Ёкономические науки/ 2. ¬нешнеэкономическа€ де€тельность
PhD,
Marekha
I.S.
Sumy State University, Ukraine
Global economic expansion of international
corporations
Choosing to pursue global economic
expansion is one of the most critical decisions made by many growth-hungry
corporations. There are a variety of factors that influence such decisions.
Here are some of the top reasons why corporations choose to expand
internationally [1]:
1. Global expansion remains a major driver of
revenue growth. Expanding into
foreign markets tends to enhance revenue growth while improving a companyТs
return on capital and reinvestment rate. Revenue growth from non-domestic
markets typically comes faster, while adding new revenue streams helps a
company to maintain security and stability.
2.
Businesses that expand internationally cultivate a broader customer base. In an era where global branding is
more critical than ever before, the acquisition of a wider customer base and a
broader brand footprint pays significant dividends. Additionally, companies
with an international presence can leverage their specific understanding of
global markets.
3.
Expansion is being driven by the desire to increase market share and open new
market. This
is particularly true for European companies, and for businesses in markets that
are underperforming economically. Companies can tap into higher profits and faster growth by entering overseas markets
with more favorable prevailing conditions.
4.
Expansion is frequently cost-saving strategy. Lowered production costs have long been a magnet for
international growth. Western companies are fully aware of the labor cost
savings they can achieve by outsourcing to China, India, Mexico, and several
Eastern European countries. A factory worker in the United States or Europe
typically costs between $15 and $30 per hour [2]. In contrast, a Chinese
factory work earns less than $1 per hour, giving China a fifteenfold to
thirtyfold advantage.†
5.
Companies are seeking what they canТt find at home. Companies
are using international expansion to fulfill needs unserved by their domestic
market.
6.
The takeaway. There
are some broadly-shared rationales driving most of todayТs expansions. These include
the desire to increase market share, lower costs, efforts to gain an edge on
competitors and access to untapped sources of skill, technology, and capital.
7.† International expansion is often a defensive
maneuver. Companies
can pursue overseas expansion as a counter to increased competition in their
own market. Companies are also prompted to pursue international growth as a
defensive tactic, gaining entry into potentially valuable markets before
competitors can do.
Global corporations are integrated via
M&A (mergers and acquisitions) mechanisms. A merger is a voluntary amalgamation of two firms on roughly equal
terms into one new legal entity [3]. An
acquisition is a corporate action in which a company buys most, if not all,
of another firmТs ownership stakes to assume control of it. An acquisition
occurs when a buying company obtains more than 50% ownership in a target
company [4].
Every day, Wall Street investment
bankers arrange M&A transactions, which bring separate companies together
to form larger ones. Two companies together are more valuable than two separate
companies. Strong companies act to buy other companies to create a more
competitive, cost efficient company. The companies will come together hoping to
gain a greater market share or to achieve greater efficiency. Because of these
potential benefits, target companies will often agree to be purchased when they
know they cannot survive alone.
†The reasons behind international mergers and
acquisitions are [5]:
1. Improving companyТs performance.
2. Removing excess capacity.
3. Accelerating growth.
4. Acquiring skills and technologies.
5. Encouraging competitive behavior.
†The field of mergers and acquisitions
continues to experience dramatic growth. †Without
question, many companies still use deals to achieve economies of scale and
improve efficiency. But increasingly, theyТre also trying to achieve
transformation. The number of reported M&A transactions and deal value worldwide
hit record levels in 2015 (Fig. 1).
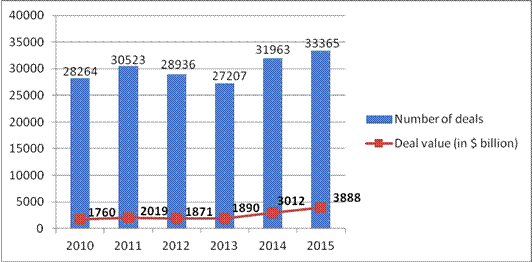
Figure 1. Global
M&A activity [6, 2]
International corporations use global
expansion to achieve economies of scale and improve efficiency. The enterprises
driving economic globalization tend to be the most economically potent: large,
fast growing, dynamic, and innovative.
References:
1. Top Reasons for Corporate Global
Expansion [≈лектронний ресурс]. Ц
–ежим доступу : http://www.ctcorporation.com/corpations.
2. Globalization Cost Advantage
[≈лектронний ресурс]. Ц –ежим доступу :
http://www.washingtontimes.com/news/2004/aug/23/20040823-084202-9845r/.†
3. Merger : Definition and Meaning [≈лектронний ресурс]. Ц
–ежим доступу : http://www.businessdictionary.com/definition/merger.html.
4. Acquisition [≈лектронний ресурс]. Ц
–ежим доступу : †http://www.investopedia.com/terms/a/acquisition.asp#ixzz4mWVyguSL.
5. Different Types of Mergers and
Acquisitions [≈лектронний ресурс]. Ц
–ежим доступу : https://www.cleverism.com/different-types-of-mergers-and-acquisitions-ma/.
6. M&A
Report. Ц Wilmer Cutler Pickering Hale and Dorr LLP, 2016. Ц 20 p.