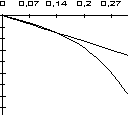Òåõíè÷åñêèå íàóêè/2. Ìåõàíèêà
D.tech.scien. Artamonova
E.N.
Saratov State Technical University
n.a. Gagarin Y.A., Russia
Reliability
of soil bases
In
this paper we study the deformation and durability cylindrical shell
on the basis of the underlying. For a basis of model building we take the model of
elastic foundation Vlasov-Leont'ev.
To account for the deformation
of the rheological base used by the integrated form
of the law of viscoelastic deformation. The resulting resolving equations are presented in increments according to the method of successive perturbation parameters V.V. Petrov [1, 2].
The approach is based on an extensive
literature review of current damage concepts included in current
mechanistic-based design procedures, soil permanent deformation laboratory
data. Design outputs are compared in terms of reliability and thickness using
these design procedures. It is shown that the provides higher reliability
values compared to the probabilistic procedure. All the existing subgrades fail
distress reliability such as rutting and top down cracking reliabilities.
Currently uses a single load P
value to deal with variability associated with subgrade
strength design. Is used to generate full scale subgrades response and
performance data for development and verification of subgrades design
criteria. The physical properties of
subgrades structures significantly influence both the response of the subgrades
to applied loads and the long-term performance.It is, therefore, of the utmost
importance that full scale test subgrades be constructed with uniformity in
material properties, layer thicknesses, and other considerations for which
non-uniformity might result in nonrepresentative and nontypical behavior and
failures. Current mechanistic-based design methods for the design of subgrades use vertical
strain criteria to consider foundation rutting.
A
considerable number of measurements of the physical properties test basis were made at all stages of construction and
after construction was completed. The
measurements were made for three purposes: construction quality control,
construction acceptance, and material characterization. The material
characterization tests were performed to provide information for theoretical
modeling and were not related to construction and contractual requirements.
In
tackling the used mathematical modeling of static viscoelastic
structural elements. You must have
the equilibrium equations, boundary conditions, and equation of state relations
for the equation of state parameter
changes on the parameters of the
external process. Boundary conditions - the simple
support.
Equation
of state in increments:
![]()
Increments of displacements of points:
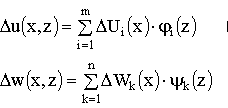
The unknown functions ![]() ,
,![]() ; and - dimensionless
; and - dimensionless ![]() ,
,![]() .
.
Moving
the base points:
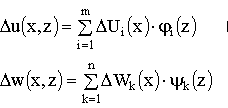
The resolving equations:
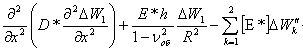
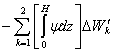
![]() .
.
Here [1]:
![]() ,
,
![]()
![]() .
.
![]() - elastic modulus.
- elastic modulus.
D*, E*- Volterra integral operators.
The
theory of hereditary creep
includes all the theories based on rheological models.
Condition of reliability ε ≤ ε
destructiv., (ε – deformation). To solve this problem
apply the variational method of Bubnov-Galerkin, the calculation is
performed on small intervals of
time.
L
= length of casing
5 m, the wall thickness h = 0,4 m, the shell
radius R = 3m, Poisson's
ratio ν = 0,35.
Plots of the stresses and strains of
the middle surface of the shell are shown in fig. 1. Taking into account nonlinear properties (curve 1) significantly affect the results of the numerical calculation [3].
figure 1
References:
1. Petrov V.V. Inozemtzev V.K., Sineva N.F.
Construction of model of the non-uniform basis at a
varied level of earth waters // Interuniversity scientific collection.- Saratov:
SSTU, 2002.- 260 p.
2.
Petrov V.V. Dimensional model of nonlinear
deformable heterogeneous base// Interuniversity scientific collection.- Saratov: SSTU, 2007.- P.6-12.
3. Artamonova E.N. On the design of
slabs on the basis of a non-uniform // Moskau: INGN,
2012.- P. 4.