Mathematics 4/Applied mathematics
Askanbaeva G.B.
Kostanay state university named after Akhmet
Baitursynov, Kazakhstan
Unitary
spaces
We are
given a complex linear space ![]() . In this space the operation of scalar multiplication of
vectors is determined if any pair of x and y vectors of
. In this space the operation of scalar multiplication of
vectors is determined if any pair of x and y vectors of ![]() space are corresponded by complex numbers called dot
product and labelled by
space are corresponded by complex numbers called dot
product and labelled by ![]() symbols, and
if for any x, y, z of
symbols, and
if for any x, y, z of ![]() space and for
any α complex number the following axioms are satisfied:
space and for
any α complex number the following axioms are satisfied:
1.
![]()
2.
![]()
3.
![]()
4.
![]() if
if ![]() ; and
; and ![]() if
if ![]()
Definition: A complex n-dimensional linear space, with
fulfilled operation of scalar multiplication of vectors, is called n-dimensional unitary space and marked
by ![]() .
.
In first, second and third axioms of scalar multiplication
of vectors we can see that
![]() (1)
(1) ![]() (2)
(2)
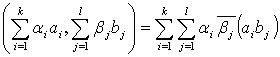 (3)
(3)
If in ![]() unitary space
unitary space ![]() basis is fixed, then vectors x
and y decompose into
basis is fixed, then vectors x
and y decompose into
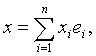
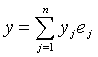 , òî
, òî 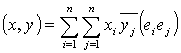
or in a matrix notation
![]()
where it is defined that
![]()
![]()
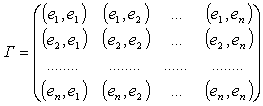 - Gram matrix
- Gram matrix
As (ei, ej)
= (ej, ei), Gram matrix satisfies the condition
![]() (4)
(4)
The star (*) denotes the transposition of matrix with
the change of elements into complex conjugates. [1]
Definition: ![]() matrix is
conjugate to matrix
matrix is
conjugate to matrix ![]() . If
. If ![]() , then matrix
, then matrix ![]() is called
Hermitian matrix. According to the condition (4), it is Gram-Hermitian matrix.
If matrix
is called
Hermitian matrix. According to the condition (4), it is Gram-Hermitian matrix.
If matrix ![]() is real, then
is real, then ![]() .
.
In a unitary space, as well as in Euclidean one,
vector length is defined by the formulation
![]() (5)
(5)
As a rule, the notion of angle between vectors in a
unitary space is not used. It is considered to be vector orthogonality or the
orthogonal property of vectors. In this case, as well as in Euclidean,
orthogonal vectors are those x and y ones which satisfy the condition (x, y) =
0.
The formulation of scalar product is as follows
![]() (6)
(6)
but for a scalar square it turns into
![]() (7)
(7)
These formulations constantly used for solving tasks
in a unitary space.
Definition: A square matrix ![]() , with the conjugate matrix
, with the conjugate matrix ![]() , is called a unitary matrix. In other words, a square
matrix
, is called a unitary matrix. In other words, a square
matrix ![]() will be unitary if
will be unitary if
![]()
In a unitary matrix columns (rows) represent the
orthonormal system of columns (rows). The product of the unitary matrix is a
unitary matrix. A unitary matrix also possesses other important qualities. The
crucial thing is that the very main matrix of changing from one orthonormal
basis of a unitary space to the other orthonormal basis is the unitary matrix.
It is obvious that a real unitary matrix is an orthogonal one. [3]
Literature:
1. Øåâöîâ Ã.Ñ.
Ëèíåéíàÿ àëãåáðà.- Ì.: Ãàðäàðèêè, 1999.-359ñ.
2. Âîåâîäèí
Â.Â. Ëèíåéíàÿ àëãåáðà. Ì.:Íàóêà, 1974.-314ñ.
3. Ãåëüôàíä È.Ì. Ëåêöèè ïî ëèíåéíîé àëãåáðå.-Ì,
Íàóêà, 1971.-71ñ.