Экономика/8. Математические методы в экономике
Serkebayeva L.T
A.Baitursynov Kostanai State University, Kazakhstan
Poverty
Assessment on the basis of the subsistence minimum
In Kazakhstan, officially
accepted method for measuring absolute poverty on the basis of the subsistence
minimum.
In accordance with the
Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan The living wage - is a necessary minimum cash
income per person equal in magnitude to the minimum consumer basket and
provides a person fulfilling the minimum requirements at the level adopted by
society at this stage of development.
The cost of the minimum
consumer basket includes the cost of the minimum food basket (70%) and the cost
of non-food goods and services (30%). The cost of the minimum food basket is
calculated monthly statistical authorities by multiplying the norms of food
consumption (20 products) on the average prices prevailing on the middle of the
month [1].
The
living wage is for:
-
assessment of living standards and the definition of the poverty line;
-
identify areas of social policy and the implementation of measures for
social support of the population;
-
study establishes minimum wage, pensions, allowances and other social
benefits.
According to the Law of
the Republic of Kazakhstan on the subsistence level: Poverty line - border
income required to meet the minimum needs of the person that is installed in
the country depending on the economic opportunities and serves as a criterion
for targeted social assistance to low-income population
The poverty line is
determined quarterly on the country and by region in accordance with the
procedure established by the Government, and more specifically the Ministry of
Labour and Social Welfare.
Indicators quantifying poverty
To assess the level of poverty and inequality in
the country use indicators:
-the proportion of the population with incomes below
the subsistence minimum and the food basket;
-depth and severity of poverty, the Gini
coefficient, the differentiation of the population by income [2].
Poverty rates in Kostanai
region in 2006-2010. are presented in Tables 1-2.
Table 1
shows the dynamics of the indicator "The share of low-income
population."
Table 1 - The share of low-income population
|
Year |
Proportion of population with incomes below the
subsistence minimum |
including |
Proportion of population with income below the food
basket |
including |
||
|
in
urban areas |
in
rural areas |
in
urban areas |
in
rural areas |
|||
|
2006 |
14,0 |
4,4 |
24,9 |
2,7 |
0,1 |
5,6 |
|
2007 |
10,4 |
4,1 |
15,8 |
0,2 |
- |
0,4 |
|
2008 |
9,0 |
5,2 |
12,3 |
0,8 |
0,5 |
1,0 |
|
2009 |
6,8 |
3,3 |
9,7 |
0,4 |
- |
0,8 |
|
2010 |
6,4 |
2,6 |
10,6 |
0,5 |
0,2 |
0,8 |
Table 2 shows the
dynamics of "Key indicators of poverty in urban and rural areas."
Table 2
– Key indicators of poverty in urban and rural areas
|
Year |
The share of the poor |
depth of
poverty |
poverty
severity |
|||
|
in
urban areas |
in
rural areas |
in
urban areas |
in
rural areas |
in
urban areas |
in
rural areas |
|
|
2006 |
4,4 |
24,9 |
0,9 |
6,4 |
0,3 |
2,3 |
|
2007 |
4,1 |
15,8 |
0,6 |
2,1 |
0,1 |
0,5 |
|
2008 |
5,2 |
12,3 |
0,9 |
1,7 |
0,3 |
0,5 |
|
2009 |
3,3 |
9,7 |
0,5 |
1,9 |
0,1 |
0,5 |
|
2010 |
2,6 |
10,6 |
0,3 |
1,7 |
0,1 |
0,5 |
We analyze
the change in poverty rates in Kostanai region.
Judging
by the pace of growth can be said that for this indicator in the period from
2006 to 2008 the rise, and from 2008 to 2010 is going to decline. Overall, from
2006 to 2010 the proportion of the population with incomes below the
subsistence minimum in urban areas decreased 40.9%.
In the
countryside, in the period from 2006 to 2009 observed a steady decline, and in
2010 a small increase. In general, the proportion of the population with
incomes below the subsistence level in rural areas decreased by 57.4%.
Analyzing
the basic rate of growth in terms of "depth of poverty" can formulate
the following conclusions:
-
depth of poverty in the urban area as a whole for the analyzed period
decreased by 66.7%;
-
the depth of poverty in rural areas and for the period under review
decreased by 73.4%
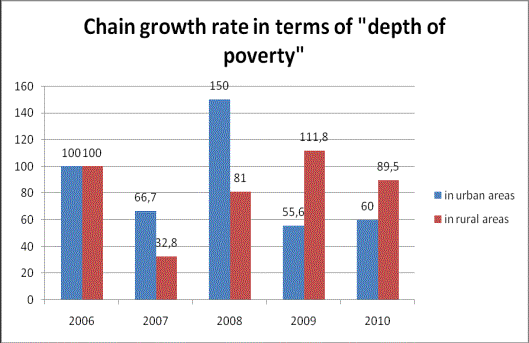
Picture 1 – Chain growth rate in terms of "depth
of poverty"
Picture 2 is a block diagram indicator "Proportion of
population with incomes below the subsistence minimum, depending on the size of
the family"
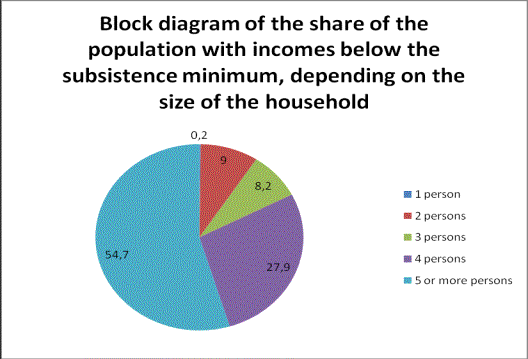
Picture 2 – Block diagram of the share of the
population with incomes below the subsistence minimum, depending on the size of
the household
Analyzing the structure diagram, we see that the
largest share of the population with incomes below the subsistence minimum
account for households of 5 or more persons. Moreover, the basic growth rates show that in the
analyzed period, this indicator increases, the increase was 16.1%.
Analyzing indicator
"Proportion of population with income below the cost of the food basket,
depending on the size of the household, we see that the largest share of the
population with incomes below the food basket also accounts for households of 5
or more persons. Moreover, the basic growth rates show that in the analyzed
period, this indicator increases, an increase of 52.9%.
Literature:
1. www.stat.kz - Агентство Республики Казахстан по
статистике. Организация обследования и анализ уровня жизни населения в
Казахстане.
2. Республика
Казахстан: оценка системы адресной социальной помощи. Заключительный отчет.
Достойный труд: комплексный подход к социальной сфере в Казахстане. Астана,
2003.Международное бюро труда, 2004.
3. Ю.Н. Тюрин,
А.А. Макаров. Статистический анализ данных на компьютере / Под ред. В.Э.
Фигурнова — М.: ИНФРА–М, 1998. — 528 с.
4. «Уровень
жизни населения Костанайской области» Статистический сборник/ 2011 – 68с. Под
редакцией К.Баримбекова