UDC 639.371
THE CORELLATION OF PADDLEFISH PARAMETERS AND INTERNAL ORGANS
Tarasenko
O. Î., Tertyshny O. S.
Kharkiv
State Zooveterenary Academy, Kharkiv
The
object of the research and relevance. Paddlefish
(Polyodon spathula
Walbaum)
is a freshwater fish, pelagic inhabitant of large rivers and clear lakes of
North America. It reaches length about 216 cm and weight of 83 kg.
The most characteristic morphological feature of
paddlefish is the presence of the rostrum on his head - flat elongated paddle-shaped
snout. The length of the rostrum is about one third of the total length of the
body. Scales on most of the paddlefish body surface is missing. In front of the
mouth opening, on the outer surface of the rostrum, there are two antennae with
length of 3-4 mm. Operculum in the back have an elongated blade, which
sometimes reaches the pectoral fins and has a distinctive spotted color. In the
difference of other sturgeon fishes, paddlefish have mouth
apparatus of non-sliding type. In paddlefish of adult age teeth are missing
[6].
Paddlefish has the brachiate filtration apparatus that
is not characteristic for the sturgeon. He is the typical planktonofag, which
is feeding by zooplankton, phytoplankton and detritus. In the process of
feeding organism is filtered out nutrients of the water by the gill stamens,
located on the cartilaginous plates of gill arches. Area of the filtration
apparatus in paddlefish is twice bigger, then in bighead carp with the same
mass. Structural feature of the gill apparatus allows to the fish to strain off
both microscopic algae and larger forms
of zooplankton [1].
Given the above, paddlefish is promising object of the
aquaculture in pond fish industry. He is not a competitor for food with most of
pond fishes, easily endures winter conditions, has tasty meat, like all sturgeon,
reaches a considerable size. All this facts makes paddlefish attractive for
growing, in both industrial and farms. At the same time, information about it
is very scarce, and many aspects, which concern of the paddlefish, have not
been studied, that determines the relevance of research.
Research
methods. Research of paddlefish has been carried out in
accordance with the methods described in the literature [2, 3, 4, 5]. Paddlefish
parameters have been determined according to the diagram (Fig. 1).
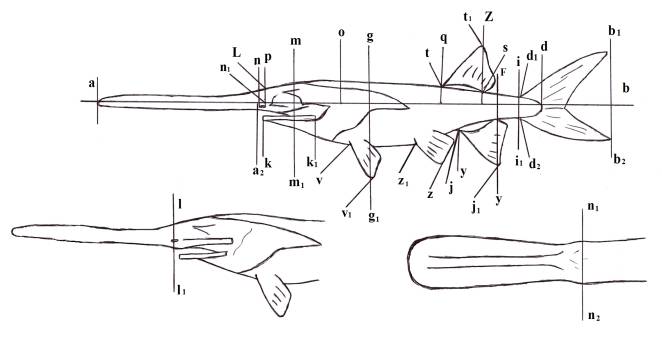
Fig.1. Scheme of paddlefish
measurement
àb – the length of the fish; ad
– the length without caudal fin;
od – the length of the body; an – the length of the snout (rostrum); np – the diameter of the eye; ðî –behindeye space; ln1
– the height of the forehead; nn2
– the width of the forehead; àà2 – the length of the upper jaw; êê1 – the length of the lower jaw; àî – the length of the head; mm1
– the height of the head near the neck; ll1 – the height
of the head through the middle of the eye; gg1
– the largest height of the body; ii1 – the smallest
high of the body; aq – predorsal distance;
zd– postdorsalnoe
distance; fd– the length of the tail
sheet;
av –antepektral distance; az – anteventral distance;
àó –
anteanal distance; qs – the length of
the dorsal fin basis;
tt1 – the largest height of
the dorsal fin; óó1 –the length of the anal fin basis;
jj1– the largest height of the
anal fin; vv1– the length
of the pectoral fin;
zz1 – the length of the pelvic
fin; vz – pektoventral distance; zó – ventroanal distance; d1b1
– the length of the upper blade of the caudal fin;
d2b2 – the length of
the lower blade of the caudal fin.
Sizes have been determined by measuring boards, tape
and calipers with electronic reading MIOL. Internal organs of paddlefishes have
been weighed with using of electronic scales. The fishes have been of the same
age (of 3 years) (Fig. 2). The number of investigated fish was 8. The males of
paddlefish have been taken for the investigation.

Fig. 2.The investigated
party of paddlefish
Research
results. The results of paddlefish measurements and weighing are
shown below in the tables 1-2.
Table 1
The correlation of paddlefish external parameters (at average of eight
fishes), cm
|
Parameters |
Indices |
Per
cent to body length |
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
The length of the body |
76,5 |
- |
|
The length of the trunk |
31,5 |
41,2 |
|
Industry
length |
45,3 |
51,2 |
|
The largest height |
10,7 |
14,0 |
|
The smallest height |
3,0 |
3,9 |
|
Predorsal
distance |
29,9 |
39,1 |
|
Predorsal distance with the rostrum |
50,0 |
65,4 |
|
Postdorsal
distance |
9,6 |
12,5 |
|
Anteanal
distance |
33,8 |
44,1 |
|
The length of the tail sheet |
5,9 |
7,7 |
|
Anteventral
distance |
24,7 |
32,3 |
|
Pektoventral
distance |
11,6 |
15,2 |
|
Ventral
distance |
9,1 |
11,9 |
|
The length of the dorsal fin basis |
6,3 |
8,2 |
|
The height of the dorsal fin basis |
9,5 |
12,3 |
|
The length of the anal fin basis |
12,9 |
16,9 |
|
The height of the anal fin basis |
7,9 |
10,3 |
|
The length of the pectoral fin |
6,7 |
8,7 |
|
The length of the pelvic fin |
5,4 |
7,0 |
|
The largest girth of the body |
27,4 |
35,8 |
|
The smallest girth of the body |
10,0 |
13,1 |
|
The length of the head |
8,8 |
11,5 |
|
The length of the snout |
19,7 |
25,7 |
|
Eye diameter |
1,0 |
13,1 |
|
Behindeye space |
8,8 |
11,5 |
|
The height of the head |
7,3 |
9,5 |
|
The width of the forehead |
4,5 |
5,8 |
|
The width between the eyes |
3,9 |
5,1 |
|
The height of the forehead |
1,2 |
1,6 |
|
The height of the head in the center of the eye |
2,7 |
3,5 |
|
The length of the upper jaw |
8,3 |
10,8 |
|
The length of the lower jaw |
7,5 |
9,8 |
|
The length of the upper blade of the caudal fin |
12,4 |
16,2 |
|
The length of the lower blade of the caudal fin |
11,5 |
15,0 |
Table 2
The correlation of paddlefish internal organs mass (at average of eight
fishes), g.
|
parameters |
data |
Percentageofbodyweight |
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
Body weight |
1128,8 |
|
|
Heart |
1,2 |
0,1 |
|
Liver |
10,5 |
0,9 |
|
Pyloric part of the stomach |
11,9 |
1,1 |
|
Fore-stomach |
2,7 |
0,2 |
|
Gall-bladder |
0,5 |
0,04 |
|
Pyloric
gland |
4,3 |
0,4 |
|
Duodenum |
2,8 |
0,3 |
|
Spleen |
1,4 |
0,1 |
|
Spiral
intestine |
12,9 |
1,1 |
|
Rectum |
0,5 |
0,04 |
|
Pancreas |
0,4 |
0,03 |
|
Swimming-bladder |
4,6 |
0,4 |
|
Oesophagus |
2,3 |
0,2 |
|
Testicle |
18,7 |
1,7 |
|
Kidneys |
1,6 |
0,1 |
Conclusions. Based on the above, we conclude that the paddlefish is valuable fish, as
all the sturgeon. It relates to the ganoid fishes, so he has cartilage skeleton
at most, that is edible. Overall about 85% of paddlefish body weight is edible,
that once again proves its prospects, taking into account also that it can be
grown in ponds, and it does not compete for food with most pond fishes, mainly
carp.
Literature
1. Andryush`enko À. ²., Àlimov S. ²., Zaharenko Ì. Î., Vovk N. ². Tehnologii vyrobnyctva ob`ectiv akvacul`tury. – Ê., 2006. – s.271-302.
2. Ìål`nik Î. P., Kostyuk V. V., Shevchenko P. G. Anatomiya ryb / Pid redakcieyu Î.P. Ìål`nyka. – Ê.: Centr uchbovoi literatury, 2008. – 624 s.
3. Ìîrfologichni doslidzhennya ryb: Ìåtodychni rekomendacii. / Pylypenko Yu. V., Rylov V. G., Kornienko V. Î., Grudko N. Î. – Herson: Êîlos, 2006. – 22 s.
4. Òårtyshnyj Î. S., Òîvstyc V. F. Rybnyctvo z osnovamy gydrobiologii. –Harkiv: Espada, 2009. – 288 s.
5. Òårtyshnyj Î. S., Panchyshnyj Ì. Î., Tarasenko Î. Î. Udoskonalennya sposobiv doslidzhen` stosovno rybnyctva. Problemy zooinzhenerii ta veterynarnoi medycyny: Zbirnyk naukovyh prac` HDZVA. Vypusk 19, chastyna 1. Sil`s`kogospodars`ki nauky - Harkiv, 2009. – s. 244-249.
6. Sherman ². Ì., Kornienko V. Î., Shevchenko V. Yu. Osetrivnyctvo / ². Ì. Sherman, V. Î. Kornienko, V. Yu. Kornienko, V. Yu. Shevchenko – Herson: Oldi-Plyus, 2011. – s. 55-58.