INFLUENCE
ESTERS ONTO PROPERTIES COLLAGEN CUTANEOUS COVERING
M.B.Shamsieva,
T.J.Kodirov, N.A.Sodikov
TASHKENT
INSTITUTE OF TEXTILE AND LIGHT INDUSTRY
Abstract
Synthesized esters
of fatty acids distilled cotton soap stock and fusel oil. Identified water
sorption properties of the original and processed collagen ester. It was found
that the reaction of the ester with the active groups of collagen are formed
strong chemical bonds.
Keywords: fatliquoring,
ester, sorption, collagen.
Fat liquoring is
one of the main processes of tanning manufacture, whereby changing the physical
and mechanical properties of the skin (strength, elongation, water
permeability, and others.) And maintain performance over a product.
Skin greasing fat
composition different consistence or aqueous emulsions of fats. Composition
Body composition and amount administered to the skin, as well as methods
defined fatliquoring views manufactured designated purpose skin and its
purpose.
The fat composition
consists at any rate vast majority of natural fats and oils, synthetic fatty
materials, and esterification products of fatty acid.
To expand the range
of fatliquoring materials for processing natural leather, the authors [1]
developed a new material fatliquoring. The starting material was used emulate,
a mixture of esters of oleic, linoleic and linolenic acids, as well as rosin
acids, and others. Emulate subjected to ethoxylation. The process introduced in
the autoclave at a temperature and pressure 130-140 0Ñ 2 atm. Based
on the processing of new material obtained fatliquoring leather with improved
physical and chemical indicators and pleasant to the touch neck.
Proposed [2] materials
based on derivatives of esters for the fatliquoring of leather, which are obtained
by reaction of esters with alcohols based Ñ8-72 and OH - groups
except glycerol or alkanediols with Ñ2-18 dimers or fatty alcohols
and monocarboxylic acids with C8-72 fatty acids with polyethylene
glycol Ñ8-24. Sulfitated primary products obtained by reaction with
concentrated sulfuric acid or diluted air with gaseous sulfur trioxide or a
combination of an organic sulfonic sulfuric acid.
Therefore,
researches on the development and application on the basis of a new series of
ester fatliquoring compositions which can be used for all kinds of fatliquoring
leather.
In accordance with
the objective of the study conducted by analysis of the products of organic
synthesis industry has shown that the bases for fattening materials are:
Distilled fatty acids cotton soap stock and fusel oil. To study different molar
ratios selected distilled fatty acids, such as oleic acid, isoamyl alcohol, to
vary the temperature and time of the reaction, the catalyst and the yield of
the ester.
The resulting ester
is a homogeneous pasty appearance, and odor, dark brown color, density ![]() = 0.878, insoluble in water, easily soluble in most organic
solvents with boiling point
= 0.878, insoluble in water, easily soluble in most organic
solvents with boiling point ![]() = 117oÑ. The main part of the ester consists of
saturated, 66.25% and 33.75% of unsaturated compounds.
= 117oÑ. The main part of the ester consists of
saturated, 66.25% and 33.75% of unsaturated compounds.
As the range of
fatliquoring materials and compositions proposed for use in the production of
skins for different purposes, increases the need for development of reliable
methods for assessing their plasticizing capability. In connection with this,
sorption studies were carried out with collagen ester.
Sorption studies
were performed on a high-vacuum apparatus with mercury closures and quartz
weights Mc Ben and BET. The measurements were performed at 25 °C and the
residual air pressure 10-3-10-4 Pa.
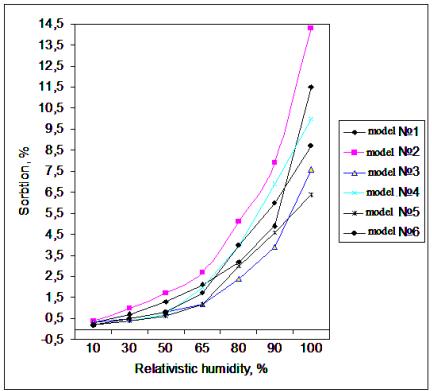
Fig. Sorption of water vapor
collagen sample (1) and introduced into collagen ester (2-6), 25 °C
temperature.
For an accurate
assessment of the size and distribution of pores conducted regression analysis
for each sample and plot were calculated and the value of the sum of squared
residuals, variance, the variance of the adequacy and standard deviation,
respectively.
Upon initial
degassing only is removed physically adsorbed water. In this regard, physical
isotherm curve is adsorption water to completely hydroxyl Ted sample [3].
The adsorption of
water on the fully hydroxyl Ted surface samples is mainly physical, although it
forms a hydrogen bond; at low pressures it is entirely reversible.
According to the
theory of Brinier, Emmett and Teller (BET) can assume the following
conclusions: in the adsorbent surface has a certain number of equivalent in
energy terms of active sites; each molecule of the previous layer is an active
center for the next adsorption of molecules adsorbed layer; reacting the
adsorbed molecules adjacent to the first and last layers are absent; may all
molecules in the second and more distant layers behave like molecules of the
liquid.
The studies found
that the reaction of the ester functional groups in the collagen are formed
mainly hydrogen bonds. As a result, it is partially deposited between the
fibers, and connects to the material of leather. Oiling is usually subjected to
wet skin, because in this state of leather fiber insulated water, more mobile
and better able to absorb the fat. In fat wet skin it penetrates more slowly
than in the dry, but it is distributed more evenly between the fibers. The
surface fibers enveloped in a film of fat which separates them and thus
prevents bonding upon evaporation of water during drying skins. Due to this,
after drying the skin remains flexible and elastic.
Introduction ester
fatliquoring composition allows obtaining a homogeneous mixture fatliquoring
which increase the viscosity grease mixtures. And also allows components to
communicate securely with the fibers of the dermis, the skin and provides a
high-strength property.
References:
1. LV Slobodskiy 03.09-12V.
128. The synthesis of new materials fattening. M., ed Ros-ZITLP. 2002, p. 13.
Table. 1 Eng. Abstract Journal. 2002. -¹9. - P.14.
2. Ya Pustylnik. 2B 174 P.
fatliquoring materials. Verwendung von Esterderivaten zur fettenden Ausrustung
von Leder: Request 19506099 Germany, MCI C 14 C 9/00 / Shenker Gilbert; Henkel
KG & A. -¹ 195.06.099.7; Stated 02.22.95; Publ. 29/08/96 Abstract Journal.
1998. -¹2. - P.15.
3. S. Greg K. Singh
Adsorption. Specific surface area. Porosity. 2nd ed. Moscow "MIR"
1984.