Marta Kopytko
PhD, associate professor, assistant professor of
Department of Economics and Economic security of Lviv State University of
Internal Affairs, Ukraine
Volodymyr Babenko
senior lecturer, Department of Mathematics,
Ivan Franko National University of Lviv, Ukraine
IMPACT OF BRIBERY ON THE PERFORMANCE
OF INDUSTRIAL ENTERPRISES IN REGIONS OF UKRAINE
The
efficiency of enterprises indicator displays gross domestic product, by region –
GRP. Economic crimes have a significant impact on industrial activities, the
number of which in Ukraine is quite high. Economic crimes should be considered
in the division of such species as crimes against property (CAP), crimes
in the sphere of economic activity (CSEA), crimes in the area of
computers and computer networks (CCOM), crimes related to service
activities (CSA), including bribery (bribe).
To
examine the gross regional product of these factors a linear model was built with
panel data with fixed effects [1].
Such a
model can be written as
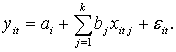 (1)
(1)
Here ![]() – value of the dependent variable for the i-th object in period t
(i = 1..n, t = 1..T),
– value of the dependent variable for the i-th object in period t
(i = 1..n, t = 1..T), ![]() – value of k explanatory variables for the i-th
object in period t, b – vector characterizing the marginal effects of
independent variables on the dependent,
– value of k explanatory variables for the i-th
object in period t, b – vector characterizing the marginal effects of
independent variables on the dependent, ![]() – constants that
reflect the effect of factors specific to the i-th object,
– constants that
reflect the effect of factors specific to the i-th object, ![]() – the remains of the model.
– the remains of the model.
The evaluation of the coefficients
b is performed from
regression using data in the form of deviations from medium objects, and
evaluation of constants ![]() – the formulas:
– the formulas:
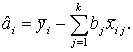 (2)
(2)
Regression
analysis of the data as deviations from the average for the objects held in the
package Statistica 8.0 [2]. The results of analysis are presented in
Table 1.
Table 1
The results of
calculating the coefficients b
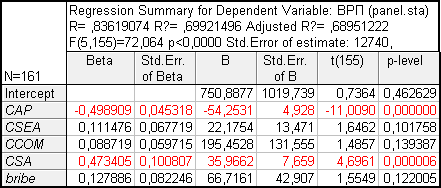
Since statistically significant coefficients were only around CAP
variables and CSA, the improved model kept only these variables. The
results of calculations are presented in Table 2.
Table 2
The results of calculating the coefficients b
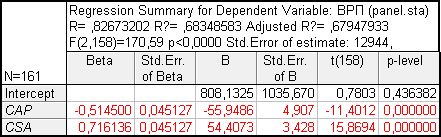
As can be seen from the Table 2, the characteristics of the model
(coefficient of determination and Fisher statistics) have not changed. In
addition, the coefficient of the variable CSA better reflects the impact
of this type of crime including bribery.
Estimates of the
constants are given in Table. 3.
Table 3
Estimates for the constants of the objects
|
Region |
Estimated coefficient ai |
Region |
Estimated coefficient ai |
|
Crimea |
19844,9 |
Mykolaiv |
19996,97 |
|
Vinnytsia |
19981,54 |
Odesa |
41197,07 |
|
Volyn |
11356,46 |
Poltava |
41443,46 |
|
Dnipropetrovsk |
85022,01 |
Rivne |
14207,94 |
|
Donetsk |
123054,6 |
Sumy |
10210,53 |
|
Zhytomyr |
10557,92 |
Ternopil |
3309,785 |
|
Zakarpattia |
6349,074 |
Kharkiv |
69024,99 |
|
Zaporizhzhia |
36746,96 |
Kherson |
12700,87 |
|
Ivano-Frankivsk |
12891,28 |
Khmelnytsky |
13077,51 |
|
Kyiv |
37709,06 |
Cherkasy |
17181,81 |
|
Kirovohrad |
9827,656 |
Chernivtsi |
-2445,92 |
|
Lugansk |
38455,6 |
Chernihiv |
14038,2 |
|
Lviv |
32550,86 |
Kyiv |
195251 |
Thus, the model can be represented as
GRP
it = ai – 55,95CAPit + 54,41CSAit (3)
The
coefficient determination of model ![]() , Fisher statistics
, Fisher statistics ![]() , and its level
, and its level ![]() , which indicates a good adequacy of the resulting model.
, which indicates a good adequacy of the resulting model.
Analysis
of the model shows that crimes against property have a negative effect on the
GRP and cause more than 25% of the variance (![]() ), and crimes in the area of performance contribute to the growth and
determine GRP over 50% of the variance (
), and crimes in the area of performance contribute to the growth and
determine GRP over 50% of the variance (![]() ).
).
References
1. Factor, discriminant and
cluster analysis [Translation from English
J. O. Kim,
C. W.
Muller, W. R. Klekk etc.; Edited by S. Enyukova] (1989), Finansy I
Statistika, Moscow, 215 p.
2. Halafyan A. A. (2007) STATISTICA 6.
Statistical analysis of the data. Third Edition, Binom-Press,
Moscow, 512 p.