Ñåëüñêîå õîçÿéñòâî.
4. Òåõíîëîãèè õðàíåíèÿ è ïåðåðàáîòêè ñåëüñêîõîçÿéñòâåííîé ïðîäóêöèè.
Professor
Telezhenko L., postgraduate Kashkano M.
Odessa
National Academy of Food Technologies, Ukraine
Mathematical modeling of the recipes of grain casseroles
with prescribed properties
It is
known that food contributing to the normal functioning of organs and body
systems is the basis of a healthy diet. Today, a promising area of
research and technological developments in the food industry is production of
food that meets the requirements of healthy nutrition. The combination of
different products provides the delivery of essential nutrients for body in the
best way. In addition, the processes of assimilation and exchange of micronutrients
are often activated in the presence of other nutrients [1]. Thus, the development of
polycomponent recipes will increase their biological value by combining
proteins with different amino acid composition. Therefore, a major line of
research in the field of healthy diet is the production of products with polycomponent
composition including both major nutrients and micronutrients such as vitamins
and minerals [2].
With
good reason, the largest segment of the human diet is occupied by cereals, to
which the human body and digestive system is genetically adapted. Cereals play a
special role in the human diet. The grain-based products, which are the main sources
of such nutrients as protein, complex carbohydrates, fiber, vitamins and
minerals, are an important part of the diet. These products are potent sources
of energy, that’s why grain-based meals are usually recommended to eat as
breakfasts. At the same time, the plant proteins of cereals and products of
their processing have unbalanced composition, and therefore monocomponent cereal-based
meals have low consumer properties. According to the theory of the rational
nutrition, people have to consume special products with optimal component
ratio. Despite the health benefit of porridges, nutrient composition of these
meals is not balanced. The problem of increasing the biological value of food
products from cereals and balancing its chemical composition is relevant, and
its solution will help to expand the range of cereal products and implement
developed technologies in production.
The objects
of the research were cereal casseroles. The task of expanding the current range
of these culinary products in food technology included changing of the grain
recipe components and additional flavor components, adjustment of the nutritional
value and improving consumer characteristics of the grain casseroles, that was
solved by mathematical modeling of the recipes. The mass fraction of essential
amino acids limiting in selected raw materials (lysine, tryptophan and
methionine) and the mass fraction of recipe components were reflected in the
limitation of the "Search solutions" add-in. As a result of the
mathematical modeling design a number of recipes were obtained, two of which
are shown in Table 1. Grain composition in developed recipes was extended to three
species. In order to obtain products with a distinct structure inclusion of the
pearl barley that contains a significant amount of soluble fiber
(β-glucans) and retains the shape of the grains during prolonged cooking was
proposed. Introduction of additional specific components helped to improve the
organoleptic properties and increased content of biologically active substances.
Table 1 – Recipes of
polycomponent grain casseroles
obtained by computer designing
|
Ingredients |
Mass fraction,% |
|
|
Recipe ¹ 1 “Golden” |
Recipe ¹ 2 “Grainy” |
|
|
Millet |
28.0 |
- |
|
Buckwheat |
19.7 |
- |
|
Rice |
12.0 |
- |
|
Pearl
barley |
- |
27.5 |
|
Wheat
grits |
- |
22.7 |
|
Maize
grits |
- |
8.0 |
|
Eggs |
27.0 |
28.0 |
|
Candied ginger |
5.0 |
- |
|
Butter |
4.0 |
3.5 |
|
Turmeric |
1.0 |
- |
|
Pignolia
nuts |
- |
6.0 |
|
Sugar |
3.0 |
4.0 |
|
Vanilla
sugar |
0.3 |
0.3 |
In
developed recipes mass fraction of sugar added into the dish was reduced to 2.5...3.3
times in comparison with analogue (wheat casserole). Reducing sugar content in
the dish, which is a source of complex carbohydrates with a low glycemic index,
provides a slight rise of sugar and insulin levels and prolonged feeling of
satiety after the consumption. Margarine, as a source of trans-fat was replaced
with butter. Some specific ingredients such as candied ginger, turmeric and pignolia
nuts were added. The protein content of eggs was increased by 2.7...2.8 times [3].
Reflecting
the part that swelling and cooking of the different types of cereals varies
rapidly, the length of hydrothermal treatment was determined by setting the
hardness changes of the grits during cooking. Reduction a product to the
culinary readiness corresponded the time at which the hardness of grits was in
the range of 0...5 ºF. The data revealed a sequence of technological
operations when cooking casseroles that are reflected at Gant chart for example
of cooking casserole "Grainy" (Fig. 1).
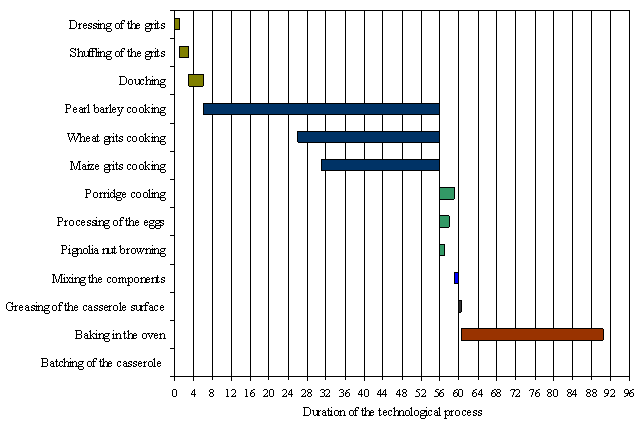
Fig. 1.
Technological process of cooking casserole “Grainy”
It
should be noted that cooked casseroles have high organoleptic properties in
addition to balanced nutrient composition. Heterogeneous texture of the
casserole “Grainy” caused by the presence of pearl barley that keeps its shape
after long grain hydrothermal treatment. Adding a small amount (6%) of roasted
pignolia nuts to the recipe gives the casserole a specific aroma and full
taste. A small mass fraction of vanillin (0.3 %) promotes the formation of fine
aroma, keeping aroma of natural materials, transformed under the influence of
cooking. Baked “Grainy” has a completely balanced recipe composition through
the optimal selection of ingredients and the inclusion of additional sources of
fat – pignolia nuts. Inclusion of the millet and candied ginger to the recipe of
casserole "Golden" gives the finished product a yellowish-golden
color. Adding of turmeric as a source of phosphorus, iron, iodine, vitamin C, B2,
B3 and C increased biological value of the product.
In such
a manner, the technology of polycomponent grain casseroles with high
nutritional value was developed by determining the compatibility of recipe
ingredients and their selection by quantitative computer-aided design and
sequencing of technological operations.
References
1. Poznyakovskii, V.M. Physiology of nutrition / V.M. Poznyakovskii, P.E.
Vloshchinskii, T.M. Drozdova. – SUI, 2007. – 352 p.
2. Reinivuoa, H. Harmonisation
of recipe calculation procedures in European food composition databases // H. Reinivuoa, S. Bellb, M-L. Ovaskainena // Journal of
Food Composition and Analysis. – 2009. – Vol. 22.
– P. 410-413.
3. Zdobnov, A.I. Collected recipes of dishes and
culinary products for catering establishment / A. I. Zdobnov, V. A. Cyganenko. – K.: A.S.K, 2002. – 656 p.
4. Telezhenko, L.M. To the question of the development
of porridge compositions with functional purpose / L.M. Telezhenko, N.A.
Kushn³r, M.A. Kashkano // Progresivny tehn³ka ta tehnolog³¿ harchovih
virobnictv restorannogo gospodarstva ³ torg³vl³. – 2013. – ¹ 1 (17). – P.
10-17.