Ph.D., docent Zaenchkovskiy,
A.E., graduate student Kirillova E.A.
Smolensk Branch of "National Research
University" "MEI"
Logistic approach in innovation practice on nuclear energy enterprises
Integrated information technologies used on nuclear energy enterprises,
in some cases allow for support of the innovation process within a single
enterprise, so supporting all stages of innovation at the level of the business
entity although they are relevant, but do not have an adequate level of support
and development. Also methodological aspects of creating virtual elements of
innovation infrastructure and the integration of these elements into a single
virtual innovation and information network is almost little explored in
practice. Practical issues of informatization innovation add up to designing
and operating portals and thematic databases whose function is mainly to
provide limited information about advertising innovation infrastructure and
innovation. It identifies the need for significant adjustment procedures to
support innovative interactions in individual scientific and industrial
complexes and holdings, and in the more general framework of associations,
including the establishment of high schools, research organizations and
infrastructural support [1].
At the same time nuclear energy is a specific type of
economic activity, having the following features:
- «fuel and raw material resource base - directly energy production -
management of radioactive waste» constitute a single complex;
- investment policy of the nuclear industry and implemented targeted
programs to ensure stabilization, safety, efficiency and accretion update
existing capacity, as well as the development, improvement of nuclear fuel
resources and facilities for the processing and disposal of nuclear reactions;
- prepare for and implementation of further cost-effective and high-tech
projects and energy complexes, which correspond to the current level of
reliability and security, including innovative technologies;
- potential market entry of thermal energy and its subsequent development
for the social sphere with the substitution of other sources of heat
production.
Today, when the Russian market is actively developing
the nuclear industry is not enough to use the legacy of the past, focusing on
extensive production with high costs, excess inventory and increase in staff
workers. Stiff competition dictates its terms, forcing enterprises to take
urgent measures that will enable them to not only survive, but also to work
effectively in the market. Efficacy and safety of work will depend on the
development of an innovative component of the nuclear industry.
In view of the above, it will be actual to use
logistic approach to managing innovation on nuclear energy enterprise. The main
idea of this approach will be to present the process of generation and
commercialization of innovation and accompanying it as a model of flow
processes [2]. At the same time the management of innovation and innovative
market performed using logistic tools capable of providing the required
managerial influence and analytical support regional targeted program of IT
development. In particular, areas such as production logistics, transportation
and distribution logistics, service management, able to function in ways to
reduce costs, identify underutilized reserves and their implementation,
determining the level of development and market readiness subsystems to the
transformations of the optimization, etc. for innovation aspect of
macroeconomic subject.
In the field of logistics management innovation
becomes scientific instruments with which various manufacturers to develop
high-tech products based programs development based on market dynamics.
Consider the types of processes which can be subject to logistic management in
innovative enterprises or industrial holding (Figure 1). External financing of
innovation implies that attraction and use of state funds, financial
organizations, individuals and non-financial organizations located outside the
region. Forms of external financing may be different: government funding, the
use of bank loans, financing through leasing and other external staffing sphere
of innovation involves systematizing processes to find and attract innovators
and staff with expertise in the organization and management in the field of
innovation for outside the region, which will achieve a new quality of
innovation and increase on this basis, the share of innovative products and
competitive. External logistics innovation resources will reduce their specific
share and / or the cost of innovation in the final decision, thereby increasing
its competitiveness. Systematization, regularization and ordering target incentives and the
promotion of innovation , coupled with the development of intra-regional human
capital will contribute to achieving the status of sustainable production
innovation, which will consider the innovation cycle within the region as regenerative
itself process that can be subjected in logistics management. Typing tasks and
optimizing processes and flows of diffusion of innovation in foreign markets
(marketing, external design, service, etc.) have already included a number of
specific elements of the marketing mix (product versions, features in its
promotion , environment, distribution channels and price , etc. etc.), and some
of them have a solution with a set of logistics techniques (the problem of
destination, traveling salesman problem, etc.).
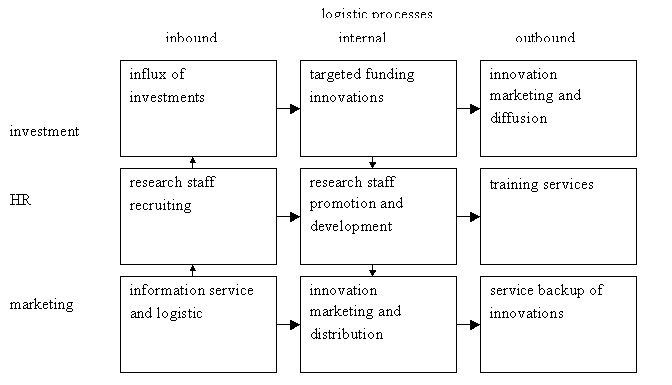

Fig. 1 – Logistic processes in nuclear
energy enterprises
Another common logistics process, which can be used on such enterprises is an assessment of the
effectiveness of management decisions, when the limitation in terms of deficit
specialists able to carry out a systematic analysis, the absence or
unavailability of information about the organization (especially in the
analysis of innovative potential competitors) make use common diagnostic
approaches decision management innovation process at the regional level as well
as in a separate economic entity, which are realized through the analysis and
the limited options available for both internal and external analysts circle
parameters.
In
general, the diagnostic parameters characterizing symptoms in the framework of
this innovative subsystem will be the input and output parameters of the
system. Input parameters can be quantitative functioning innovation sphere (number
of innovative organizations, the volume of innovative products and services,
etc.); output parameters: duration of the innovative projects (duration of the
phases of the innovation cycle), the amount of released product innovation, the
quality of this product and its relevance to foreign markets, etc.
The
internal state of the system, information about which is much more difficult to
obtain structural parameters described. In turn, the parameters are divided
into structural and functional resource. Resource parameters characterize the
structural deterioration (physical and moral), aging, residual power supply
resources (labor, material, technical, information, financial) and organizational
resources (technology, methods, organizational structure). Functional
structural parameters characterize rationality, the efficiency of the system
with respect to the use of resources and institutional capacities, as well as
to the control action.
In conclusion, we
note that the conceptual proposals for innovative infrastructure nuclear energy
enterprise on logistic approach can be used as an evidence-based guidance
material not only directly but subjects of innovation and specialized
authorities in the development and implementation of strategic activities in
innovation with the main trends of socio-economic development.
References:
1.
Babkina O.N. Development of regional
economy based on innovation // Young scientist. 2011. ¹4. Ò.1. - Ñ. 135-136.
2.
Gonchar K.B. Industry Innovations:
design can not borrow // Problems of Economics. – 2009. - ¹9.