Cand.Tech.Sci. Potapov A.V.
Volga region branch
Moscow State University of Railway Engineering (MIIT)
Transport system of the city
in a context of environmental problems
The
modern city transport system (TS) of Russia doesn't maintain criticism. To
understand that it is necessary to make for improvement of its work, and thus
to improve to some extent quality of life to two thirds to the Russians who are
living in city conditions and daily participating in transportation process, it
is necessary to study a question of the principles of the structure of
effective city transport system. In the course of studying, design and
designing it is important to define, by what criteria it should be estimated.
As M.G.Krestmeyn considers, target criteria of efficiency of the of the city
are known standards of expenses of time and street road network (SRN) capacity
at perspective level of automobilization [1, page 3]. Speaking in other words, TS
of city will be rational if the sum of time of movement of the population and
movements of freights is minimum, and the number of participants of movement
and volume of freights will be maximum (![]() ) for a certain period of time.
) for a certain period of time.
For the purpose of
comprehensive study of a question of criteria of an assessment of the TS of the
city we will imagine the ideal city with an area of S and one vehicle in this
city. In such hypothetical city there
are no constructions and vehicles which would prevent this vehicle to move in
any direction and to reach desirable result (transportation of people and (or)
freights) with the minimum expenses of time at this level of development of
equipment. The probability of
achievement of this result will be equal.
As one vehicle, probability of participates in the TS of this city that
the number of participants will be maximum, it is possible to determine by a
formula:
![]() , (1)
, (1)
where - ![]() - probability of that the number of participants will be maximum;
- probability of that the number of participants will be maximum; ![]() - maximum number of
participants of movement.
- maximum number of
participants of movement.
As these events are independent, the TS will
be the most effective with probability:
![]() , (2)
, (2)
where ![]() - criterion of an assessment of the TS of the city;
- criterion of an assessment of the TS of the city; ![]() - probability of movement of
people or freights with the minimum expenses of time;
- probability of movement of
people or freights with the minimum expenses of time; ![]() - probability of that the number of participants of movement (people or
freights) will be maximum;
- probability of that the number of participants of movement (people or
freights) will be maximum; ![]() - maximum number of participants of movement.
- maximum number of participants of movement.
Now
we will imagine other situation. In the
same hypothetical city with an area of S there are constructions, natural or
artificial obstacles, reserve territories, etc., Square S1, and also
other vehicles with a total dynamic dimension:
![]() , (3)
, (3)
where ![]() - a total dynamic dimension of vehicles;
- a total dynamic dimension of vehicles; ![]() - dynamic dimension
- dynamic dimension ![]() the vehicle;
the vehicle; ![]() - number of the TS vehicles of the city. Then the TS of the
city will be the most effective with probability:
- number of the TS vehicles of the city. Then the TS of the
city will be the most effective with probability:
![]() , (4)
, (4)
where ![]() - criterion of an assessment of the TS of the city;
- criterion of an assessment of the TS of the city; ![]() - square of the city;
- square of the city; ![]() - the area built up
or reserve, etc. territories;
- the area built up
or reserve, etc. territories; ![]() - total dynamic dimension of vehicles;
- total dynamic dimension of vehicles; ![]() - street road network area.
- street road network area.
As, ![]() , (5)
, (5)
where ![]() - the area built up or reserve, etc. territories;
- the area built up or reserve, etc. territories; ![]() - square of the city;
- square of the city; ![]() - street road network area, finally, we have:
- street road network area, finally, we have: ![]()
 , (6)
, (6)
where ![]() - criterion of an assessment of the TS of the city;
- criterion of an assessment of the TS of the city; ![]() - square of the city;
- square of the city;
![]() - total dynamic dimension of
vehicles;
- total dynamic dimension of
vehicles; ![]() - street road network area.
- street road network area.
And at ![]()
![]() . In two extreme
cases
. In two extreme
cases ![]() =0 and
=0 and ![]() =
=![]()
![]() =0. After function
differentiation
=0. After function
differentiation![]() on
on ![]() the maximum value of criterion
is found
the maximum value of criterion
is found ![]() at
at ![]() . The flat problem is so
solved. The volume problem is
solved similarly:
. The flat problem is so
solved. The volume problem is
solved similarly: 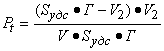 , (7)
, (7)
where ![]() - criterion of an assessment of
the TS of the city;
- criterion of an assessment of
the TS of the city; ![]() - volume of city space;
- volume of city space; ![]() - total dynamic volume of vehicles;
- total dynamic volume of vehicles; ![]() - street road network area;
- street road network area; ![]() - the established high-rise dimension in SRN.
- the established high-rise dimension in SRN.
And at ![]()
![]() . So, at aspiration
of the area of a street road network to infinitely big size, the criterion of
an assessment of the TS of the city can be determined by the relation of total
dynamic volume of vehicles to the volume of city space. At continuous improvement of the TS of the
city, its approach to ideal when
. So, at aspiration
of the area of a street road network to infinitely big size, the criterion of
an assessment of the TS of the city can be determined by the relation of total
dynamic volume of vehicles to the volume of city space. At continuous improvement of the TS of the
city, its approach to ideal when ![]() , it is possible to reach ideal model of city settlements - the
city," turning from "mechanism" in "organism"; the city in which all elements start
interacting among themselves [2, page 105]". In the modern cities the area of a street road network
, it is possible to reach ideal model of city settlements - the
city," turning from "mechanism" in "organism"; the city in which all elements start
interacting among themselves [2, page 105]". In the modern cities the area of a street road network ![]() doesn't exceed 10%,
the total dynamic dimension of vehicles at o'clock "peak" makes about
50% of the street road network area.
doesn't exceed 10%,
the total dynamic dimension of vehicles at o'clock "peak" makes about
50% of the street road network area.
Thus, estimating
the TS of the modern Russian cities including Saratov, by the offered
criterion, it is possible to conclude that their efficiency doesn't exceed (2 …
3) %. The transport problem of the modern cities traditional methods can't be
solved. For this purpose it is necessary to change and town-planning and
architectural fabric of the city. The analysis of technical solutions in the
field of town-planning shows that most effectively the transport problem is
solved in the cities of the futurologists consisting of the area with
infinitely large number of routes (thus ![]() ) and one grandiose building, containing hundreds thousands and even
million people, and also all elements of the city - housing, cultural -
consumer services, production, etc. [2, page 135]. Rather effectively the
transport problem is solved in the city in which architects put houses on
columns ("city-wood") [2, by page 140], as much as possible releasing
an urban area, thus
) and one grandiose building, containing hundreds thousands and even
million people, and also all elements of the city - housing, cultural -
consumer services, production, etc. [2, page 135]. Rather effectively the
transport problem is solved in the city in which architects put houses on
columns ("city-wood") [2, by page 140], as much as possible releasing
an urban area, thus ![]() also aspires to infinitely
big size.
also aspires to infinitely
big size.
Development of a
transport network in volume of city space (on the earth, underground and over
the earth) will allow to increase efficiency modern the city TS, at least,
three times. Transport builders actively master today land and underground
space of the city. Thus the elevated space practically isn't used by them
though now there are considerable practices on construction of constructions of
trestle type, trailing and guy designs, etc., but, unfortunately, in city
conditions they have no broad practical application. The city architecture
could become more harmonious and economically effective with application of trailing
designs. Poles of such designs could serve as a basis for residential buildings
or offices. On each administrative region with the population in 200 - 300
thousand people one pole suffices. Thus poles of each area can be connected
trailing designs for high-speed movement and communications (warm gas supply,
water supply, power supply, communication, etc.).
The municipal and
regional authorities, having available very poor budgets, won't be able to
solve transport problems of the cities at modern level. Local means only cover
expenses on repair of the transport inheritance which has got from the last
century. Therefore, in our opinion, the uniform state program is necessary for
the optimum solution of transport problems of the largest and large cities of Russia.
For introduction and experimental approbation of this program by the author it
is offered to use conditions of such average city of Russia, as Saratov.
It was established above that the transport
system of the city will be the most effective, when ![]() , under a condition if the dynamic dimension of vehicles is equal to a
half of the area of a street road network. Considering this situation, we find
the area of vehicles on a formula:
, under a condition if the dynamic dimension of vehicles is equal to a
half of the area of a street road network. Considering this situation, we find
the area of vehicles on a formula:
![]() , (9)
, (9)
where ![]() - the coefficient depending
on speed of movement,
- the coefficient depending
on speed of movement, ![]() .
.
Further, we find number of cars on a formula:
![]() ,
(10)
,
(10)
![]() - number of cars;
- number of cars;
![]() - area of vehicles;
- area of vehicles;
![]() - average area of the car.
- average area of the car.
Knowing number of
cars, it is possible to find need amount of oxygen at their operation:
![]() , (11)
, (11)
where ![]() - need amount of oxygen at
operation of cars;
- need amount of oxygen at
operation of cars;
![]() - efficiency of cars;
- efficiency of cars;
![]() - operation time, hour;
- operation time, hour;
![]() - consumption of oxygen at
operation of cars, cubic m/hour.
- consumption of oxygen at
operation of cars, cubic m/hour.
The daily general
need of the city for oxygen is estimated on a formula:
![]() , (12)
, (12)
where ![]() - daily city need for oxygen;
- daily city need for oxygen;
![]() - daily need amount of oxygen at
operation of cars;
- daily need amount of oxygen at
operation of cars;
![]() - daily need amount
of oxygen at operation of the industrial, construction, agricultural, trade and
municipal enterprises of the city;
- daily need amount
of oxygen at operation of the industrial, construction, agricultural, trade and
municipal enterprises of the city;
![]() - daily need amount
of oxygen for the live world of the city, including and people.
- daily need amount
of oxygen for the live world of the city, including and people.
Need square of a
green zone for the city (![]() ) can be defined, knowing how many oxygen allocates one tree per day (
) can be defined, knowing how many oxygen allocates one tree per day (![]() ) and the area of one tree (
) and the area of one tree (![]() ), on a formula:
), on a formula:
![]() . (13)
. (13)
Thus, on housing,
the industrial, construction, agricultural, trade and municipal enterprises of
the city, and also a reserve of an urban area, there is an area (![]() ) which can be determined by a formula:
) which can be determined by a formula:
![]() , (14)
, (14)
where ![]() - square of an urban area at housing, industrial, construction,
agricultural, trade and municipal enterprises, and also reserve;
- square of an urban area at housing, industrial, construction,
agricultural, trade and municipal enterprises, and also reserve;
![]() - square of the city;
- square of the city;
![]() - area of city SRN;
- area of city SRN;
![]() - area of a green zone of the city.
- area of a green zone of the city.
Thus,
becomes obvious that transport, environmental, architectural problems of the
city need to be solved in a complex, and for this purpose it is necessary to
learn to estimate objectively a state of environment of activity of the person,
and on the basis of this assessment to formulate practical recommendations
about its improvement.
Literature:
1 . Krestmeyn, M.
G. of a problem of formation of the main street road networks big Cities /
Krestmeyn M. G. / Survey information "Problem of big cities". - M.:
MGTsNTI, 1986, âûï. 9, 32 with.
2 . Lebedev, Yu. S.
architectural bionics / Yu. S. Lebedev, V. I. Rabinovich, E. D. Polozhay//Under
edition Yu. S. Lebedeva. - M.: SI, 1990. -269 with.