Khusainov F.F., Khakimyanov M.I.
Ufa State Petroleum Technological University
Designing
of wireless sensors
Technological
processes in fuel and energy complex of industry, such as production,
transportation and refining of oil and gas, require deep introduction of
automatic control systems. These modern control systems are multi-level
complexes that provide maximum performance and reliability of process plants
during the entire cycle.
The
equipment of automatic control systems include sensors, different controllers,
control stations and channels of data transmission, which can be, wired,
optical, radio modem, cellular and satellite.
More
recently, at designing such systems, there has been a trend towards the use of
wireless technology as the use of sensors with wire interface often causes
certain difficulties associated with mounting the sensors on moving and
rotating objects, where the cable quickly wears out and breaks, as well as the
installation of a remote and distant places. Also it should be noted that the
organization of wireless communication channels, in most cases is much cheaper
than laying the special cable networks [1, 2].
However,
the use of wireless sensors associated with some operational disadvantages,
such as the need for regular replacement of batteries, the range of radio
transmission and of limited use because of the climatic conditions.
Decision
of the above disadvantages could be the use new types of chemical batteries
(lithium, silver-zinc and others) that have a high capacity (up to 10 A • h or
higher), and keep working in a wide range of temperatures (at temperatures down
to -30 ... 40 º C and below), as well as the emergence of new low-power
electronic parts and radio interfaces for the design of sensors for long life
operation without battery replacement [3].
One
of the most promising ways to solve the problems described above is the use of
alternative sources of energy: solar, heat, voltage generated by piezoelectric
generator in the sensors of weight and strength.
Figure
1 shows a block diagram of a load cell with a wireless interface, which is
powered by the electricity generated by the piezoelectric generator. The device
is used for the registration dynacards of sucker rod pumps, driven by a pumping
unit.
The
load cell is installed in the node rope suspension of pumping unit and measures
the effort generated between traverses with the reciprocating motion of the
rod. The load cell comprises a sensing elements SE, measuring circuit IC,
analog-to-digital converter ADC, a microcontroller and a radio transmitter IC
RP. Power to all elements of the sensor from a battery that is recharged with
electricity generated by the piezoelectric generator GHG its continuous cyclic
loading.
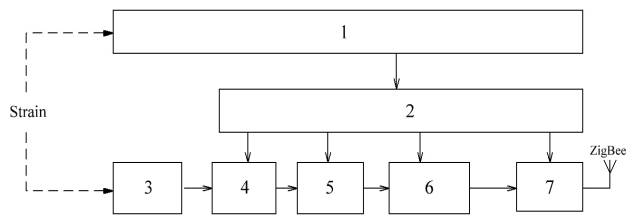
1 – piezoelectric
generator; 2 – battery; 3 – sensing elements; 4 – measuring circuit; 5 – analog-to-digital converter; 6 – microcontroller;
7 – radio transmitter
Figure 1 – Block diagram
of a wireless load cell with piezoelectric generator
All
electronic components of the sensor should have low power consumption, and in
between measurements switch into a "sleep mode." Modern
microcontrollers have quite energy efficient. In the "sleep mode" is
provided to the consumption of 100 nA, the internal clock consumes 800 nA.
Details of some of these MCUs are presented in Table 1 [4].
Table 1 -
Comparison of microcontrollers
|
|
MSP430F21X1 |
PIC16LF72X |
PIC18F14K50 |
PIC24F16KA102 |
|
Pin Count |
20/24 |
28/44 |
20 |
20/28 |
|
Flash-memory of programs |
4-8 |
3.5-14 |
8-16 |
8-16 |
|
EEPROM Data Memory |
- |
- |
256 |
512 |
|
RAM, byte |
256 |
368 |
768 |
1536 |
|
Consumption in
the "sleep", nA |
100 |
20 |
24 |
25 |
|
Time out from
the "sleep", mks |
3 |
5 |
5 |
1 |
|
Consumption of WDT, nA |
700 |
500 |
450 |
420 |
|
Consumption of RTC, nA |
700 |
500 |
790 |
520 |
|
Consumption when operating at a frequency of 1 MHz, uA |
250 |
110 |
170 |
195 |
It
should be noted that while reducing the level energy consumption of sensor
developers limited speed and metrological characteristics of the device. Since
the use of various software algorithms of digital signal processing, filtering
and integration can significantly increase the current consumption of the
microcontroller.
Thus,
there may be made the following conclusions:
1
The advantage of wireless sensors is the ability to install in remote and
distant places, moving and rotating objects, where the use of devices with a
wired interface is difficult.
2 Modern
microelectronic element base allows the design of low-power devices that can
provide continuous operation with battery.
3 When
using alternative renewable sources of energy can significantly increase the
continuous operation of wireless sensors.
References:
1. NI Wireless Sensor Networks: [site]. URL: http://sine.ni.com/np/app/main/p/ap/imc/lang/ru/pg/1/sn/n17:imc,n21:11297/.
2. Introduction to Wireless Sensors: [site]. URL: http://www.omega.com/prodinfo/wirelesssensors.html.
3. M.I. Khakimyanov. Wireless
technologies in industrial sensors // Improving the reliability and energy
efficiency of electrical systems and complexes: Interuniversity collection of
scientific papers / Editorial Board.: V.A. Shabanov. Ufa: USPTU, 2010. 189-198 p.
4. Compare 8-bit PIC® MCU Architectures: [site]. URL: http://www.microchip.com/pagehandler/en-us/family/8bit/architecture/home.html.