DEMANDS TO THE JUMPING
HORSE
Lutsenko M. V.,
Petrushko N. P.
Kharkov State
Zooveterenary Academy, Kharkov
The
object of the research and relevance. The
investigation has been carried out on jumping horses with the age of 7-15 years
from the equestrian sporting school of Kharkov State Zooveterenary Academy
(KSZA).
Jump – is a specific behavioral
act, which needs intensive activity of main physiological systems of horse
organism. At a jump a powerful biomechanical efforts develop in horse impellent
apparatus.
Measurements have great significance for jumping
horses [1]. Height in withers for jumping horse of high sporting class isn`t desirable less, than 167 cm. Horses of
hobby class can have a height from 160 cm. Because a horse with a height of 170
cm can clear a hurdle 110-120 cm due to gymnastics, and a horse with a height
of 160 cm must make considerable shoved effort. Lack of height can be
compensated by the lengthening of trunk only on 2-3 cm, because too lengthy
horses aren`t able for jumping, because of bed impulse conduction and back
trauma danger.
Horses with a height more than 177 cm are used in a jumping
seldom. Because at this height very large weight comes down on horse`s joints
during the landing. These horses are often unfit for sport by 13-15 years. Besides
that, at this weight correlation of “effective muscular mass” to the total body
weight begins to decrease and more “ineffective weight” falls per unit of
muscular fibre. Therefore, efficiency of motive apparatus decreases. Optimum
index of mass for jumping horse of high sporting class is 3,4-3,7. In last time
specialists prefer that this index will be about 3,4, because of increasing
speed of jumping routes passing and additional demands to the horse endurance. Shortening
of trunk isn`t desirable and can consist 2-3 cm, because it leads to
considerable lowering of the back suppleness. Thus, desirable measurements for
jumping horses are: the height in the withers (HW) - 167 - 169 ñm, the length of the trunk (LT) - 164 - 166 ñm, the girth of the chest (GC) - 193 - 195 ñm, the girth of the metacarpus (GM) - about 22 cm.
The necessity to verify the above information on
practice determines the relevance of the research.
Research methods. All measurements have been taken by measuring tape and measuring stick, index
of mass has been calculated by the method described in special literature.
Analysis of jumping technique has been carried out on the base of photo and video
stuffs of trainings and competitions.
Research results. Comparison of the best jumping horses from the equestrian sporting school
of KSZA measurements with the desirable measurements are shown in the table 1.
Table 1.
Indices of measurements of jumping horses from the equestrian
sporting school of KSZA
|
Name |
HW, ñm |
GC, ñm |
GM, ñm |
Index of mass |
|
Ficus |
160 |
188 |
22,0 |
3,4 |
|
Sens |
164 |
188 |
20,5 |
3,1 |
|
Hala |
162 |
193 |
20,0 |
3,3 |
|
Barina |
170 |
194 |
21,0 |
3,2 |
|
Rosinka |
163 |
186 |
19,5 |
3,0 |
|
At average |
163,8 |
189,8 |
20,6 |
3,2 |
|
Desirable measurements |
167-169 |
193-195 |
about 22 |
3,4-3,7 |
Jumping horses of the equestrian sporting school yield
to optimal indices for horses of this way of using by these measurements and index of mass. But they take part in
the competitions of different level enough successfully (table 2) [4]. Because measurements haven`t
decisive significance without the biomechanical and the right technique of a
jump.
Table 2.
Information about taking part in jumping competitions
of horses from the equestrian sporting school of KSZA
|
Name |
Kind of sport |
Amount of starts |
Local competitions |
Regional competitions |
Allukrainial
competitions |
||||||
|
1 places |
2 places |
3 places |
1 places |
2 places |
3 places |
1 places |
2 places |
3 places |
|||
|
Ficus |
jumping |
24 |
1 |
3 |
- |
4 |
2 |
3 |
- |
1 |
- |
|
Sens |
jumping |
19 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
- |
|
Hala |
jumping |
19 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
3 |
2 |
3 |
- |
- |
- |
|
Barina |
jumping |
16 |
2 |
2 |
3 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
- |
- |
- |
|
Rosinka |
jumping |
16 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
- |
- |
- |
Analysis of horse jump biomechanical.
Immediate before jump
horse “gathers”, thus it takes a posture, which is promoted to accomplishment
of powerful shove and to realize of suitable flight trajectory [2].
At the clear of a hurdle
at first forelimb take off the Earth and rush upwards together with the humeral
belt. Hindlimb become straight sharply and push off the ground to forward and
upward (fig. 1). During the shove horse`s mass gain a supply of kinetic energy,
which allows to realize all following phases.
Figure 1 – Phases of horse jump
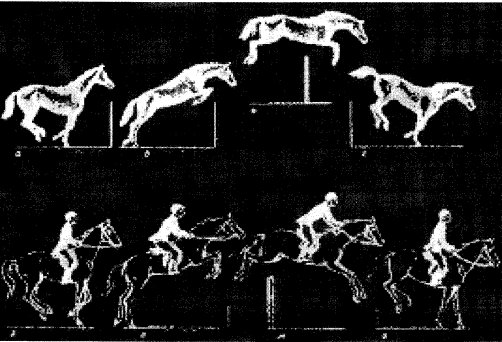
After horse`s tearing
off the ground supply of kinetic energy couldn`t be supplement. Their rational expenditure
by means of redistribution of biomechanical efforts and beginnings of reactive
accelerations has decisive significance.
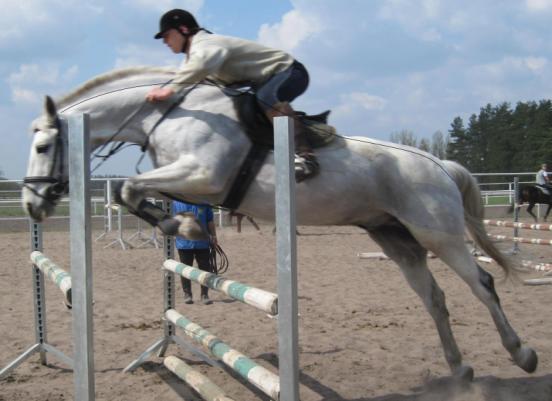
When the humeral belt of a horse is
transferred through the hurdle, its pelvic part is much lower. Then the humeral
belt passes on the horizontal flight, after that a horse sharply throws
forelimb and a head downward (fig. 2). At some short moment it creates the
spine bend named “baskul” (fig. 3). Namely active “throw” of the head and
humeral belt downward creates that additional reactive force, which is
necessary for raising of horse`s trunk to the level of the hurdle height and
transferring of pelvic belt and hindlimb through it. If arched state will be taken
before a jump, that is to sink the horse`s head, then first centre of mass will
sink down just before a jump and horse must to spend more energy for jump [3].
Figure 2 – gelding Ficus

Figure 3 – gelding Ficus

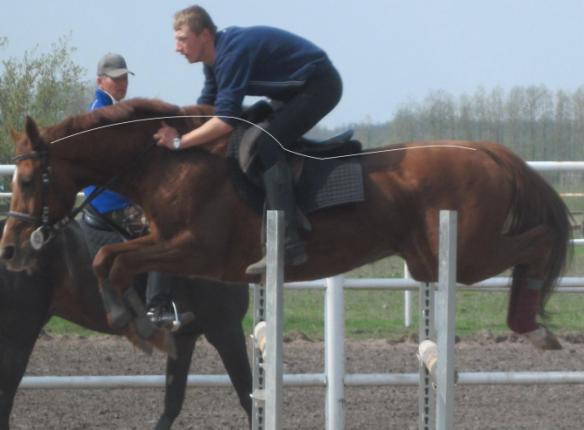
At the passing over a hurdle the stretch
into a string, when the head, neck, trunk and limbs are on a one straight, is
ideal for horse.
Maximal height of a jump depends on the centre of weight and mass arrangement.
Maximal speed of a hurdle`s clear depends on a speed of approach to the hurdle,
a speed of a horse forehand raising on the angle of repulsion, a speed of the
hindlimb repulsion and the optimal trajectory of a jump. Parts of horse`s body
must move as much as possible quickly relatively of each other for the achieved
of maximal speed of a jump [5].
Figure 4 – mare Rosinka

Conclusions. Horse`s exterior and measurements have direct
influence on its sporting achievement in a jumping. But the right technique of
jump, which can considerably compensate shortcomings of the exterior, plays decisive
significance. That`s way at the horse`s choose it`s necessary to follow by complex
estimation of its exterior and jumping features.
Literature
1. Dyurst U. Exter`er loshadi // Perevod
s nemetskogo V. A. Markson /. U. Dyurst. – Ì.;L.:
Sel`hozgiz, 1936. – 343 s.
2. Zemlyanskij V. N. Î
nekotoryh zakonomernostyah v biomehanike dvizheniya i opory loshadi
kak factorah, vliyayush`ih na eyo osnovnuyu productivnost` / V. N. Zemlyanskij //
Avtoreferat dissertaciya na soiskanie uchonoj stepeny doctora selskohozyajstvennyh
nauk. – Ê., 1956. – 20 s.
3. Laskov À.À. Podgotovka loshadej verhovyh porod dlya sporta i eksporta. Vyezdka
molodoj sportivnoj loshadi / À.À. Laskov // Konevodstvo i konnyj sport, 2004.
- ¹ 2. – s. 25 – 26.
4. Rezultaty podscheta
rejtinga loshadej KSSH HGZVA.
5. Latka Î.Ì., Bondarenko Î.V., Volkov D.À. / Rekomendacii z vyprobuvan` konej ukrains`koi verhovoi porodi za ruhovymy ta strybkovymy yakostyamy / Î.Ì. Latka i dr. – ²Ò
UÀÀN. – Harkiv, 2006. – 8 s.