Master student Terekhova A.A.,
Ph.D.Dyakov I.A.
Tambov State Technical University, Russia
The use of carbon nanotubes in electrical engineering
Carbon nanotube is a long cylindrical graphite
rolled strips with thickness up to several tens of nanometers and length up to
several centimeters with a carbon frame structure. Under this structure include
larger molecules are connected only to carbon atoms. At the ends of nanotubes
are usually formed by hemispherical heads (Fig.1).
Carbon nanotubes come in different shapes and
sizes – straight and curved, single layer and multilayer. Despite the fact that
at first glance they seem very fragile, actually they are quite durable
material that has been proven by many studies. It was found that carbon
nanotubes are characterized by such properties as tensile and bending, i.e.
under the influence of various mechanical loads the elements do not break and
are broken, and this suggests that they can adapt to different voltages.
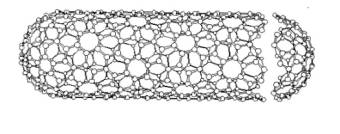
Fig. 1 Idealized model of single-layer
carbon nanotubes
Due to characteristics such as bending strength
and conductivity of carbon nanotubes used in many fields: as additives to
polymers as absorber of electromagnetic waves, in the manufacture of various
sensors and capacitors, to transform electricity, in the production of
composites with the aim of strengthening their structure and properties.
Repeated experiments conducted by different
scholars, show that carbon nanotubes are the most rugged and tough of all known
materials - a material with a record
high values of ultimate tensile strength (~60
GPA) and young's modulus (≈ 1 TPA). It is connected with perfection of
structure and the strong sp2 chemical bond between the carbon atoms that
comprise the nanotube.
Nanotubes are also good heat conductors along
the tube, showing properties, so-called, unimpeded conductivity or
superconductivity. However, across the axis of the nanotubes have high thermal
insulation properties.
An interesting feature of carbon nanotubes is
that they can be metallic or semiconducting depending on their diameter and
chirality. As a result of the synthesis is usually a mixture of tubes, two
thirds of which have semiconducting properties, and one third metallic.
Metal tubes usually have a chair structure
(Fig.2A) and semiconductor zigzag (Fig.2B) and spiral (Fig. 2B).
Metallic and semiconducting carbon nanotubes
differing conductivity metal can conduct current at a temperature of 0 ° C, and
the semiconductor only at elevated temperatures.
Widespread use of carbon nanotubes in
electrical engineering possible due to the fact that they can transmit currents
with a density higher than the most conductive metals, such as copper. So a
single layer of nanotubes pass currents of density up to 109 A/cm2, and the
multilayer is up to 100 µa/cm2, and copper at such values of current density
melts.In addition, when the resistance is comparable to copper, and carbon
nanotubes is four times easier.
Carbon nanotubes outperform copper by such
indicators as the coefficient of thermal conductivity along the axis. For
copper it is equal to 400W/(m×K), for nanotubes 500 -5500 W/(m×K).
Another advantage of nanotubes is due to cold
emission of electrons, an along the tube axis of the electric field. The field
strength in the vicinity of the top part hundreds of times higher than the one
that exists in the volume, which leads to anomalously high values of emission
current at a relatively low external voltage and allows the use of nanotube
macroscopic system as a cold emission cathodes. The degree of emission of
carbon nanotubes can be used in the manufacture of flat panel displays and touch
control panels.
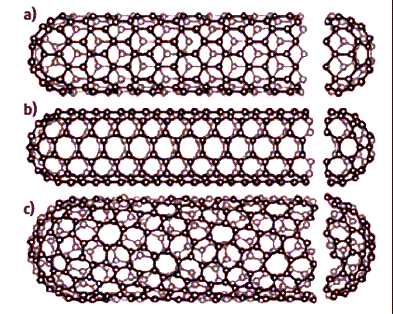
|
б) |
Fig.2 Types of carbon nanotubes:
a – chair structure; b – zigzag structure; с – helical structure
The application of carbon nanotubes in the
production of various electrical devices is one of the most promising
directions of work of scientists around the world. Due to the properties of the
nanotubes described above, their use in the production of, for example, cables
and wires is quite beneficial. Due to its lightness and high conductivity
cable, manufactured with the use of carbon nanotubes will significantly surpass
its copper predecessor, which makes its production more profitable.
The authors propose to use carbon nanotubes in
the manufacture of various parts of electrical machines. For example, the brush
for electric machines that are special conductive parts of the current
collection devices that provide a sliding contact between the stationary and
rotating parts of the machine and serve to supply or drain current, when you
add in the production of carbon nanotubes in them will last longer than usual.
Or, for example, nanomodification coating of housings of electric motors will
improve their heat-transfer properties. Such measures will allow to increase
the service life of electric motors, which will significantly reduce costs in
their operation.
Currently, due to their properties carbon
nanotubes are one of the most promising materials used in many industries.
Despite their shortcomings, such as toxicity, the use of nanotubes in
electrical engineering due to the need to create a new material the properties
of which will be an opportunity to reduce the cost of production and operation
of electrical equipment.