Averin I.A., Igoshina S.E., Pronin I.A., Karmanov
A.A., Antropova N.V.
Penza State University, Penza, Russia
Determination
of the Concentration and Average Cluster Size in Sols, Undergoing Coagulation
by IR Spectroscopy
1.
Physico-chemical mechanisms of formation of fractal aggregates in sol-gel
systems.
When forming
nanostructures in
sol-gel systems
the process of
sol coagulation occurs.
In this time polymer aggregates (clusters) are
growing. They have a nearly spherical shape. This growth is under the Smoluchowski
equation considering fractal organization units [1, 2]. Its assumption decision
that the concentration of clusters in sol after some infinite time interval is
negligibly small compared with the initial concentration of nanoparticles. It
is as follows:
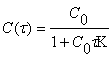 (1)
(1)
where C(τ) - the
concentration of clusters in the time τ after the
start of coagulation; C0 - initial concentration of
particles, K - constant determined only the sol composition.
Based on
Smoluchowski equation (1) and the assumption that the number of nanoparticles
in the cluster is defined as C0/C, we obtain an
expression for the average size of a fractal aggregate:
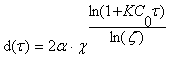 (2)
(2)
where α - the size of a single nanoparticle; ζ - the number of composite particles in the fractal aggregate at each stage fractalization in assumption that the transition to the next step does not occur until the previous spherization; χ - growth rate of unit diameter.
2. Using IR spectroscopy to
determine the concentration and the average cluster size in sols undergoing
coagulation
Consider the IR spectra
of multiplex infringements of total internal reflection (ATR) of ortho-silicic
acid sols in the coagulation process at different initial concentration of
nanoparticles (figure 1). It is known that the clusters formed during the
coagulation of ortho-silicic acid sol [3, 4], composed of Si(OH)4.
The absorption peak in the spectral range (950-980) cm-1
characterizes the valence vibration of Si-OH.
IR spectra assay allows
to establish the relationship between the transmittance of infrared radiation
and the coagulation time of sols, which is expressed by the equation:
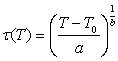 (3)
(3)
where a=2,236·10-3,
b=0,5 – some constants; T0 – a
constant depending only on the initial concentration of nanoparticles in the sol (with
Ñ0=8,992·1026 m-3 - Ò0=0,127; with
Ñ0=1,349·1027 m-3 - Ò0=0,072).
According
to these concepts, equations (1) and (2) with (3) allow to determine the
concentration and average size of nanoparticles in sols by IR spectroscopy at
different initial concentration of nanoparticles (figure 1 and 2).
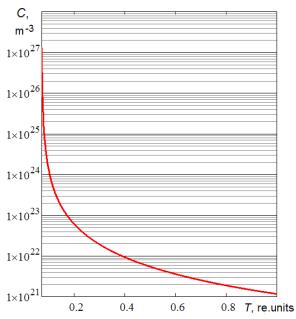
Figure
1. The dependence of the concentration clusters of
orthosilicic acid sol transmittance on infrared radiation (Ñ0=1,349·1027
m-3)
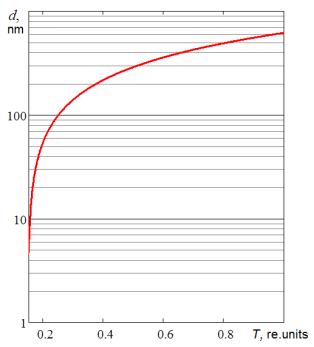
Figure
2. The dependence of the average size clusters of
orthosilicic acid sol transmittance on infrared radiation (Ñ0=1,349·1027
m-3)
Thus, this method [5]
allows to determine the average size and concentration of fractal aggregates
sols undergoing coagulation by IR spectroscopy.
This work is financially
supported by the Russian Ministry of Education, state task number 2014/151
(project 117).
References
[1]
Pronin I A and Goryacheva M V 2013 Surface and Coatings
Technology 235
835-840
[2]
Pronin I A Pronin
I A, Dimitrov D T, Krasteva L K, Papazova K I, Averin I A, Chanachev A S,
Bojinova A S, Georgieva A T, Yakushova N D, Mochnikov V A 2014 Sensors and
Actuators A 206 88-96
[3]
Moshnikov V A, Gracheva I E,
Kuznezov V V, Maximov A I, Karpova S S, Ponomareva A A 2010 J. Non-Cryst.
Solids 356 2020-2025
[4]
Krasteva L V, Dimitrov D T, Papazova
K I, Nikolaev N K, Pechkova T V, Moshnikov V A, Gracheva I E, Karpova S S,
Kaneva N V 2013 Semiconductors 47
586-591
[5]
Averin I A, Igoshina S E, Karmanov A A, Pechersky R M,
Pronin I A RU 2502980 C1