Comprehensive treatment of diabetic macular edema
patients on the background of type 2
Shelkovnikova T.W., Takhchidi Kh.
P., Balashova L.M.,
Katsadze Y.L.,Shishlyannikova N.Y.
Kemerovo, Kemerovo Oblast Clinical
GBUZ Eye Hospital
Moscow, Russian State Educational
Institution National Research
University of Pirogova
St. Petersburg, Federal Russian
Institute of Haematology and Transfusion
Kemerovo, Kemerovo State Medical
Academy, Russian Ministry of Health
Purpose. The study of clinical, laboratory, morphometric
parameters of macular edema in patients with DR on the background of DM 2.
Comparison of the effectiveness of drug treatment DMO dalargin sulodexide and
their integrated use in combination with laser coagulation of the retina in
patients with DR.
Materials and methods. 50
patients (100 eyes) with DR-2 diabetes. Of these, the nonproliferative diabetic
retinopathy (NPDR) - 12 patients (24 eyes); with preproliferative (PPDR) - 13
patients (26 eyes); with proliferative (PDR) - 25 patients (50 eyes). Used
ophthalmic research methods; Laboratory methods: standard screening methods,
special methods of investigation of the hemostatic system.
Results and conclusions. Reduced levels
of performance components of the hemostatic system in patients with diabetic
macular edema (DME) indicates a decrease in thrombogenic situation in the
microvasculature of the retina. Declining: vWf, VIIIf, protein C, SFMK, correlates with a
decrease in the incidence of DME (R1 -0,96, R2- 0,93; R3 - 0,97; R4 - 0,99), the
clinical picture and the stabilization of the DR pathological process.
Keywords: comprehensive treatment, diabetic macular
edema, endothelial dysfunction, hemostasis, diabetic retinopathy.
Introduction. Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is one of the leading causes of blindness and
visual disability in the population due to the pathology of the vision.
Effective treatment for clinically significant forms of diabetic retinopathy
are non-pharmacological correction (panretinal laser coagulation of the retina
and vitrectomy), drug treatment of diabetes mellitus (DM), which is a priority
for the payment of microcirculation of the retina [1]. Laser surgery has a
number of significant drawbacks, seeking recourse retinal edema or intraocular
neovascularization different genesis, laser coagulation leads to damage of the
pigment and the neurosensory retina endothelium. Side effects of laser
photocoagulation of the retina affect the quality of life and patients. Search
for treatment of DR and DME, as effective as existing and accompanied by
significantly less damage to surrounding tissues, leading to the emergence of
new technologies [2].
In the development of DR significant role played by the state of
the endothelium and the basement membrane of the vascular wall. Significant
importance is the synthesis of heparin violation - glycosaminoglycan (GAG), a
component of the basement membrane and form the active surface layer of
endothelial cells of the retina. Application geparanoidov such as Wessel Due F
(sulodexide) having a tropism to vascular wall, adsorbing primarily (90%) of
the endothelium can restore the normal density of the negative charge of
basement membrane pore retinal microvasculature [3, 4, 5].
In the pathogenesis of DHS big role choroidal dysfunction,
leading to secondary disfuktsii adjacent retinal pigment epithelium. In recent
years, it is shown that opioid neuropeptides, such as Dalargin, capable of
improving regional microcirculation, enhance the repair and regeneration of
tissue, inhibiting the activity of lipid peroxidation, thereby improving the
state of the endothelium and the capillary basement membrane of retinal
microvasculature [4].
As markers of endothelial dysfunction is considered: von
Willebrand factor (vWf) - adhesive glycoprotein synthesized by the endothelium
of blood vessels; plasma vWf forms a complex with factor VIII, whereby the
latter is activated and receives protection from nonspecific proteolysis. Soluble fibrin monomer complexes (SFMK),
formed during the degradation of molecules of soluble fibrin by the action of
plasmin. This is one of the earliest markers thrombinemia and hypercoagulation
syndrome. Protein C - physiological anticoagulant. Activated protein C (APC)
inactivates Factors Va and VIII clotting in the presence of its cofactor -
protein S, thereby preventing the transfer of prothrombin to thrombin; MTA
stimulates secretion of plasminogen activator by endothelial cells and thus
stimulates fibrinolysis [6].
Purpose. The study of clinical, laboratory, morphometric parameters of macular
edema in patients with DR on the background of type 2 diabetes.
Comparison of the effectiveness of drug treatment DMO dalargin
sulodexide and their integrated use in combination with laser coagulation of the
retina in patients with DR.
Materials and methods. 50 patients (100
eyes) with DR-2 diabetes. Of these, the nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy
(NPDR) - 12 patients (24 eyes); with preproliferative (PPDR) - 13 patients (26
eyes); with proliferative (PDR) - 25 patients (50 eyes). Patients with DA:
neovascularization (NV) of the optic nerve (optic disk) - less than 1/3 PD; HB
retina - less than 0,5 PD. Focal macular edema met in 21% of cases, flat
diffuse macular edema - 18%, 54% of cases - high cystic macular edema, 7% -
mixed forms of diabetic macular edema.
Age of the
patients was - 45-62 years old. Men - 20 pers., Women - 30 persons. Blood
glucose levels in the blood - 8,7 ± 2,4 (mmol / l). Experience 2 diabetes from
1 year to 10 years. Complications of type 2 diabetes - hypertension and
coronary artery disease - 45 people., Macroangiopathy of the lower limbs - 25
pers., Diabetic nephropathy - 7 pers., Stroke - 2 persons.
Laboratory studies conducted in laboratory
hemostasis Regional Clinical Hospital ¹ 1 Kemerovo. The material for the study
was deoxygenated blood.
Specific methods of research conducted on
thrombophilia automated coagulometer methods using reagent kits «Dade Behring»
and «Siemens»: definition of activity vWf, antithrombin III, APS, factor VIII
in plasma; determination of resistance to the active factor V protein C (RAPS);
quantitative determination of soluble fibrinmonomernyh complexes (SFMK), a firm
"Technology-standard"; and agregatogramma with inducers of
aggregation ADP ristomycin, collagen, epinephrine.
Detection of lupus antigen (EA) was performed
using "dilution" of thromboplastin, kaolin, Russell viper snake
venoms, lebetoksa, ehitoksa, and confirmatory tests with plasma donor and
corrective phospholipids.
Patients in plasma diagnostics performed
PCR trobofilicheskih gene mutations: Leiden mutation of coagulation factor V
(resistance to activated protein C), prothrombin gene mutation G20210A,
methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene polymorphism (S677TMTHFR; MTHFR 1298).
In the examination
of the patients used the standard ophthalmic (visometry, tonometry, perimetry,
direct ophthalmoscopy) and special research methods: (fundus examination with
Goldman lens with aspherical lens "+ 78", fundus fluorescein angiography
at the fundus camera «Topkon», Japan; optical coherence tomography (OCT) on the
unit RTVu-100 firms Optovue (USA) computer perimetry.
Patients with diabetic macular edema
with clinical forms of retinal LK DR conducted in the form of "focal lattice"
on laser installation «NIDEK» (Japan) Nd: YAG, λ = 532 nm. by the standard
method with the following parameters: diameter 100 mm coagulates, exposure -
0.1-0.15 seconds, the number koagulyatov- 150-400. Used: Dalargin 0.3-0.5 ml
under the conjunctiva or parabulbarno number 10 (patent number 2,198,641 "Method
for the treatment of eye diseases" from 20.02.2003, the). Dalargin 1,0ml
¹10. intramuscularly, then sulodexide LE 600, intramuscularly number 10, then
250 LU sulodexide two times daily - 30 days.
Results and
discussion. Growth
indicators vWf, VIIIf and protein C correlates with an increase in the
incidence of diabetic macular edema in patients with NPDR, PPDR and PDR (R1
-0,93 correlation coefficient vWf with macular retinal thickness in patients
with clinical forms of DR; R2 -0, 93, the correlation coefficient level of
factor VIII with a thickness of the retinal macula in patients with clinical
forms HLR; R3 - 0,84 correlation coefficient of activity of protein C with the
thickness of the macula of the retina in patients with clinical forms HLR; R4 -0,96
SFMK correlation coefficient with a thickness of the retina macular patients with clinical forms DR).
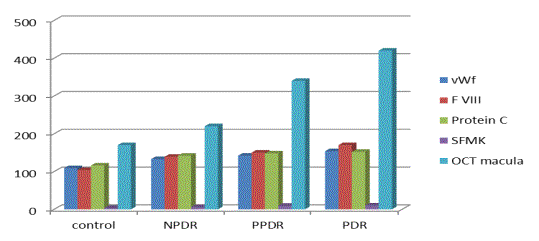
Illustration 1. The dependence of
DME hemostatic parameters prior to treatment.
vWf - activity of von Willebrand factor,%; F VIII - Activity Factor
VIII,%; Protein - Protein C activity,%; SFMK - mg%; OCT of the macula - the
thickness of the retina, um.
Growth indicators of
endothelial dysfunction (vWf, factor VIII, APS, SFMK) is correlated with an
increase in the incidence of diabetic macular edema and retinal thickness in
the macula in patients with DR. Propotevanie retinal capillaries leads to
retinal edema, diffuse due to leakage of plasma and locally in the formation of
microaneurysms. The first ends with a "soft exudates" and racemose
degeneration, and the second -"hard exudates" (Illustration 2).
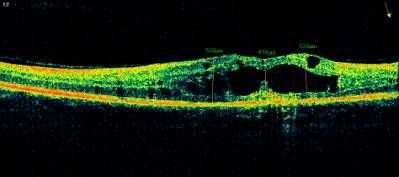
Illustration. 2. Eyeground of the patient to claim 52, with the PPDR
with DHS before treatment.
Analysis of the results of
some parameters of hemostasis and endothelial dysfunction (vWf, factor VIII,
APS, SFMK) and the thickness of the retina in the macula in patients with
clinical forms of DR after the treatment dalargin Vessel Due F, combinations of
these drugs with LC showed that there is a decrease thrombogenic activity in
the microvasculature of the retina, reducing the permeability of the
capillaries of the retina, which leads to the resolution or DHS, or to a
decrease in the thickness of the retina in the macula.
Reducing the values of some
parameters of hemostasis and endothelial dysfunction (vWf, factor VIII, APS,
SFMK) is characterized by stages of DR decrease thrombogenic activity in the
microvasculature and reduced permeability of small vessels of the retina,
leading to the resolution of the DHS.
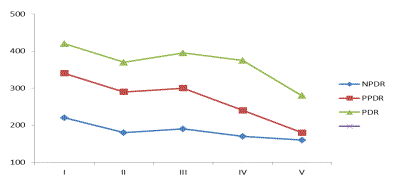
Illustration 4. Changes in the macular retinal thickness depending on the
method of treatment.
I - before treatment; II- Dalargin; III-
sulodexide
IV- Dalargin + sulodexide; V - Dalargin
sulodexide + + LKS
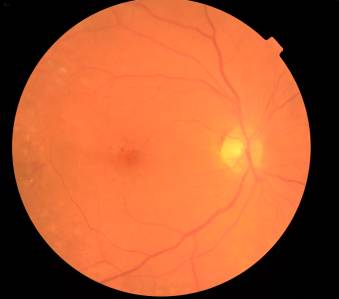
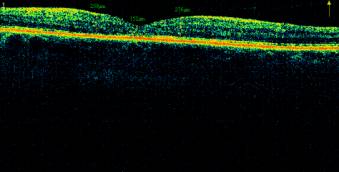
Illustration 5. The fundus and OCT macular
patient M., 52g. PPDR with DHS to resolve after combined treatment and LC.
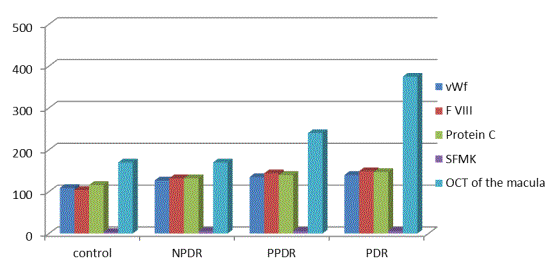
Illustration 6. Results of treatment in combination with DIR LC retina, depending on certain parameters hemostasis endothelial dysfunction and retinal thickness.
vWf - activity of von Willebrand factor,%; F VIII - Activity Factor
VIII,%; Protein - Protein C activity,%; SFMK - mg%; OCT of the macula - the
thickness of the retina, um.
After combined treatment in
combination with LC noted a slight decrease of the correlation coefficient for
two factors of endothelial dysfunction (vWf, VIIIf), respectively, to 0.89 and
0.84. This is caused by autoimmune
inflammation in the retina, as indicated by detection of antibody volchanochnopodobnogo
type (VA) 10%, in conjunction with the Leiden mutation in coagulation factor V
in patients with DME amid type 2 diabetes. We can assume that LK exacerbates
autoimmune inflammation of the retina in these patients. Therefore, the use of
LC is possible only after conservative treatment dolarginom, retinoprotektorami
and drugs, reducing vascular endothelium. In addition, laser coagulation of the
retina can be recommended only after the laboratory control of hemostasis.
Conclusions. 1. When
choosing a method of treatment must be considered clinical laboratory and
morphometric parameters characterizing the clinical picture of diabetic macular
edema (vWf, factor VIII, APS, SFMK, macular OCT) using an integrated approach
with the use of sulodexide, dalargina and laser photocoagulation of the retina.
2. It is important
to carefully select patients with DHS on the background of the DR type 2 for
the LC retina, paying special attention to the study of hemostasis at BA and
Leiden mutation of coagulation factor V.
References:
1. N.A. Gavrilova, O.E. Tishchenko
Effect of sulodexide on endothelial function in patients with diabetes and
diabetic retinopathy / Ophthalmology - diabetes diabet.- M., 2011.-¹ 2.- Ð.66-68.
2. Gatsu M.V. Complex system functionally
saving technologies lazerhirurgicheskih treatment of vascular and degenerative
diseases of the retina // Abstract of dissertations. on competition account.
degree of Ph.D. - Moscow-2008.- 50ð.
3. Ivanova N.V., Yarosheva N.A. Imbalance in
the hemostatic system and endothelial dysfunction in patients with diabetic
retinopathy // Eye magazine. - 2008.- ¹ 3. - Ð.33-37.
4. Il'inskii O.B., Spevak S.E., Solovyov A.I.,
et al. 1 Abstracts of All-Union Conference "Neuropeptides: their role in
physiology and pathology," Tomsk.- 1985.- Ð. 58- 59.
5. Ishchenko I.M., Milenikay T.M.The
effectiveness of the drug Vessel Due F diabetic patients with nonproliferative
retinopathy and preproliferative // Farmateka.- 2009.- ¹ 3.- Ð. 82-86.
6. O.G. Shilov New aspects of the pathogenesis
and treatment of diabetic retinopathy // Abstract of dissertations. on
competition account. degree of Ph.D. - Krasnoyarsk.- 2012.- 49ð.
About the Authors:
1. Shelkovnikova Tatyana, Senior Lecturer, Department of Ophthalmology,
MD, a doctor of the laser unit. (t.shelkovnikova@gmail.com, tel. +
7-923-618-19-72)
Kemerovo State Medical Academy of the Ministry of Health of Russia,
Kemerovo
2. Katsadze Junona Leonidovna, Ph.D., Professor, Senior Researcher,
Laboratory coagulation FSI Russian Research Institute of Hematology and Blood
Transfusion, St. Petersburg.
3. Takhchidi Khristo Periklovich, MD, Professor, Vice-Rector of the
medical work, GOU VPO Russian National Research University of N.I. Pirogovà Russian Ministry of Health, Moscow
4. Balashova Larisa Maratovna, MD, Professor, Head of the Central
Research Laboratory, GOU VPO Russian National Research University of N.I.
Pirogova Russian Ministry of Health, Moscow
5. Shishlyannikova Nina Yurievna, Ph.D., assistant professor of
biological, overall, Bioorganic Chemistry and Clinical Laboratory Diagnostics
Medical University KemGMA Health Ministry, Kemerovo.