Medicine/8. Morphology
ScD,
professor Petrenko V.M.
Centre for reabilitation of
motionless patients, St.-Petersburg, Russia
VISCERAL
LYMPH NODES IN ABDOMINAL CAVITY OF DEGUS: SPECIFIC FEATURES OF ANATOMY
Lymph nodes (LN) in abdominal
cavity of degus are not described in literature. I study these LN in 10 degus of 2-3 months old of both sexs by
preparation after fixation in 10% neutral formalin.
All investegated LN have bean΄s
shape. I divide them (fig.
1,2)
by topography on two groups: 1) the central LN, they lie about
celiac-mesenteric artery (1) and caudal mesenteric artery (1); 2) the
peripheral LN, they lie along branches of celiac-mesenteric artery hepatic,
splenic and cranial mesenteric arteries and ending branches of the last artery.
The short trunk of celiac-mesenteric artery in degus is the common beginning of
celiac and cranial mesenteric arteries. Small paraaortic or retropancreatic LN
(1), which lies about celiac-mesenteric artery, is the common for two groups of
LN the celiac and the cranial mesenteric.
Celiac artery divides on hepatic and splenic arteries at once. I find small
hepatic LN (2) on the left side from hepatic portal vein, small gastric or subpyloric
LN (1) between stomack and bulb of duodenum, small pancreatic LN (2) about
splenic artery and vein, between body and tail of pancreas. Splenic LN (2), the
most small among all visceral LN in the abdominal cavity, lie near hilus of
spleen and tail of pancreas. The cranial mesenteric artery in degus is short
because it divides on ending branches about duodenojejunal flexure. Own cranial
mesenteric or pancreaticoduodenal LN (3-4) surround bifurcation of soname
artery moreover the right of them (1-2) adjoin to its right branch and the left
of them (2) to the left branch
(ileocolic artery). I find conjestion of these LN at the beginning of common
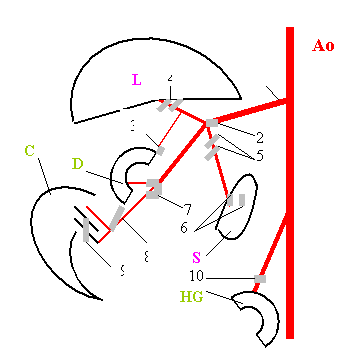 Fig. 1. Scheme
of placing of visceral lymph nodes (LN) in abdominal cavity of degus: Ao aorta; L liver; S spleen; D duodenum; C caecum; HG hind
gut; 1 celiac-mesenteric artery; 2 paraaortic LN; 3 gastric LN; 4 hepatic
LN; 5 pancreatic LN; 6 splenic LN; 7 pancreaticoduode-nal LN; 8 ileocolic
LN; 9 ileocaecal LN; 10 ρaudal mesenteric LN on the ρaudal mesenteric artery.
Fig. 1. Scheme
of placing of visceral lymph nodes (LN) in abdominal cavity of degus: Ao aorta; L liver; S spleen; D duodenum; C caecum; HG hind
gut; 1 celiac-mesenteric artery; 2 paraaortic LN; 3 gastric LN; 4 hepatic
LN; 5 pancreatic LN; 6 splenic LN; 7 pancreaticoduode-nal LN; 8 ileocolic
LN; 9 ileocaecal LN; 10 ρaudal mesenteric LN on the ρaudal mesenteric artery.
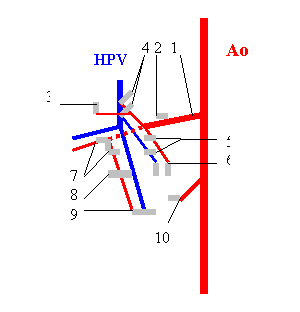 Fig. 2. Scheme
of placing of visceral lymph nodes (LN) in abdominal cavity of degus: Ao aorta; HPV hepartic portal vein; 1 celiac-mesenteric artery; 2-10 visceral
LN (desig-nations as on Fig. 1).
Fig. 2. Scheme
of placing of visceral lymph nodes (LN) in abdominal cavity of degus: Ao aorta; HPV hepartic portal vein; 1 celiac-mesenteric artery; 2-10 visceral
LN (desig-nations as on Fig. 1).
root of mesentery
and mesocolon, between duodenojejunal flexure and head of pancreas, near
confluence of right and left roots of cranial mesenteric vein. Ileocolic LN
(1), the most large among visceral LN in the abdominal cavity of degus, lies at
the end of common root of mesentery and mesocolon, about end of bundle of ileocolic blood vessels, about division of
ileocolic artery on the end branches. Ileocecalis LN (1), unstable, with sizes about
(a little smaller than) ileocolic LN, lies on the base of caecum, its medial
(right) surface, between initial part of ascending colon and end of ileum, but
in connection with ileum. So visceral LN in abdominal cavity of degus are
situated along odd visceral branches of abdominal aorta, among different inner
organs. The head of pancreas separates paraaortic, hepatic and pancreatic LN
(cranially) from pancreaticoduodenal LN (caudally), the common root of
mesentery and mesocolon pancreaticoduodenal LN from ileocolic LN, the base of
caecum ileocolic LN from ileocecalis LN, loops of intestine and ascending
colon cranial and caudal mesenteric LN.
Earlier
I studied visceral LN in abdominal cavity of white rat [1,2] and guinea-pig
[3]. Quantity of these LN in abdominal cavity variates among investigated rodents:
the largest in rat, the least in degus. These LN are situated always along
odd visceral branches of abdominal aorta celiac, cranial and caudal
mesenteric arteries and their branches. The largest numerous and variative
groupe of these LN I find about cranial mesenteric artery, the least about
caudal mesenteric artery (1-2). Special topography, reduction of general quantity
and subgroups of central cranial mesenteric LN in degus correlate with features
of its regional organogenesis, first of all the least liver among these
rodents. Just liver regulates interactions between another organs and vessels
in abdominal cavity of mammals, their growth and placing, including anlage LN.
REFERENCES
1. Petrenko V.M. Topography
of mesenteric lymph nodes in rat // Europ.J.Nat.Hist. 2011. N 4. P. 6.
2. Petrenko V.M. Lymph
nodes in basin of coeliac artery in rat // Europ.J.Nat.Hist. 2011. N 6.
P. 6.
3. Petrenko V.M. Visceral
lymph nodes in abdominal cavity of the guinea-pig. Topography and
classification //
Europ.J.Nat.Hist. 2013. N 1. P. 28-29.