Economics/11.Logistics
dr.
sci. Pistunov I.M.
State
Higher Educational Institution “National Mining University”, Dnipro, Ukraine
Order Quantity Optimization
Economic activity of an enterprise may involve
concentration of major part of its financial resources in inventory holdings.
Inaccurate demand appraisal can cause conservation of firm's cash in the
inventory balance as well as inefficient warehouse usage. Therefore, effective
order planning is to become one of the most important issues for operation manager.
Optimal order quantity determination should be based on analysis of current
order plan with taking into account other factors, such as: season, storage
capacity, duration of delivery etc. Effective order quantity plan enables
enterprise to forecast firm’s financial indicators, to plan material and
technical foundation development, to project costs with remote in time income
and to build business relationships with customers and suppliers, banks and
other parties. Thus, none investor, creditor or bank would loan the enterprise
which cannot give a clear prediction of its financial condition for the period
up to repayment.
Wilson
EOQ Model
The classical Wilson EOQ Model
determines order quantity that minimizes the total holding costs and
ordering costs. The framework is limited when it comes to quantity discounts
and storage deficit. Assumptions of the model: demand quantity for the period
is known, order period is constant, unit shipment is instant. Optimal order
quantity is estimated by the formula:
![]()
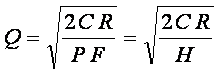 ,
,
where Q –
optimal order quantity, C – fixed
cost per order, R – demand quantity, P – purchase unit price, F
– interest rate, H – annual holding cost per unit.
Statistical
approach
Cumulative was build in order to distribute a whole
range of possible values of random variable observations on the d intervals. Interval's upper limit of a
random variable is estimated as:
dmax(i)
=xmin +(xmax – xmin)i/d,
where, i -
number of interval [1, d]; xmax,
xmin - the largest and the smallest value of a random variable in
the sample, respectively. Upper limit of interval i is also the lover limit (i + 1) interval. Lower limit for 1-st
area equal to xmin,
while upper limit of the last interval
is equal to - xmax.
Tentatively, the number of intervals or bins can be
defined as:
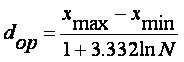 .
.
Offered
approach
The
optimal order quantity can
be estimated using the methods of economic-mathematical
modeling. Software package MS Office
Excel and its Solver add-on were used to implement set task for “UPK Invest Dnipro”.
Optimization problem will be set as follows:
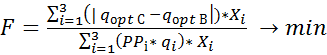 .
.
Constrains:
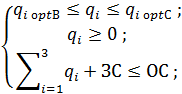
where OC–
warehouse capacity, ÇÑ –
remains of stock, qopt C -
optimal order quantity according to statistical method,
qopt B -
optimal order quantity according to Wilson EOQ model, Xi
- deficit matrix
of product i (1 - yes, 0 - no)
(matrix size 1x3), PÐi - profit on product i sales, qi - the optimal order quantity for product i.
To estimate the elements of the deficit matrix condition
"if" was used to automatically determine the need. For example, if
the remains of the composition is less than 1500 kilo or 25 bags, the order is
obligatory (Xi =1) .If
remains exceed 1500 kilo, the order is not required (Xi=0"). Provided that the calculation of order
requirement will be driven automatically, by means of MS Excel order
requirement is calculated as follows: =IF(Xi<150;1;0).
To implement this optimization model, it was decided to use the formula
"if" because of certain difficulties in MS Excel usage in practice,
so look for future models of its construction will be as follows:
![]() ,
,
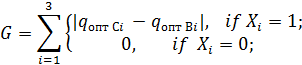
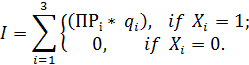
To calculate the lower limit of the optimum order
volume Wilson's model used, and the statistical method to determine the upper
limit. The main advantage of the proposed model is the possibility to choose
product to order (matrix needed) and composition taking into account.