Òåõíè÷åñêèå íàóêè/5.Ýíåðãåòèêà
Engineering science
candidate Biryulin V.I. , engineering science candidate Khoroshilov
N.V., engineering science candidate Larin O.M., engineering science candidate Sergeev S.A., teacher Gorlov
A.N.
South West State University, Kursk,
Russia
Teacher Gorlova Y.S.
Industrial institute, Economic-computer technical secondary
school, Kursk, Russia
The basic problems in the field of manufacture and
consumption
of electric power in the Russian Federation
In the article manufacture and
current consumption questions in the Russian Federation are considered.
Keywords: fuel and energy
complex, power resources, consumer
During the last years domestic economy power
consumption has increased on 46 % at the average power resources expenses for
metal manufacture and other base power-intensive production have increased on
30 %. Electric power losses in a network of the general using have grown to 130
billion in kilowatt/h per
annum or to 13,5 % from output volume. At the same time each saving percent of
power resources provides the national income growth on 0,
35-0,5 % [1].
Principal deterioration causes of power use are
industrial production recession, deterioration of the energy-requiring and
power making equipment which has reached 60–70 %. Constantly the cost share of
power resources is growing in expenses structure for production.
To 40 % of all energy carriers used in the country it is spent
irrationally either in the form of real losses or in economy which doesn't give
concrete useful effect at the consumer burdening an account part of all levels
budgets.
During the last years power consumption growth of domestic economy
corresponds to unproductive consumption of 400 million tons of conditional fuel
per annum. Per unit of output production in Russia it is spent energy in 2,5
times more than in the USA in 3 times more than in Western Europe countries. As
a rule the industrial output is noncompetitive and many kinds of the most
power-intensive production are laid off. Present level preservation of power
consumption of industrial production encourages unlimited import of consumer
goods and raw materials export finally.
In
connection with the general production slump in Russia negative changes have
occurred during last 8 years and in branches of fuel-energy complex (FEC).
Untimely non-payments for fuel and energy have caused an investment crisis in
fuel-energy complex (FEC) having excluded almost budgetary sources of capital
investments completely. In connection with it natural leaving capacities in FEC
branches isn’t compensated the capacities’ design resource advances input of
new capacities in electric power industry in several times, financial
possibilities allow to support operating fixed capital hardly. Since 1999
advancing growth of power consumption in comparison with a capacity growth is
observed. The consumption volume and demand projection for the electric power
is shown in figure 1 [2].
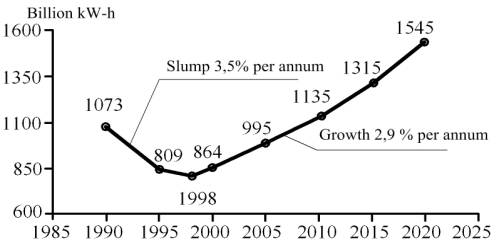
Figure 1. The consumption volume and demand projection for the electric
power in Russia
Now the
Russian industry and the country population has deficit of the electric power. Deficit of the electric power is characterized by
following factors: a lack of generating capacities in peak loadings and
connection refusals of new consumers.
With
the crisis phenomena stabilization view in power supply of the Russian economy
and social sphere the state document «Power strategy of Russia over the period
to 2020» has been developed.
Power
strategy is guided by the forecast of long-term development of the country with
increase rates of 5 % a year and increase in a total internal product (gross
national product) in comparison with 1998 not less than in times (see figure 2)
[2].
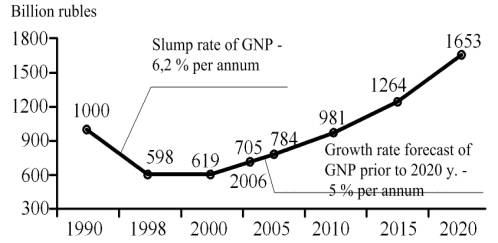
Figure 2. Dynamics of the Russian Gross national product
In
order to FEC were provided with resources with a predicted level of economy
development it is necessary on the one hand to provide growth of manufacture
and deliveries to home market of power resources and with another – it is
essential to raise efficiency of their use and carry out active power saving up
to the policy.
The
performed calculations within the work limits over power strategy show that
three quarters of power consumption
necessary growth can and should be
compensated by rigid administrative measures (standards, power supervision,
power audit), modernization and structural reorganization of the economy
expressed in share growth of hi-tech branches and manufactures and also
services’ spheres (see figure 3) [2].
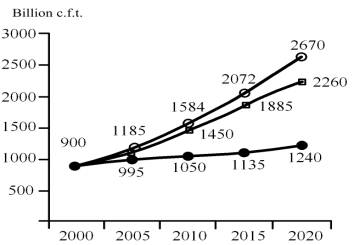
Figure 3. Fuel and energy resources requirement of a power saving up
policy by variants
The
power savings potential of the Russian economy is defined by three following
basic components:
1.
Specific power consumption decrease of economy in connection with improvement
of use of available industrial potential and relative decrease in power inputs
at gross national product growth. This factor will prove at the decrease
expense in specific power expenses at additional load of available capacities.
Mainly this factor operated at the first stage, in 2000-2005.
2. In
power consumption decrease of economy in connection with its structural
transformations expressed in increase of a share of (little) consumed services
in structure of gross national product and power saving up transformations of
industrial production structure. As a result the specified power-consuming
industries share to the end of the period should decrease 2005-2010 from 45, 5
to 34, 9 % and not power-intensive – to increase from 36, 0 to 43, 7 %.
3. Technological power savings. The power savings
potential which the national economy has, realized at the expense of highly
effective technologies use and organizational actions (first of all at the
industrial enterprises) is estimated by power strategy in 45–50 % from all annual
volume of internal power consumption in Russia.
Prescribe
1.
Power efficiency in Russia: the latent reserve [Text]: the report / World Bank,
the International financial corporation and CANAF, 2008.
2.
Mastepanov, A.M., Power strategy aspects of Russia [Text]/A.M. Mastepanov
//Power efficiency. 2001. ¹3. p.15 – 23.