Kussainova A., Ondybaóeva S.B., Bulgakovà O.V.
L.N.Gumilyov Eurasian National
University
The
polymorphisms of DNA reparation genes -XRCC1 and XRCC3 in the Kazakhstan population.
Lung cancer ( LC
) is a leader in the structure of cancer incidence of men, who suffer from it
almost 7 times more likely than women . According to the International Agency
for Research on Cancer, in the world each year nearly 1 million new cases of
lung cancer registered, 60 % of cancer patients die from this disease.
The main causes
of carcinogenesis is a failure in the control of processes of proliferation,
DNA reparation, apoptosis and detoxification of carcinogens, not only due to
genetic and epigenetic disorders, but also caused by the variability of gene
function due to genetic polymorphism.
There are several
genetic polymorphisms in genes whose products are involved in DNA reparation
mechanisms. XRCC1 enzyme plays a key role in the excision repairtion of DNA.
Actually described
three encoding polymorphisms of gene XRCC1 in the codons 194 (Arg to Trp), 280
(Arg to His), and 399 (Arg to Gln). Arg399Gln polymorphism of 10th exon affects
its central domain, which is required to activate the BER (base excision
repair). There is evidence that this polymorphism is associated with lung
cancer risk , but an analysis of published data showed quite contradictory
results about polymorphism Arg399Gln and its association with lung cancer .
As for
polymorphisms Arg194Trp and Arg280His, there was no association with lung
cancer risk in European population . Wang and others carried out 30 studies of
polymorphism XRCC1 Arg399Gln in form of case-control studies and 16 studies of
polymorphisms Arg194Trp. Their results showed that the specific XRCC1 codons
399 and 194 may affect the predisposition to lung cancer.
In the process of
reparation of double-strand DNA breaks and recombination of DNA reparation is
likely involved XRCC3. DNA double strand breaks - the most common form of DNA
damage caused by radiation exposure, reparation is possible by means of two
mechanisms - reparation by homologous recombination (HRR - homologous
recombination repair) and reparation of non-homologous end (non-homologous
end-joining). HRR mechanism consists at least of 16 protein components,
including XRCC3. Polymorphism of XRCC3 in exon 7 leads to the replacement of an
amino acid at codon 241 (Thr241Met), which may affect the function of the
enzyme and/or interaction with other proteins involved in the reparation
process of DNA damages. In many literary sources mention a significant
reduction in the risk of lung cancer in the European population for carriers of
polymorphism XRCC3 T241M. However, studies of this polymorphism conducted in Asian
populations revealed no significant association between the XRCC3 T241M and the
development of lung cancer. It can be assumed that the inconsistency of these
results may be due to differences in ethnicity, lifestyle and spread of the
disease. In connection with the above, we set a goal - to study population
characteristics of DNA reparation genes polymorphisms (XRCC1 and XRCC3) in the Kazakhstan
population of healthy people, chosen as a control group for the study of the
role of polymorphisms of genes XRCC1 and XRCC3 in the pathogenesis of lung
cancer.
The study
included 70 volunteers without lung pathology. Of all the surveyed 73% were
males, 27 % - females, the age range was from 42 to 80 years (60,2 ± 8,6
years).
Genomic DNA was
isolated from whole venous blood, followed by phenol- chloroform extraction (
K. Davis , 1990).
Evaluation of genes
polymorphisms was performed by PCR and PCR - RFLP analysis (conditions see in
Table 1). Visualization of PCR - RFLP reaction was conducted by gel
electrophoresis. The amplification or restriction products were analyzed in
agarose or polyacrylamide gel. 2% agarose gel was used.
Table 1. Analysis conditions of
locus polymorphism of studied genes
|
Gene |
Sequence of primers |
Annealing temperature (°C) |
Restriction enzymes |
|
XRCC1 Arg194Trp |
5´GCCCCGTCCCAGGTA3´, 5´AGCCCCAAGACCCTTT3´ |
57 |
PvuII |
|
XRCC1 Arg399Gln |
5´CAAGTACAGCCAGGTCCTAG3´,
5´CCTTCCCTCACTGGAGTAC-3´ |
55 |
NciI |
|
XRCC3 Thr241Met |
5´GCCTGGTGGTCATCGACTC3´ R 5´ACAGGGCTCTGGAAGGCACT GCTCAGCTCACGCACC-3´ |
60 |
NcoI |
The genotype
frequencies of gene XRCC1 Arg194Trp in the kazakh population was as follows:
homozygous carriers of the normal allele Arg/Arg accounted for 73% of the total
(51/70), the heterozygote Arg/Trp 16% (11/70), and homozygous for the mutant
allele Trp/Trp 11% (8/70), respectively. Thus, these data suggest the
prevalence of normal variant alleles Arg/Arg in the control group represented
by healthy people without lung pathology. Figure 1 shows the results of
PCR-RFLP analysis of XRCC1 Arg194Trp polymorphism.
500
b.p 1
2 3 4 5
6 7 8 9 10
![]()
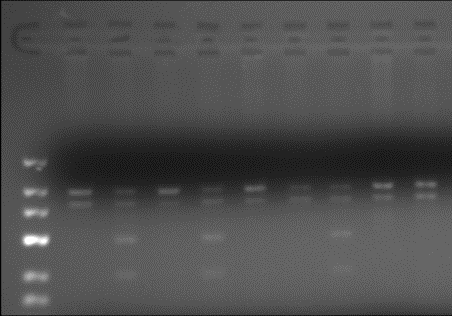
Figure 1 - Examples of
identification of genotypes in the gene XRCC1
Arg194Trp
The tracks 3,5,8 are
heterozygous variant Arg / Trp (fragment length after restriction 490/294/196
b.p.).
In the case of
polymorphism of XRCC1 Arg399Gln homozygous carriers of the normal allele Arg/Arg
accounted for 37 % of the total (26/70), heterozygous Arg/Gln 26% (18/70), and
homozygous for the mutant allele Gln/Gln 37% (26/70), respectively.
Thus, in the
control group of healthy individuals was equal to the number of carriers of
both normal alleles Arg/Arg, and mutant alleles Gln/Gln.
In the Kazakhstan
population are homozygous carriers of the normal allele XRCC3 Trp/Trp is 26% of
the total (18/70) , heterozygous Trp/Met 72% (50/70), and homozygous for the
mutant allele Met/Met 2% (2/70). These data suggest the prevalence of heterozygous
variant allele Trp/Met in the control group represented by healthy people
without lung patholog .
Figure 2 shows
the results of PCR-RFLP analysis of the polymorphism of XRCC3 Thr241Met.
200
b.p
![]()
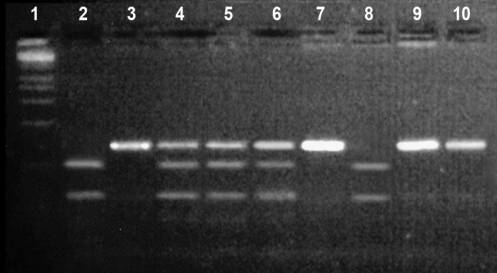
Figure 2 - Examples of identification of genotypes in
the gene XRCC3 Thr241Met
Tracks 2, 8 are homozygous mutant variant Met/Met (fragment length after
restriction 97/39 b.p.); 3,7,9,10 tracks - homozygous normal allele Trp/Trp
(136 b.p.); tracks 4,5,6 - heterozygous allele Trp/Met (fragment length after restriction
136/97/39 b.p.)