E.V.
Bolovin, A.S. Glazyrin.
Department
of Electric Drives and Equipment, National Research Tomsk Polytechnic
University, Tomsk, Russia
Laboratory testing dynamic
identification of the real induction motor parameters
Abstract
In this paper a laboratory testing dynamic
identification of induction motor parameters is presented. The error of
identification of the parameters is analyzed using the developed method.
Key words: induction motor, identification, difference schemes.
Introduction
Testing consisted of two phases. The first step -
removing and receive visual transients of induction motor. The second step –
the definition of induction motor parameters and calculation of error estimates
of the parameters.
The test procedure
For the testing was used the real
induction motor with the following specification:
- Rated power Pn = 22 kW;
- Nominal voltage Un = 190/330 V;
- Rated frequency fn = 50 Hz ;
- Stator resistance R1= 0,106 ohms ;
- Reduced resistance of the rotor R¢2
= 0.067 ohms ;
- Leakage inductance of the stator winding
L1σ = 0,684 mH ;
- Reduced to the stator leakage inductance
of the rotor winding L¢2σ = 0,667 mH ;
- The resulting inductance due to the
magnetic flux in the air gap of the machine Lm = 24,711 mH;
- Number of pole pairs zp = 2 ;
- Moment of inertia of the motor J = 0.5962 kg·m2 ;
- Nominal speed ωn = 157 rad/s ;
Processes for identification of parameters
![]() ,
, ![]() (Fig.
1) and
(Fig.
1) and ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() (Fig. 2) were build and compare them with the actual
values.
(Fig. 2) were build and compare them with the actual
values.

Fig.1. Transients assessments ![]() ,
, ![]() and identification models of asynchronous
squirrel-cage motor .
and identification models of asynchronous
squirrel-cage motor .
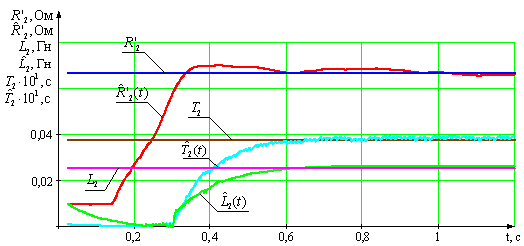
Fig.2. Transients assessments ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() identifying models of asynchronous
squirrel-cage motor
identifying models of asynchronous
squirrel-cage motor
Rms relative error of assessment given to
the stator resistance of the rotor:
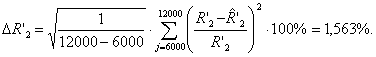
Rms relative error of assessment
equivalent inductance of the rotor winding:
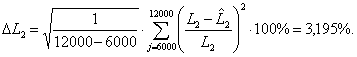
Rms relative error of assessment
equivalent inductance of the stator winding:
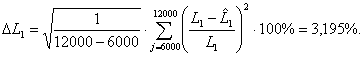
Rms relative error of assessment resulting
inductance due to the magnetic flux in the air gap of the machine :
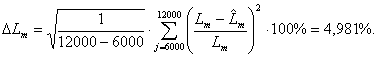
Rms relative error of assessment
equivalent time constant of the rotor:
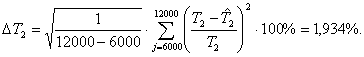
Conclusion
The difference between actual and estimated values are less
than 5 percent, respectively, the identification of
induction motor parameters based on
difference schemes is effective.