экология/6. Экологический мониторинг
Zaitseva A.S., Arlyapov V.A., Grishaeva A.R.
Tula State University
Development of biosensors based on
modified SWCNTs and the immobilized glucose oxidase enzyme
To date, the actual
development is the use of the modified single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNTs)
with carboxyl groups as a material for creating a highly sensitive biosensor
based on the direct electron transfer (III generation). The perfect single-wall
nanotube is a graphite cylinder in a folded plane formed by the regular
hexagons, which are located at the vertices of carbon atoms. Depending on the
angle of folding SWCNTs can have very different physical and chemical
properties, such as conductivity, magnetism, strength, so they are widely used
in nanoelectronics and nanomechanics.
The electroanalytical
chemistry and biosensors are widely used electrodes made of carbon materials.
Such electrodes have a wide range of polarization potentials, low background
currents, good reproducibility and ease of regeneration signal of the working
surface. Biosensors based on carbon nanotubes have high sensitivity and
conductivity. The direct electron transfer is a way to mediator-less current
registration of the substrate oxidation by direct oxidation of reduced enzyme
on the electrode (Figure 1). This paper presents a biosensor based on modified
SWCNTs using the glucose oxidase enzyme.
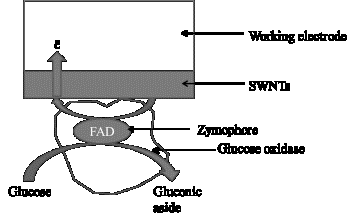

Fig.
1.
Schematic representation of the work of the III generation biosensor with
direct electron transfer based on modified SWCNTs and the glucose oxidase enzyme.
The advantage of using an enzyme is its high
specificity, as well as direct electrical contact between the redox center of
the enzyme and the electrode, and that allows the direct transfer of electrons.
Initially, aging was carried out in a mixture of SWCNTs suspension of
concentrated nitric and sulfuric acids (1:3) by treatment with ultrasound for 3
hours at room temperature (Figure 2). Ultrasound oxidation and split SWCNT
causes increase their dispersibility in the solvent, and the possibility of
joining in the field of functional groups fault.
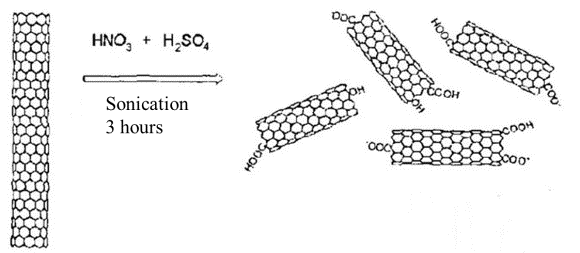

Fig. 2. The oxidation
(modification) of SWCNT mixture of acids under the influence of ultrasound.
Identification grafted functional groups
carried on Fourier transform infrared spectrometer FSM 1201
("Monitoring", Russia) in the infrared spectrum of the radiation.
During prolonged sonication main product is the formation of carboxyl groups,
which is the absorption spectrum in the range of 1714-1734 cm-1,
consistent with the literature (Weibel M. K., 1971).
Amperometric measurements made using a working
carbon-paste electrode with directly deposited on the surface of the electrode
slurry oxidized SWCNT and the enzyme glucose oxidase. The measurements were
made at an operating potential -450 mV, which was selected by voltammetry. The
resulting potential is consistent with the literature data (Wu X., 2009).
With the use of glucose as a substrate were
determined metrological and analytical characteristics of modified SWCNTs biosensor.
Long-term stability of the enzyme sensor was 9 days; range of detectable
concentrations of glucose 0.024 - 1.000 mmol/dm3. Also, a comparison
was made of certain characteristics of the developed biosensor based on modified
single-wall CNTs with an analogue-based multi-walled CNTs (Rogaleva N. S., 2012).
Features biosensor modified SWCNTs several times higher than those of similar
biosensor MWCNTs: the minimum reporting level allows determining the lower
concentration than that of a similar biosensor.
This work was
supported by the grant of the President of the Russian Federation (contract № 14.Z56.16.5425-МК)
and by the grant of the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (contract №
16-48-710959 р_а)
References:
Weibel M. K., Bright H. J. The glucose oxidase
mechanism interpretation of the pH dependence //Journal of Biological
Chemistry. 1971. V. 246. N. 9. PP. 2734-2744.
Wu X. et al. Direct electron transfer of glucose oxidase immobilized in an ionic liquid reconstituted cellulose–carbon nanotube matrix //Bioelectrochemistry. 2009. V. 77. N. 1. PP. 64-68.
Rogaleva N. S. et al. Amperometric biosensor
modified with multiwalled carbon nanotubes for glucose determination //
Biotechnologia Acta. 2012. V. 5. N. 1. PP. 53-61.