Karachun V.V, Mel’niñk V. N.
National Technical University
of Ukraine «KPI»
THE
GYROSCOPIC REAKTION IN ROTOR`S SIREN
Efficiency of rotary pneumatic siren work determines mainly by available minimum distance between planes of rotor and stator. For real structures this value is
3·10-5 – 7·10-5 m. In these conditions most
accurately reproduces the modulation function and,
accordingly, the desired spectrum of radiation.
However, as it turned out, static and dynamic
balancing of fast-revolving rotor
as essential at the work does not prevent the
emergence of disparity and smoothing-out of
surfaces of disks with inevitable
further development of this phenomenon. The implications are obvious -
excessive increases of unsustainable consumption of air and bending of form
of modulation function.
Let is find out the nature
of emerging effect. Rotary pneumatic siren is
on rolling basis, ie on the surface of the Earth, which has angular velocity of daily rotation (fig. 1)
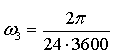 rad sec-1.
rad sec-1.

Axis of rotation of the rotor, for example, forms with meridian line an angle
ψ (yaw angle). Quickly rotating heavy rotor
of siren is a system with two degrees
of freedom. One realizes with its own rotational movement around its axis of geometry and angular symmetrywith angular velocity ![]() , the
other – rotation of lead shaft together with planted on him rotor around the axis, perpendicular to the axis of
the shaft by the amount proportional to the radial play Δ of bearings.
, the
other – rotation of lead shaft together with planted on him rotor around the axis, perpendicular to the axis of
the shaft by the amount proportional to the radial play Δ of bearings.
Availability of vertical
component
ω1 of angular velocity of daily rotation of the
Earth (|ω1| = ωÇsinφ, where φ - latitude of place) results in an gyroscopic
moment
![]() ,where I - axial moment of inertia of the rotor and the shaft with bearings, which tries to establish axis
of its own rotation of rotor of siren parallel to the vector
,where I - axial moment of inertia of the rotor and the shaft with bearings, which tries to establish axis
of its own rotation of rotor of siren parallel to the vector ![]() (fig. 1). Therefore, under the
influence of gyroscopic moment the rotor will take a new position (dotted
line), variations in the vertical plane to an angle α from the original.
(fig. 1). Therefore, under the
influence of gyroscopic moment the rotor will take a new position (dotted
line), variations in the vertical plane to an angle α from the original.
Due to the appointed,
the rotor bearings will feel extra pressure ![]() . According to the third Newton law, bearing reaction to
this pressure will make in value and be opposite
in direction to gyroscopic pressure. It
is absolutely clear the equality of gyroscopic moment
. According to the third Newton law, bearing reaction to
this pressure will make in value and be opposite
in direction to gyroscopic pressure. It
is absolutely clear the equality of gyroscopic moment ![]() and moment of bearing reaction
and moment of bearing reaction ![]() , ie
, ie ![]() (fig.2).
(fig.2).
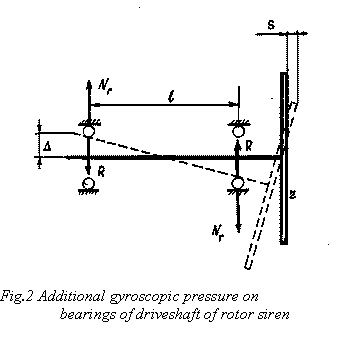
So, it will occur delay of disc of rotor and
stator. In addition, it will decrease cosα times the effective
area of windows of siren
and thus increase nonproductive expenditure fmin of air flow, resulting in reduce of level of generic aerodynamic noise for value
ΔP = 20lg (1 – fmin/fmax), dB.
It is clear that
the modulationfunction will also
change.
If the gap between the rotor and stator disks
missing, then f=0 at the closed windows. And f=fmax=f0 with open windows (f0 - air flow in the absence of gap between discs with
open windows).
To improve the quality of reproduction of
aerodynamic noise, and thus reduce unproductive expenditures of aur and
increase service life of siren, it can be as one of the options, to enter the
automatic correction of the initial minimum distance between the ends of the
vertical diameters of discs of rotor and stator. When regulating siren, the
clearance between the rotor and stator disks is about 0,03-0,07 mm.
Revibration
camera, with the siren, is
beong installed in the horizontal tilting platform, mechanically
connected to the shaft of engine which control winding is
connected to a specified latitude
and differential amplifier, connected to the sensor of non-destructive testing. Usung signal of latitude setting device, the engine provides the driving
motion to the platform around the
vertical of a place with
angular velocity
ω'1 = - ωÇsinφ,
compensating thereby influence of the vertical component of angular
velocity of daily rotary motion of the Earth. Using signals of sensors of non-destructive
testing through differential amplifier receives additional stress on the
control winding of engine
which is proportional to existing inequalitie between the ends of the vertical diameters of the
rotor and stator. The appearance of additional speed ![]() of platform will serve as expression gyroscopic moment
of platform will serve as expression gyroscopic moment
![]() ,
,
thus, the disc of rotor of siren takes the position along the stator disk
plane (to appear equal distances between the ends of the vertical diameters).
To avoid cross-impact of angular velocities, a platform should be always
horizontal.
Therefore, on the index of work quality of rotor siren influence kinematic excitation of the basics,
including speed of daily movement of the Earth. The analysis of phenomena shows
that neglecting this influence is
unacceptable. Hence appears the need of monitoring and
electrodynamic regulatation of some parameters of rotor siren
not only in its static state in retrain period (static and dynamic balancing), but always during its work. Offered
solution can avoid this drawback.
Summarizing it should be drawn attention on the fact that when axis of own rotation of rotor of siren
does not coincide with the meridian line at the angle ψ, component of angular velocity of daily rotation of the Earth
ω″2 = ωÇcosφsinψ,
which points to the west, will also serve as the emergence of gyroscopic
reaction and forced movement of the rotor (fig. 3). Obviously, the component
ω′2 = ωÇcosφcosψ,
which is parallel to the vector of kinetic moment of the
rotor will not affect the dynamics of siren (with a small yawn).
 Beyond the focus is still the analysis of kinematic effects (oscilation) and power (vibration) excitation of the
foundation. Certainly this influence is sufficiently significant, but doesn’t serve the purpose of data research.
Beyond the focus is still the analysis of kinematic effects (oscilation) and power (vibration) excitation of the
foundation. Certainly this influence is sufficiently significant, but doesn’t serve the purpose of data research.
So, joining
together the rotor axis with meridian line,
you can completely eliminate the influence of the horizontal component ω2 of Earth's
rotation on work of rotor siren. If to orient the axis of rotation of rotor parallel to the line WE (West-East), the impact of
cross-component of angular velocity of Earth is
the maximum.