Строительство и архитектура
/4. Современные строительные материалы
O. Shynkevych, Y. Lutskin,O.
KOICHEV, O. GARA
Odessa State Academy of Civil
Engineering and Architecture (Ukraine)
Influence
of silica-containing component of the chemo-biogenic origin on the structure and properties of composites on
silicate matrix
Composites on a
silicate matrix differ from silicate concrete of autoclave hardening in that
they are made on the basis of a three-component complex-activated
silicate-concrete mixture modified with alkaline and mineral additives and they
harden at a temperature of 85°C and normal atmospheric pressure. Due to the
implementation of the complex activation of a highly mobile silicate-concrete
mixture, which is one of the technological features of obtaining this type of
composites, energy-saving production modes are provided. Composites and
products based on them are characterized by reduced density at sufficiently
high values of strength, water, crack resistance and heat capacity, thanks to
which comfortable conditions are created with a stable temperature regime
throughout the day [1, 2,
3].
As components of
binder, quicklime, ground together with quartz sand, chemically active
amorphous-crystalline silica of chemo-biogenic genesis with an optimum specific
surface area is used. The introduction of a quartz sand component of chemically
biogenic origin in the form of a tripoli with different specific surface and
ultra-dispersed porosity in the binder component provides a multifunctional
effect on the structure and properties of composites on a silicate matrix.
To date, there
are no clear ideas about the functional role and effect on the structure and
properties of silica-containing components of chemo-biogenic genesis, which
were previously used either as active mineral additives or fillers. It should
be noted that both the term "filler" and the term "mineral
additive" do not disclose the mechanism of action of these components on
the features of structure formation and the properties of composites.
A comparative
analysis of the influence of the specific surface of the quail on the change in
the structure and properties of the silicate matrix on the one hand and the
porous composites based on it, modified with alkali-containing additives, on
the other. The analysis was carried out on the basis of experimental and
statistical modeling of data from two full-scale experiments [3,
4].
The relative
influence of the δY
specific surface of the quail and its comparison with the influence of other
factors studied on the changes in the properties and parameters of the
structure of the silicate matrix and porous composites are visualized in the
form of bar charts.
It is shown that
the influence of the specific surface of a trefoil on the change in the
properties of the silicate matrix is equivalent to the effect of the hardening
conditions (Fig. 1).
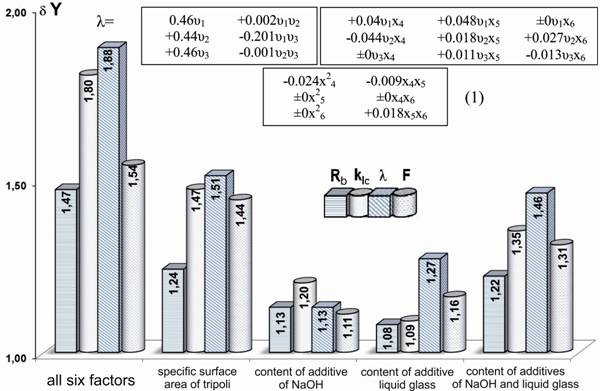
Figure 1 The
relative influence of the studied factors and their interactions
on the change of properties
On the change in
the properties of porous composites, the influence of the specific surface of a
trefoil is equivalent to the effect of two alkali-containing additives.
It should be
noted that if the influence of the specific surface of the quail significantly
exceeds the effect of the hardening conditions separately for the silicate
matrix and the effect of each of the alkali-containing additives separately for
porous composites, then the interaction of the specific surface of the quail
with the same factors multiplies their influence on the structure and properties
of the silicate matrix and porous composites.
Based on the
analysis, a mechanism for the formation of the structure and properties of the
silicate matrix was proposed and justified [3, 4].
It is shown that the particles of the trembling contribute to the "physical"
consolidation of the structure of the silicate matrix and the formation of
intermittent capillary structures, including due to intrinsic microporosity. In addition, as a result of the high
sorption capacity, the pores of the quiver may be a matrix for the formation of
ultra-dispersive hydrosilicates whose properties differ from the properties of
calcium hydrosilicates formed in the free space of the mixture, which
facilitates the production of porous composites with high physical and
mechanical properties.
Thus, trepel performs a multifunctional role. Based on the
analysis of the results of experimental statistical models, a significant
influence of the specific surface of the quail has been established, which is
comparable to the effect of hardening conditions on the silicate matrix,
including TMT, and for porous composites based on it - with alkaline activation
of the mixture.
Acting as a
"physically active" component, it provides a reduction in the density
and thermal conductivity of the material. As a component of a binder with
ultra-dispersed porosity, the tremor influences the mechanism of formation of
the structure and properties of the composite and their change in time, being a
nanoreactor for the formation and growth of ultradisperse calcium hydrosilicates inside the particles
of the tripoli.
References
1. Shinkevich
E.; Lutskin E.; Gnyp O.; Koichev A.; Dotsenko J.: The
Influence of Modification of the Structure of Silicate Materials on Their
Properties After Non-autoclaved Hardening, Proc. of the 8th Int. Symp. Brittle Matrix Composites 8, Warsaw, Octoder 2006,
517-525.
2. Shynkevych O. Nanotechnological and
Energy-saving Methods of Production of Building
Com-posites / O. Shynkevych,
Y. Lutskin, O. Koichev, G. Bondarenko, A. Tertychnyi, I. Myronenko // MATEC Web Conf. – Volume
116, 2017. – P. 01015 (10).
3. Shinkevich E.; Sidorova N.; Lutskin E.; Sidorov V.; Politkin S.: Raw Mix
for Obtain Modified Silicate Materials and Method of Its Prepare, Declared
patent # 64603 A, 7 C04B28/20, Ukraine, 2004.
4. Lutskin Y.; Shinkevich E.: Aerated
Complex Activated Composites on Silicate Matrix of Thermal-moisture Hardening,
Proc. of 14th Int. Congress on the Chemistry of Cement / Abstract
Book, Volume 2, Beijing, October 2015, 632.