KARACHUN
V.V.
NATIONAL TECHNICAL
UNIVERSITY OF UKRAINE "IGOR SIKORSKY KYIV POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE"
ZERO DISPLACEMENT OF THE
MOVING PART OF THE FLOAT GYROSCOPE IN THE STOCHASTIC SPACE OF PERTURBING
FACTORS
External inciting - kinematic and acoustic
– are considred as the processes determined
in time. Analytical providing of accordance of the of gyroscope parameters with the
nameplate requirements
in operating terms was satisfied by two differential equations
of the first and second approximation:
![]() (1)
(1)
![]() . (2)
. (2)
Thus,
the right part of the equation
(1) contained the
parameters of the
fuselage angular motion and acoustic vibration of the float surface in an obvious
form, in other words, acoustic vibration of the float surface [1] -
![]() , (3)
, (3)
or more precisely -
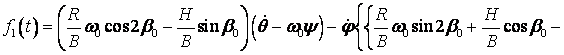
![]()
![]() ,
,
where ![]() is
a derivative in time from the
turning
angle about the sensitive axis of the device.
is
a derivative in time from the
turning
angle about the sensitive axis of the device.
In
its turn, the right part of equations (2) contains not only
the functions of the aircraft tossing and acoustic
vibration of
the float surface, but also the equation solution (1). Using the expression, the right part can
be written down as follows -
![]()
![]()
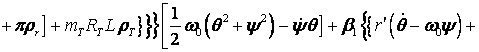
![]() (4)
(4)
![]()
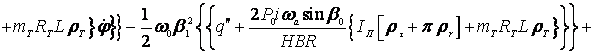
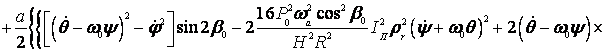
![]()
![]() .
.
At the determined character of external
inciting factors, task was traced to determination of the stable constituent of
the right part of the expression (4), in
other words
![]() ,
, ![]() 1,2 is a number of approximation and the systematic
error of ARS was calculated by
the formula -
1,2 is a number of approximation and the systematic
error of ARS was calculated by
the formula -
![]() . (5)
. (5)
On the contrary, when
the aircraft tossing and acoustic vibration of
the float surface have a stochastic structure, it
should be considered as the expected value
of instrumental errors. Thus
![]() . (6)
. (6)
Assume matematical expectation
of values ![]() and
their derivatives in time equals
zero. Mathematical expectation of
products of these values, at the same
time, can contain stable constituents.
and
their derivatives in time equals
zero. Mathematical expectation of
products of these values, at the same
time, can contain stable constituents.
For denotation of mathematical expectation
of values ![]() ,
,![]() ,
,![]() ,
,![]()
![]() ,
, ![]() and so
on, the symbols
and so
on, the symbols ![]() ,
,![]() ,
,![]() ,
,![]() ,
,![]() ,
, ![]() . From now
we can use formula (5) and calculate the instrumental errors in the moment
of time t. Mathematical expectation of the products
. From now
we can use formula (5) and calculate the instrumental errors in the moment
of time t. Mathematical expectation of the products ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() can
have stable constituents. We will denote them by symbols
can
have stable constituents. We will denote them by symbols ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() etc.
etc.
It is known from
the theory of chances, if
![]() , then mathematical expectation of the
products of two
these functions, calculated in various moments of time, is called the “correlation function of connection” :
, then mathematical expectation of the
products of two
these functions, calculated in various moments of time, is called the “correlation function of connection” :
![]() .
.
If ![]() , then this
function is called the autocorrelation function of
the stochastic process -
, then this
function is called the autocorrelation function of
the stochastic process -
![]() .
.
At ![]() we receive dispersion
of the stochastic process
we receive dispersion
of the stochastic process ![]() :
:
![]() .
.
On condition of stationarity of
the process we have -
![]() ;
; ![]() .
.
Dispersion of the stationary process is a stable value. Further on stationarity of process is not obligatory.
So we have:
![]()
![]()
![]()
Then
![]()
![]()
![]() (7)
(7)
Averaging of function
![]() can
be obtained without efforts, if the given correlation functions of connection,
which are present in expression
(7) of the combinations
can
be obtained without efforts, if the given correlation functions of connection,
which are present in expression
(7) of the combinations![]() ,
,![]() ,
,![]() ,
, ![]() ³
³ ![]() .
.
We will use the obtained correlation for the calculation of "shift of zero" in the first approximation. For this purpose
we take ![]() and
and![]() . In other words, we assume the absence of systematic rotation
of the base relatively
to the ingoing axis of the device. From here
the obvious equalities follow -
. In other words, we assume the absence of systematic rotation
of the base relatively
to the ingoing axis of the device. From here
the obvious equalities follow -
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() (8)
(8)
Averaging in time of
mathematical expectation of
"zero shift" is
determined by
the formula
![]()
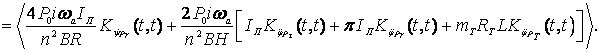 (9)
(9)
If we
use the known correlations
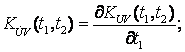
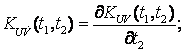
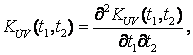
expression (9) can be written
down a little different:
![]()
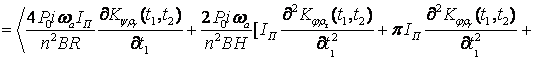
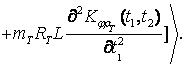 (10)
(10)
Thus, for determination of "zero
shift" in the
first approximation, it
is enough to know
the correlation functions of connection
between the
pitch angle ![]() and
resilient radial moving of the float side surface
and
resilient radial moving of the float side surface ![]() , and also
between the yaw
angle
, and also
between the yaw
angle ![]() and
radial
and
radial ![]() and
tangential
and
tangential ![]() moving
of the float side surface. In addition, it
must be known the correlation function of connection between
the yaw angle
moving
of the float side surface. In addition, it
must be known the correlation function of connection between
the yaw angle ![]() and
bend vibrations of the float’s end under the
action of acoustic wave. These functions can be determined experimentally.
and
bend vibrations of the float’s end under the
action of acoustic wave. These functions can be determined experimentally.
If we take
up the angles of the aircraft tossing and resilient
moving of the
float under the action of penetrating
acoustic radiation
as casual and stationary constrained functions, in other words, as those, for which the mutual correlation functions depend only on the
difference of moments of time
![]() , then it
is possible to write down
the following correlations -:
, then it
is possible to write down
the following correlations -:
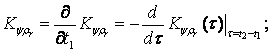
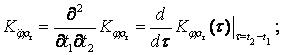 (11)
(11)
![]()
![]()
The "zero shift" will be calculated from (10), using the correlation (11) :
![]()
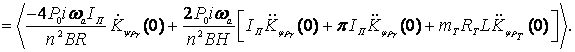 (12)
(12)
We will illustrate the
proven data. We
will calculate
the "zero
shift", for example,
at the following type of correlation
functions of
the connection -
![]()
Then
![]()
![]()
After a substitution
in the formula (12)
we have:
![]()
![]()
![]() . (13)
. (13)
We will pass to the
second approximation. The
right part of the equation
(11) contains two
types of elements – those, which do not
contain the decision of equation of the first
approximation ![]() and, opposite, those, which contain this
decision. The function
and, opposite, those, which contain this
decision. The function ![]() will
be written down as -
will
be written down as -
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
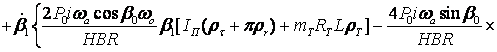
![]()
![]()
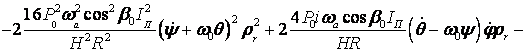
![]()
![]() .
(14)
.
(14)
Thus, we will obtain:
![]()
![]()
![]()
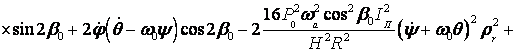
![]()
![]() ;
;
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
The mathematical
expectation of function ![]() can
be pointed now as a sum
of two elements
can
be pointed now as a sum
of two elements
![]()
and
further on we will to continue the calculation. If necessary,
it is possible
to define the third or
further approximations [2].
For the solution of the given task
we only will analyze
the first approximation.
Literature: