Avramenko S.N.
State-run
Institution of the Secondary Professional
Education of College of Architecture and Construction ¹7
Analysis of the core competences among
students of the construction department’s resource center
There are
several types of competencies in the professional area: special (subject)
competencies which define the actual possession of the profession; general
professional (general subjects) competence related to several subject areas or
professional activities, which should possess a graduate within his profession,
key (basic, universal) competence (generalized methods of action to ensure
productive performance of professional activities, i.e., a person's ability to
put into practice their competence [1, c. 12]), promoting high-quality solution
of various problems from different areas of knowledge and implementation of
social and professional roles and functions. Generic knowledge and skills
determine the competence of the individual (expertise - the ability
(willingness) of a specific activity with the knowledge and skills, including
not only professional, but also personal qualities [2, p. 70]) and they are the
most important components.
Key competencies are invariant
with respect to the subject area, which are characterized, including skills:
acquire knowledge, create / convert, organize / train and use knowledge. These
skills are in demand in any profession, because in a globalizing world,
possession of highly qualified specialists is permanent. With respect to
persons employed in the construction industry, the key (base) competencies are
the following: understanding the nature and social significance of the profession and manifestation of interest towards it, ability to organize the own
activities, to determine the methods and ways to perform professional tasks,
evaluate their performance and quality; address problems, assess risks and make
decisions in emergency situations, the ability to search and use information,
necessary for the effective performance of professional tasks, professional and
personal development skills to use ICT in their professional activities, the
ability to determine the problem of professional and personal development,
engage in educate ourselves, consciously planned training, orientation in terms
of frequent change of technology in professional activities.
The main characteristics of the
modern labor market are the high dynamics of innovation, flexibility,
variability, new demands on job seekers. In this case, the requirements of
employers are not limited to the format of "knowledge" of
competitors, and focus on their commitment to continuing self-education and
upgrading professional skills, the ability to take responsible decisions and
actions in unusual situations, critical thinking, business communication and self-management
behaviors and activities. Competitiveness is a specialist in many respects
depends on his ability to acquire and develop skills which can be used for
different situations in life. Thus, the requirements of employers are focused
on the presence of key competitors (basic) skills. The high level of competence
of workers and professionals is now considered as the most important
competitive advantage of some organizations over others.
Based on a list of employers’
requirements, it can be assumed, that the core (basic) competences
are made up of a number of individual competencies, only total mastery of which
gives the desired result, in order to meet the demands of the modern labor
market. These competencies include:
·
professional competence, characteristic of the presence of a person of necessary
knowledge and skills which represent
the basis of professional activity and the individual's ability to consciously
apply this knowledge in practice;
·
social competence, which can be regarded as the aggregate of formation of
the personality traits related to the cognitive sphere, providing a deep and
comprehensive insight into the psychological characteristics of the society, in
which the professional activities of the individual;
·
communicative competence, which represent a person's ability to adequately
assess himself and his place in society, the right to determine personality
traits and emotional states are partners in communication, select and apply the
best ways of dealing with others and apply them in the process of
communication, interpersonal events to predict;
·
information competencies, which are a complex knowledge of the individual
in the field of information and communication technologies, as well as its
ability to apply this knowledge in practice, in other words - make information
literacy of a person;
·
ethno-cultural competence, which are commonly regarded as the personal
qualities, necessary for the possession of modern humans to effectively
socialize in different areas of multicultural society;
·
educational competence, due to personal-activity approach to education, the
educational requirement for the preparations necessary for socially important and
productive activity of a person;
Mastering by the students of necessary
knowledge, skills and abilities, depends on the content of teacher’s training
of any profession and his understanding of the importance of building of
students' core competencies. One of the leading roles is played by the
principle of active approach of the teacher, as according to V. Shadrikov,
"Educational activity is the activity which is expressed in a meaningful
development of the learner, learning the basics of their culture, the full
development of his faculties, where teacher and student advocate as equal
subjects of the educational process" [3, p. 12].
Modernization of
vocational education in Russia is aimed to bringing
the results of its operations into
compliance with the requirements of the
individual, society and the state as a whole. In
order to identify the importance of educators’ understanding
of the availability of key (core) competencies
for students, was conducted a
case study among teachers and administrators colleges in
Russia on the base of the Resource Center of the State-run budget
educational institution of secondary vocational education of College of
Architecture and Construction number 7 (Moscow). The
respondents were offered to
make their mind from possible answers on
the subject of compulsory acquisition of listener’s key (base) competencies.
Figure 1
shows the results of sociological analysis, conducted in October and November of
2011 on the basis on of the Resource
Center of the State-run budget educational institution of secondary vocational education of College of
Architecture and Construction number 7 among
the teachers and managers of universities in
Russia. It was found that the leading competences to
meet the demands of the modern labor market are
the following: professional (59.4%), social (12.6%), communication (5.6%), information (9.8%),
ethno (8, 1%) of
competence and others (4.5%).
The overall majority
of respondents assessed the
key (core) competence
of the individual as an important
source of socio-economic
development.
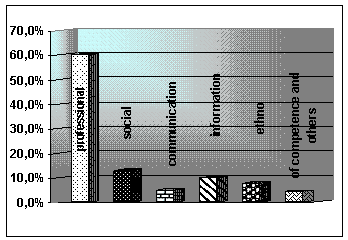
(Fig. 1)
Compulsory
presence of key competences (in respondents’ pinion)
As was
illustrated by this study, in the vocational
education system in Russia, the majority of teachers are inclined to evaluate the key (basic) competence of
personality as an important resource for regional socio-economic development.
Literature:
1.
Korsakov S.V. Portfolio of manager’s
competences // Competences and expertise of a modern specialist. Issue of articles.
– M.: Granitsa, 2011. – p. 7-33;
2.
Nevmerzhitskaya
E.V. Ethno-oriented training of particularities of
non-verbal foreign language communication // Competences and expertise of a
modern specialist. Issue of articles.
– M.: Granitsa, 2011. – p.
33-70;
3.
Shadrikov
V.D. Methodics of assessment of quality level for teachers.
Institute of education content of the State university – Higher School of
Economics. Moscow, 2010. – p. 174.