominator of Pistunov’s
optimal portfolio model.
This
inequality ensures the implementation of the premise that the risk of the
portfolio should not exceed pre-specified risk frontier. The counterpart of this constrain
is also present in the Markowitz model, as well as set beforehand expected portfolio return. But the
model Pistunov-Sitnikov allows to omit the definition of such values
as predefined profit and risk. On the top of that, the index that
characterizes risk (βi)
is present in the denominator. Therefore, the Sharp’s model constrain is discarded
completely. So a simplified version of the denominator is multiplied by the
denominator of Pisunov’s model and the numerator remains unchanged.
Thus, Integrated Pistunov-Sitnikov-Sharpe model is
(2).
The model was tested on real
data of equities of the energy sector, traded on the New York Stock Exchange
with next results (table 1). Especially for this comparison
criterion of relative riskiness was developed, that is calculated according the
formula:
Vr = R/M,
where R
– risk,
à M – rate of return of asset.
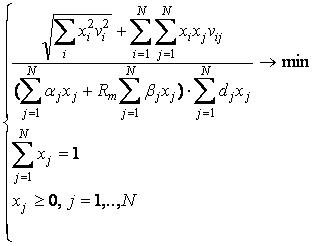 (2)
(2)
Table 1 - Comparison of calculations on optimization models
|
Model |
A |
AE |
DTEE |
EI |
En |
PSEG |
Vr |
|
Developed
integrated model |
23% |
34% |
23% |
6,6% |
1,7% |
13% |
0,0007 |
|
Pistunov-Sitnikov
model |
23% |
43% |
25% |
3,1% |
0,0% |
6,9% |
0,0008 |
|
Sharpe model |
0,0% |
0,0% |
23% |
52% |
25% |
0,0% |
0,0472 |
|
Markowitz (risk
minimization) |
92% |
8,5% |
0,0% |
0,0% |
0,0% |
0,0% |
0,1028 |
|
Markowitz
(profit maximization) |
21% |
79% |
0,0% |
0,0% |
0,0% |
0,0% |
0,1036 |
Legend for
corporations: A – Ameren, AE – American electric, DTEE – DTE Energy, EI – Edison
international, En – Enbridge, PSEG –
Public Service Enterprice Group,
The
obtained results indicate that the developed integrated model is the most
effective among models considered on the rate return criteria. This conclusion
is supported with the criterion of relative riskiness that was developed
specially for this study. The relative riskiness (0.000702) is minimal for the
portfolio formed on integrated model.