INFLUENCE OF GADOLINIUM TO PROPERTIES OF
STRUCTURES
OF METAL-GLASS-SEMICONDUCTOR
Bobokhujaev
Ê.U., Nazyrov D.E., Vlasov S.I.
Kuchkarov B.H.
National University of Uzbekistan, Tashkent
The purpose given
work is a study of the influence gadolinium on the generation-recombination
performances features of the structures metal-glass semiconductor. The doping
by gadolinium was carried out by a diffusive at 12000Ñ within 5 clocks from raising
dusting on a surface of silicon SEP-15 of metal gadolinium. For fabrication of the test structures was
used glass of the type Pb0-SiO2-B203-Al203-Ta205
(Pb0-52%, SiO2-29%, B203-12%, Al203-6%
Ta205-1%), inflicted on surface silicon (SEP-15 with crystallography
orientation <111>) from powder,
with the following heating (T=6800C)
As main method of the study was used method of high -frequency C-V features [1]
and relaxation under constant temperature of capacities of the structures metal-glass semiconductor, in process of
the increasing the charge of inversion layer
[2].
It is discovered,
that high-frequency (150 kHz) the volt-farad performances of structures with an
impurity of gadolinium are displaced in field of negative voltages in
comparison with control structures. Such
behaviour of the Ñ-V features to point to forming the
additional positive charge on border of the section semiconductor insulator [3].
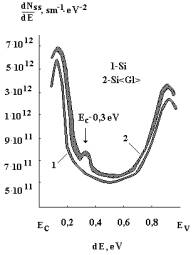
The distribution of the density of the surface states
over the bandgap of silicon for control
(1) structures and for structures with admixture of gadolinium (2) is shown on figure 1. It was used on 5 structures in each event. From brought figure is
seen that in structure with admixture gadolinium density of the surface
conditions more. In all structures with gadolinium the local maximum of density
of surface states in around of energy EÑ-0,35 eV is watched.
According to commonly accepted notions, the formation of maxima in
spectrum of density of surface states is related to impurity centers localized
in the space charge region of the semiconductor. Presence defect centre in
approach borders of the section semiconductor-glass must bring about increase
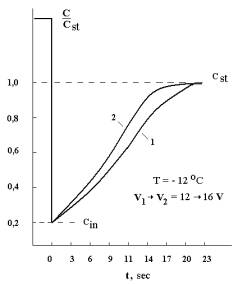
the velocities to surface heat generation of the carriers of the charge. On figure
2 are shown temporary dependencies of relaxations of capacities control (1)
structure and structure with admixture gadolinium (2). Broughted dependencies
were measured at a
frequency of 150 kHz and temperature -12 0C, after switching the voltage from 12 to 16 volts. From brought figure is seen that velocity relaxations of capacities
for structures with admixture gadolinium more than for control structures.
|
|
|
Fig.1. The
distribution of the density of the surface states over the bandgap of silicon for control (1) structures and for
structures with admixture of gadolinium (2). |
|
|
|
Fig. 2. Temporary dependencies of relaxations of
capacities control (1) structure and structure with admixture gadolinium (2). |
Based on above results, it possible do following conclusion. Modification on
spectrum of density of surface states in structures with impurity of gadolinium
is caused by localized of electrically active impurity centers in the
semiconductor near to the silicon-glass
interface.
References
[1]. L.S. Berman and A.A. Lebedev.
Deep-level transient spectroscopy of semiconductors. Nauka. Leningrad. 1981. [2]. M.Zerbst. Z. Angew. Phys.
V.22, P.3039, 1966. [3]. S. Sze. Physics
of semiconductor devices. Wiley, New York. 1984.