Alibekova A.R, Agilbaeva M.J
Ecological problems of thermal
power plants.
Three «E» characterizes
the modern period of human development: energy, economics, and ecology. Energy
in this series has a special place. It is decisive for the economy and for the
environment. From it depends crucially on the economic potential and well-being
of people. She has the strongest impact on the environment, ecosystems and the
biosphere as a whole. The most acute environmental problems (climate change,
acid rain, general pollution and others) directly or indirectly related to the
production or energy use. Energy primacy belongs not only to the chemical, but
also in other types of pollution: heat, aerosol, electromagnetic and
radioactive. Therefore, it is no exaggeration to say that from the solution of
energy problems depends on the possibility of solving major environmental
problems. Energy - it is the branch of production, which develops an
unprecedentedly rapid pace. If the population in today's boomers doubles in
40-50 years, the production and consumption of energy that happens every 12-15 years.
At that rate of population growth and energy, power- avalanche increases not
only in cumulative terms, but also in per capita terms.
TPP produce electricity
(up to 75% of total electricity production of the world) and thermal energy,
with all the material mass of the fuel has converted into waste entering the
environment in the form of gaseous and particulate combustion products (Fig.
1). These wastes time (the combustion gas 5, when burning anthracite 4 times)
greater than the mass of fuel consumed. Released into the environment
combustion determined by the type and quality of fuel, as well as by its
combustion. Currently, about 70% of total electricity production TPP provided
condensing power.
All the thermal energy of the world annually emits Earth more than 200
million tons of carbon dioxide, more than 50 million tons of various
hydrocarbons, nearly 150 million of sulfur dioxide, more than 50 million tons
of nitrogen oxide, 250 million tons of fine aerosols. No one doubts that this
"activity" thermal power contributes significantly to the imbalance
of steady circular processes in the biosphere, which began to manifest itself
more clearly in recent years. Imbalance is marked not only harmful substances
(oxides of sulfur and nitrogen), but also for carbon dioxide. This imbalance
include increasing energy production based on fossil fuels may, as many now
believe, in the long term lead to significant environmental consequences for
the entire planet.
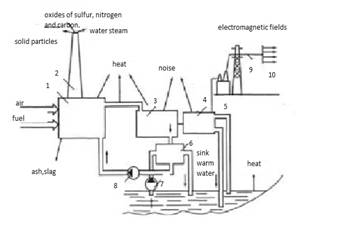
Fig. 1. Effect of TPP on the environment:
1 - boiler,
2 - smoke pipe 3 - turbine 4 - generator 5 - substation, 6 - condenser 7 -
condensate pump, 8 - feed pump 9 - transmission line, 10 - electricity
consumers.
The process of the production of electricity at
thermal power plants also accompanies the emergence of various polluting
effluents associated with the process water treatment, conservation and washing
equipment, hydraulic transport evils slag waste, etc. These wastewater
discharges into water bodies with detrimental impact on their flora and fauna.
The establishment of the closed water systems this effect has reduced or
eliminated.
Large amount of water used in various TPP heat
exchangers for condensing exhaust steam, water, oil, gas and air-cooling. For
this purpose, water has abstracted from a surface source and ramjet circuit
after use in these devices has returned to the same sources. This makes the
water in the pond is used a lot of heat and creates a so-called thermal
pollution it. This kind of pollution affects the biological and chemical
processes, that determine the livelihoods of plants and animals, that inhabit
the natural reservoirs, and often leads to their death, intense evaporation of
water from the surface of reservoirs, changes in hydrological flow characteristics,
increases the solubility of the rocks in the boxes of reservoirs, the
deterioration of their health state and climate change in some areas.
The main sources of water pollution are thermal
turbine condensers. Among them has given approximately half to two thirds of
the total quantity of heat obtained from the combustion of fossil fuel, which
is equivalent to 35-40% of the energy of the fuel used.
Serious environmental problems associated with solid
waste TPP - ash and slag. Although ash has collected in bulk various filters,
yet the atmosphere as emissions TPP annually receives about 250 million tons of
fine aerosols. The latter can significantly alter the balance of solar
radiation at the earth's surface. They are the condensation nuclei for water
vapor and precipitation formation, and getting into the human respiratory
system, and other organisms to cause various respiratory diseases.
Table 1. Influence of extraction of fuels on the environment and biosphere
|
The
technological process |
Influence on the elements of environment and the biosphere |
Examples of chain reactions |
|||
|
Air |
Soils and subsoils |
Water |
Ecosystems and human |
||
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
|
- liquid
(oil) |
Hydrocarbon contamination on
evaporation and leakage |
Damage or
destruction of soils in the exploration and production |
Oil pollution due to leaks |
Destruction and damage
ecosystems in mining areas and oilfield construction |
Soil pollution, water
pollution by oil and chemical reagents. |
|
- Solid (coal, shale, peat, etc.) |
Dust from blasting and other
works, combustion products, etc. |
Destruction and severe
contamination of soils near businesses |
Strong violation of the
aquifers |
Basically through the water
pollution and hydrobionts |
Loss of
the consumer taste or properties of water and fishery products |
Serious problem TPP is
near storage of ash and slag. This requires large areas that has not used for a
long time, and are centers of heavy metal accumulation and increased
radioactivity.
There is evidence that
if all of today's energy based on carbon, the emissions of CO, would amount to
20 billion tons per year (now they are close to 6 billion tons / year). This is
the limit beyond which such projected climate change, which will determine the
disastrous consequences for the biosphere.
Some solutions to the environmental problems of thermal power plants.
1. Use and
improvement of treatment facilities. Currently, many trapped in the TPP mostly
solid emissions by using different types of filters. The most aggressive
pollutant - sulfur dioxide in many TPP has not captured or trapped in limited
quantities.
2. Reducing income
sulfur compounds into the atmosphere through the preliminary desulfurization
(desulfurization) coal and other fuels (oil, gas, shale oil) by chemical or
physical methods. These methods could extracted from the fuel from 50 to 70% of
the sulfur prior to its combustion.
3. Big and real opportunities to reduce or stabilize contaminants in
revenues associated with environment saving.
Conclusion
This article discussed the main sources of pollution, their types, and
their impact on the biosphere. After reviewing, the authors have proposed
solutions to these problems.
List of literature
1. V.I. Kormilitsyn, M.S.
Tsitskshivili, Y.I. Yalamov "Fundamentals of Ecology", publishing
house - Interstyle, Moscow 1997.
2. N.A. Voronkov "Ecology
- general, social, applied", publishing - Agar, Moscow 1999.
3. V.M. Garin, I.A. Klenow,
V.I. Kolesnikov "Ecology for technical
colleges", publishing - Phoenix, Rostov-on-Don in 2001.