Economic sciences
Matviyenko
T.O.
post-graduate
student, chair of accounting and audit
Taras
Shevchenko National University of Kyiv
USAGE OF AUDIT RESULTS ON
TAX AND CHARGES LIABILITIES IN TERMS OF ENTERPRISES’ TAX PLANNING
Annotation. Organization
principles of enterprises’ tax management were revealed. Main directions of
usage of audit results on tax and charges liabilities when making management
decisions substantiated. This will allow to extend scientific papers on audit
problems and improve tax planning at enterprises in Ukraine and in the world.
Keywords: liabilities,
taxes, charges, tax management, audit, tax planning
². Introduction. Problem definition. Unstable
development of the national economy requires from enterprises to concentrate
attention to improvement of their financial and resources' provision, searching
ways of effective activity support. Favorable financial position and solvency
of enterprises are evidenced by ability to timely redeemed indebtedness to
other enterprises-contractors, financial institutions, tax authorities. However
tendencies, presented in financial and economic activity of enterprises, do not
bring positive results. As of January 1, 2010 current liabilities of business
entities generally in Ukraine amounted to 1352,9 bln. UAH, it increased by 6,7
% as compared with the previous year. Moreover the worst situation is observed
in enterprises of hotel and restaurant business (+22,8 %), health care and
social services provision (+20,0 %), as well as in industrial enterprises
(+15,8 %) (table).
Table
Current liabilities on types of economic activity
as of January 1, 2010 *
|
Type of economic activity |
Liabilities, bln. UAH |
% prior previous year |
|
agriculture,
hunting, forest management |
50,4 |
110,9 |
|
industry |
484,5 |
115,8 |
|
building
|
75,1 |
104,7 |
|
commerce;
auto service, repair of household goods and personal demand items |
637,2 |
106,8 |
|
trade
of automobiles and motorcycles, its maintenance and repair |
46,5 |
98,9 |
|
wholesale
trade, brokerage |
543,0 |
107,7 |
|
retail
trade; repair of household goods and personal demand items |
47,7 |
106,0 |
|
hotel
and restaurant business |
6,4 |
122,2 |
|
transport
and communication business |
69,6 |
99,8 |
|
financial
activity |
73,6 |
101,8 |
|
real
estate activities, leasing, engineering and provision of services to business
entities |
295,1 |
80,2 |
|
education |
0,4 |
105,4 |
|
health
care and provision of social aid |
2,0 |
120,0 |
|
provision
of utility and individual services; activity in the field of culture and
sport |
10,4 |
102,2 |
|
Total |
1705,4 |
126,1 |
* Made
by author on the basis of [1]
In such conditions a necessity arises in organization
of effective system in tax management at domestic enterprises, which could
quickly respond to onrush changes in social-economic and tax environment of the
country. Complete and comprehensive information about enterprise’s activity and
taxation of main and specific economic transactions can be obtained under audit
results of accounts and financial statements. Therefore management of
enterprises require services of audit firms oftener for confirmation of
accounting accuracy for liabilities on taxes and duties, tax and financial
statements, as well as making management decision concerning improvement of
financial and tax policies of enterprises on the basis of auditor’s
conclusions.
Analysis of research papers and publications in
question. Problems of efficiency enhancement of
enterprises’ activity on the whole, as well as optimization of taxation in
particular, were studies by specialists of various profiles: economists,
managers, financial experts, check-men, analysts. Among foreign scientists the
following are worth noting: Å.À. Arens, P.S. Chandra, ².Ì. Karasyova,
V.P. Suits, À.D. Sheremet and others. In domestic science this
problem was researched by such scientists:
V.D. Bazylevych, Ì.Ò. Bilukha, N.². Dorosh,
Ye.V. Kalyuga, G.². Kupalova, Î.À. Petryk, V.Ya. Savchenko,
B.F. Usach and others [2-10]. They defined main
approaches to methodology and organization of economic activity audit, its
individual subjects. They developed conceptual frameworks of financial
planning, assets management, raising and using of financial resources, forming
of short-term and long-term financial strategies on the basis of analysis
results and activity audit of business entities. But still less attention in
scientific literature is devoted to tax planning and usage of audit results on
tax liabilities and charges in enterprises’ management. Therefore these and
other issues require further research and clarification.
²². Task definition. The purpose of this
article is research of tax management organization and substantiation of priority
directions for the usage of audit results on tax liabilities and charges in tax
planning of enterprises. For this purpose achievement the following tasks were defined:
-
coverage of organization bases for tax management and planning at
enterprises;
-
forming of conceptual directions of audit results usage on tax
liabilities and charges when making managerial decisions.
²²². Presentation of main material. Effective management of tax liabilities provides forming of tax
management system or carrying out functions on establishment of tax compliance
within corporate management of enterprise. Information base in tax planning is
accounting information, reports of internal control system and audit results.
Important medium of information collection about
enterprise’s activity shall be accounting system, which comprises data about
financial operations of business entities, assets condition, acknowledgment and
redemption of indebtedness, as well as accounting policy principles and
reporting preparation. With the purpose of control and efficiency enhancement
of enterprises functioning management shall create and organize work of internal
control service. Its functions comprise: monitoring of enterprise’s settlements
condition, taxation accuracy of transactions and prevention of unreasonable
exceeding of enterprise’s tax liabilities, which can cause additional financial
expenses in form of penalty sanctions. Reliable information about condition of
accounting and reporting system can be obtained at the expense of audit
results, carrying out by independent external bodies– auditors and audit firms.
In the process of audit, first of all they check internal control system, then
– budget settlements accounting, tax and financial statements.
That’s why when making managerial decisions managers
have to be governed by auditor’s conclusions, which give full and comprehensive
information about economic activity of a business entity. Besides, due to audit
results finctioning expediency of internal control service can be determined.
Activity of modern enterprise is directed at profit maximization, therefore
managers’ task consists of selection of two of the existing alternatives –
create and finance the work of internal control service or engage external
experts for audit.
Managers consolidate information about economic
activity and define further policy and strategy of activity by making
managerial decisions. Investigating philosophic meaning of category “decision”
we came to conclusion, that this is the process and result of purpose selection
and means for its achievement [11, p. 558]. That is, making management decision
is carried out by means of passing defined stages of object research. On the
other side such process stipulates achievement of stated purpose and has
economic expediency.
Therefore making
management decision concerning tax policy of business entity shall be
considered as the selection process of
optimum variant for economic activity organization and selection of further
development strategy of an enterprise on the basis of comprehensive study of
enterprises’ budget settlements condition. It shall be provided by carrying out
of overall analysis of accounting information and report documentation of
internal control system tax liabilities, as well as at the expense of complex
audit of tax and charges indebtedness.
We are of the opinion that results of tax liabilities
audit should be used when carrying out such measures of tax management: development of key
principles of tax policy, optimization of tax burden, avoidance of tax penalties and interests, search of reserves
for reducing of taxes payable and budgeting of tax flows
(fig.).
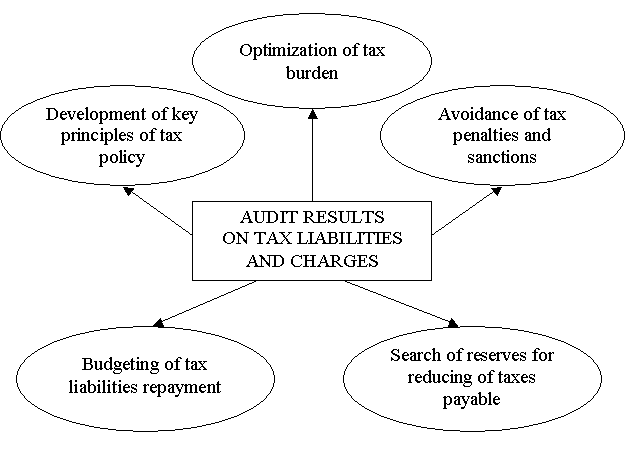

Fig. Directions of audit results realization on tax
liabilities and charges*
* Developed by author
Let’s consider tax measures in more details, which
will contribute to improvement of tax liabilities and charges planning at
domestic enterprises. Development of key
principles of enterprise’s tax policy. Selection of enterprise’s tax policy
is an important stage of its activity organization, because further accounting
and reporting organization of tax liabilities depends on it, as well as other
accounting objects associated with it. Results of selected taxation strategy
are stated in regulations of accounting policy of an enterprise.
Besides, at management’s own discretion, it can be
written in a seprate document – tax policy of an enterprise. Though making such
document is not regulated and requested by any regulatory legal act, we believe
that it should be made at enterprises with the considerable share of taxation
operations and level of tax burden more than 15 %. Similar to regulation
on accounting policy such document must contain such three important
components: legislative and methodological provision tax liabilities and
charges accounting, technical components of accounting process and
peculiarities of accounting and reporting organization of taxes payable.
Optimization of tax
burden. Another important element of tax management
shall be tax planning. It is carried out according to selected tax policy. In
the process of planning results of analysis and audit of economic activity have
important role, on the basis of which strategy of further actions should be
selected. On this stage it is expedient to study results of carrying out of
analytical and other audit procedures with the purpose of optimization ways
search for tax liabilities and charges, budgeting of its redemption. Besides,
under the results of audit one can determine availability of overpaid taxes and
charges to budget and estimate possibility of tax compensation. Result of tax
planning shall be forming of complex measures for improvement of tax
compliance, as well as methods as regards tax and charges liabilities
redemption.
Reduction of tax payments by means of its optimization
and planning should contribute to increase in enterprise’s profits, as well as
meet the interests of owners, managers and employees of an enterprise. But this
dependency is not always traced directly. Reduction of one taxes can cause
increase in others, as well as tax interests from the state tax authorities.
That is why the most effective means concerning increase in profitability is
not mechanical reduction of taxes but minimization of tax burden with
simultaneous growth of production, sales volumes and activity efficiency i.e.
building of effective management system of enterprise and making decisions
concerning optimization of the whole structure of economic activity. It is
possible by means of funds investment, released in the result of taxation
optimization, to production, development of an enterprise in general, as well
as its separate assets. Taxation optimization and tax planning must maintain
price competitiveness of enterprises by means of effective management of taxes
and charges, which are included in goods and services price [8]. Besides, it
must assist in obtaining of economic benefits and increase of transparency of
accounting and control system of tax and charges liabilities.
Avoidance of tax
penalties and interests. With the purpose of tax
burden minimization management of enterprises applies to rather doubtful
measures concerning minimization of tax and charges liabilities, which can
contravene provisions of tax legislation or comply with it formally. But it
should be realized that minimization of tax expenses within short-term period
can cause considerable tax penalties and interests in the long view. That is
why issue of economic expediency of such measures is doubtful, because its
application influences not only on possibility of financial benefits loss, but
also on enterprise’s image among creditors, enterprises-contractors and tax authorities.
Judicial doctrines are widely used in world practice,
which are used by controlling authorities for differentiating of real economic
transactions from such that are used by business entities exclusively with the
purpose of gaining tax benefits. Such doctrines include: essence over form and
business purpose. Doctrine of essence superseding over form means the
following: legal consequences of economic transaction must be defined in a
greater degree by essence and expediency of its fulfilment, but not by legally
executed documents. According to doctrine of business purpose, a purpose must
be defined first of all, under which such operation is carried out. If an
agreement is concluded, under which tax benefits are stipulated for
enterprises, but substantiation of such operation necessity is absent, such
agreement can be considered invalid [9]. Therefore when making management
decisions concerning optimization of taxation lawfulness of realization should
be clearly established and application expediency should be confirmed by way of
estimation of economic effect from applied tax measures.
Search of reserves
for reducing of taxes payable. Work of analytical
service of an enterprise is directed at investigation of economic activity
condition, analysis of its main indexes and search of additional attraction
sources or release of monetary assets. Stated information concerning financial
compliance of enterprises can be obtained under the results of analytical
procedures, which are used by auditors in the process of tax and charges
liabilities checking. On the basis of generalization of received data from
internal and external sources of audit tax managers have to reveal facts of
untimely budget settlements and optimize structure of tax payments. With this
purpose it is worth optimizing of taxation system with the help of tax policy
forming and development measures on improvement of accounting and reporting of
tax and charges liabilities. Effective means of enterprise’s tax liabilities
monitoring is budgeting and financial plans forming.
Budgeting of tax
liabilities repayment. Tax budgets - rather widespread
monitoring practice of tax liabilities condition in the world. It allows to
monitor facts of liabilities acknowledgment, redemption and timely detect
outstanding liabilities. Financial plans are formed on the basis of budgets,
which determine usage directions of financial resources of an enterprise,
including for taxes and charges liabilities repayment. Besides, it is necessary
to form minimum reserve for budget settlements, that will allow to make tax
payments in time and without delays and prevent expenses occurrence of the
enterprise, connected with coverage of charged penalties and interests.
When
forming budget of tax flows it is worth considering not only charged and
payable taxes and charges but also amounts of penalties and interests for
untimely budget settlements. Therefore we suggest to use the following approach
when planning taxes and charges liabilities repayment:
![]() ,
,
where ![]() – taxes and charges
liabilities, which are mature in accounting period,
– taxes and charges
liabilities, which are mature in accounting period,
![]() – charged tax
liabilities,
– charged tax
liabilities,
![]() – amount of taxes and
charges, repaid from the state budget,
– amount of taxes and
charges, repaid from the state budget,
![]() – penalties and
interests, charged for untimely payment of taxes and charges to budget,
– penalties and
interests, charged for untimely payment of taxes and charges to budget,
![]() – overpayment of
taxes and duties, which will be accounted in future accounting periods.
– overpayment of
taxes and duties, which will be accounted in future accounting periods.
Thus,
mentioned calculation method of taxes and charges liabilities allows monitor
the whole process from its acknowledgement to repayment. Budgeting is rather
effective in terms of high productivity of activity, because it helps reveal
outstanding amounts of taxes and charges and prevent application of penalty sanctions
by state tax authorities.
In the
process of budgeting for redemption of tax liabilities it is expedient to
estimate condition of budget settlements, activity peculiarities for the
previous period, availability of specific taxation operations, changes in tax
legislation, in operating activity, carrying out of new types of activity etc.
Therefore budgets can be formed also in separate kinds of taxes and charges,
that will assist in research of taxes structure change and its flows. Besides,
it is necessary to define amount of tax payments and outstanding tax
liabilities for the future period. Budgeting of taxes and charges liabilities
should be carried out simultaneously with financial flows planning, because
such measures allow to determine reserves for coverage of enterprises’
indebtedness.
²V. Conclusions. Within modern unstable
economic conditions role of audit is only strengthening as a principal
instrument for accuracy and transparency confirmation of financial statements. Audit results of tax liabilities allow to obtain complete and
transparent information concerning budget settlements condition of enterprises
and before other contractors, latent liabilities, information falsification as
a result of mistakes and deliberate tax evasion. Audit results of tax
liabilities should be used when carrying out of such measures of tax
management. With the purpose of effective management of tax flows it is
expedient to use audit results in such
directions: development of key principles of tax policy, optimization of tax
burden, avoidance of tax penalties and interests, search of reserves for reducing of taxes payable and
budgeting of tax flows. It will contribute to achievement of socio-economic and
financial effects from carrying out taxation operations and increase of credit
rating of an enterprise and confidence of other creditors, tax authorities,
business structures.
References
1. Current liabilities by type of economic activity:
[Archives 2008-2010] [Electronic resource] // State Statistics Committee
of Ukraine. – Access mode: http://ukrstat.gov.ua.
2. Arens A. Auditing
An Integrated Approach [Hardcover] / Alvin A.
Arens, James K.
Loebbecke, Randy Elders, Mark Beasley. –New Jersey : Prentice Hall,
2000 – 823 p.
3. Brownlee R.E.
Corporate Financial Reporting : Text and Cases / R.E. Brownlee, K.R. Ferris, M.E.
Haskins. – Boston :
Irwin/McGraw-Hill, 1998. – 928 p.
4. Chandra P. Financial
Management : Theory and Practice / Prasanna Chandra. – Tata McGraw-Hill
Publishing Company Limited, 2004. – 936 p.
5. Elliot B. Financial Accounting and Reporting / B. Elliott, J. Elliott. – 12-th ed. – England : Pearson Education, 2007. – 889 p.
6. Hawkins D.F.
Corporate Financial Reporting and Analysis : Text and Cases / D.F.
Hawkins. – Boston :
Irwin-McGraw-Hill, 1997. – 944 p.
7.
Áàçèëåâè÷ Â.Ä. Ìåòàôèçèêà ýêîíîìèêè : ìîíîãðàôèÿ /
Â.Ä. Áàçèëåâè÷, Â.Â. Èëüèí. – Ê. : Çíàíèÿ, 2010. – 925 ñ.
8.
Áàðóëèí Ñ.Â. Íàëîãîâûé
ìåíåäæìåíò : ó÷åáíîå ïîñîáèå [Ýëåêòðîííûé
ðåñóðñ] / Ñ.Â. Áàðóëèí,
Å.À. Åðìàêîâà, Â.Â. Ñòåïàíåíêî. – Ìîñêâà : ÎÌÅÃÀ-Ë, 2008. – 268 ñ. –
(Áèáëèîòåêà âûñøåé øêîëû). – Ðåæèì
äîñòóïà : http://www.litru.ru/br/?b=95871&p=1.
9.
Äæààðáåêîâ Ñ.Ì. Ìåòîäû è
ñõåìû îïòèìèçàöèè íàëîãîîáëîæåíèÿ [Ýëåêòðîííûé ðåñóðñ] / Ñ.Ì. Äæààðáåêîâ. – Ìîñêâà : ÐÃÁ, 2008. – Ðåæèì äîñòóïà : http://books4study.org.ua/kniga454.html.
10.
Äîðîø Í.². Àóäèò : òåîð³ÿ ³ ïðàêòèêà : ìîíîãð. / ͳíà ²âàí³âíà Äîðîø. – Ê.
: Çíàííÿ, 2006. – 495 ñ.
11.
Ôèëîñîôñêèé
ýíöèêëîïåäè÷åñêèé ñëîâàðü/ Ðåäêîë. : Ñ.Ñ. Àâåðèíöåâ,
Ý.À. Àðàá-Îãëû, Ë.Ô. Èëüè÷åâ è äð. – 2-å èçä. – Ì. : Ñîâ. ýíöèêëîïåäèÿ, 1989. – 915 ñ.