Yemelina N., Teleuova A.
Karaganda
Economic University, Kazakhstan
The
lag model of interaction of investment and economic growth in the Republic of
Kazakhstan
The
role of investment in the economy of Kazakhstan is of great importance, because
they largely shape the future of the country, its regions, each economic entity
- investments made today are the basis of future prosperity. In turn, the
current economic condition is largely predetermined by past investments.
According
to Marchenko, the value of the investment is that the implementation of their
functions is a necessary condition and the foundation the following:
- restructuring of social production, the balanced development of all
sectors of the economy;
- the expanded reproduction;
- the acceleration of scientific and technical progress;
- ensuring defensibility of the state;
- development of financial markets, the banking sector;
- improving the quality of goods and services, ensuring their
competitiveness;
- protection of the natural environment, the solution of environmental
problems;
- increase in employment and reducing unemployment;
- international cooperation;
- social development [1].
Definitely
the effective use of investment business entities to the state's economy is
crucial, especially with regard to scaling up investment. When the desired
level of efficiency, investment leads to sustained economic growth.
Dependence
on the investment growth factor expressed by gross and net investment was
underlined by Kobozev.
Gross
investment - is the amount of invested funds allocated in fixed capital in a
certain period of time, these include investments to expand and upgrade [2].
Net
investment reflect the full amount of gross investment, which is reduced by
depreciation for the period. The amount of the investment determines the phase
of development of the economy [2].
Based
on this, the following causal relationships were established:
- The production capacity leads to expand production the economy is on the
rise in the development stage, if the amount of the gross investment is more
than depreciation charges.
- If the gross investment and depreciation charges are equal, the economy
has the same amount of investment, both incoming and consumed, it is
characterized by a lack of economic growth.
- If depreciation charges are more than the value of gross investment,
investment declines, reduced productive capacity, there is an economic
downturn.
Investment
process affects the development of the economy in a balanced mode, when the
amount of net investment affects the change in the economy, causing a
multiplier effect. In other words, in a recurring flow of investment
expenditure and revenue expenditure of one subject are becoming income to
other, the initial fluctuations volume of investment leads to repeated, each
time decreases, the change in income.
This
multiplier effect can act in the opposite direction. While reducing of
investment costs it would be a reduction of revenue. Therefore, the role of
investment in the economy that is necessary to ensure a certain coefficient
multiplier and to ensure conditions for a permanent investment activity. [3]
In
economic theory, economic growth is defined as "an increase in the volume
of economic activity as a result of increasing the number of factors of
production used or development of technique and technology" [4].
Sustained
economic growth of any country should be based on the existing objective
reality of economics and politics and be a reflection of the long-term
socio-economic development of the country as its main component.
Early as the end
XX century have determined that the primary purpose of economic growth is to
"increase the volume of production of goods and services, improving their
quality, providing better quality of life". [5]
The state as a
market participant should pursue policies to stimulate economic growth in order
to ensure the development of the national economy in its most important
industries. This policy must be coordinated with fiscal, investment, credit and
other economic policies. This relationship is necessary because it is able to
provide sufficient stability of the country as a complex sociosystem in market
conditions in order to achieve economic growth.
Sustained
economic growth is fundamental to improving the welfare of the population and
therefore the growth parameters can be used as the objective function at
modeling of many states. GDP growth ensures the welfare of the population, the
possibility of the development of enterprises and industries, and may increase
the country's competitiveness on the world stage, etc. Therefore, the policy of
most states is aimed to promote economic growth.
In our opinion,
for the dynamic sustainable development of economy of Kazakhstan is necessary
to stimulate production, to invest financial resources in the manufacturing
industry, create new machines, equipment and final products. Economic growth
without development of all sectors of the national economy is impossible.
However sectors of the economy cannot work if they do not have any invests.
That is why the government pays great attention to the state and development of
the investment policy of the country.
State investment
policy describes the dynamics of the following indicators: total investment,
share of investment in gross domestic product (GDP), share of real investments
of the total investments, total amount of real investments, share of real
investment flows to fixed assets and others.
Indirectly
but quite objectively characterize the state of the investment activity growth
rate of the main macroeconomic indicators: national income, GDP and GNP,
industrial production, release of major industrial products, agricultural
production, productivity of social labor and others.
Objectivity
of these indicators is in the assessment of investment activity, which related
to the fact that their growth is inconceivable without investment. These
indicators are certain extents characterize the efficiency of investment. If
the growth rates of these indicators outpace the growth rate of investment, it
is a clear sign of efficiency investments and vice versa.
In
turn, the mechanism of interaction between economic growth and investment,
which is formulated by the Nobel Prize P. Samuelson as the "principle of
the accelerator», is: real GDP growth leads to an increase real investments, in
turn, real investments rise leads to a response GDP growth. Important in this
principle is that a real investment refers only to increase the cost of fixed
capital (buildings, machinery and equipment) and industrial stocks, i.e.
investment in fixed capital.
In
connection with the foregoing, it seems interesting to determine the impact of
changes in the volume of investment in fixed capital to the dynamic (increase /
decrease) of gross domestic product of Republic of Kazakhstan.
We
have built a dynamic model of the Almon distributed lag to identify this
relationship. The main advantage of Almon’s method is versatile and it can be
used at modeling processes, which are characterized by different structures
lag.
General
view of the distributed lag model:
![]()
To
construct the model we used statistical data on GDP in the Republic of
Kazakhstan and the amount of investment in fixed capital in the period from
2000 to 2013 (Table 1).
Table
1: Trends in GDP and investment in fixed capital in the Republic of Kazakhstan
(2000-2013)
Millions
tenge (KZT)
|
Year |
GDP |
Investment in fixed capital |
|
2000 |
2 599 901 |
595 664 |
|
2001 |
3 250 593 |
943 398 |
|
2002 |
3 776 277 |
1 099 986 |
|
2003 |
4 611 975 |
1 327 864 |
|
2004 |
5 870 134 |
1 703 684 |
|
2005 |
7 590 594 |
2 420 976 |
|
2006 |
10 213 731 |
2 824 523 |
|
2007 |
12 849 794 |
3 392 122 |
|
2008 |
16 052 919 |
4 210 878 |
|
2009 |
17 007 647 |
4 585 298 |
|
2010 |
21 815 517 |
4 653 528 |
|
2011 |
27 571 889 |
5 010 231 |
|
2012 |
30 346 958 |
5 473 161 |
|
2013 |
34 140 040 |
6 052 907 |
|
Note: The data of the official Internet resource
Agency on Statistics of the Republic of Kazakhstan |
||
Construct
a model for distributed lag l = 3:
![]()
assume
that the lag structure is described by a polynomial of second degree:
![]()
It
is necessary to determine which effect is given investments in fixed capital
relative to GDP in the period of 3 years.
To
calculate the parameters of this model is necessary to transform raw data into
new variables z0, z1, z2 by the following formulas:
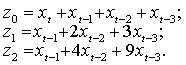
Table
2: Calculation of new variables.
|
Year |
GDP |
Investment in fixed capital |
Z0 |
Z1 |
Z2 |
|
2000 |
2 599 901 |
595 664 |
|
|
|
|
2001 |
3 250 593 |
943 398 |
|
|
|
|
2002 |
3 776 277 |
1 099 986 |
|
|
|
|
2003 |
4 611 975 |
1 327 864 |
3966912 |
4773774 |
10234554 |
|
2004 |
5 870 134 |
1 703 684 |
5074932 |
6358030 |
14218390 |
|
2005 |
7 590 594 |
2 420 976 |
6552510 |
7659370 |
16915014 |
|
2006 |
10 213 731 |
2 824 523 |
8277047 |
9811936 |
21186488 |
|
2007 |
12 849 794 |
3 392 122 |
10341305 |
12777527 |
27841583 |
|
2008 |
16 052 919 |
4 210 878 |
12848499 |
16304096 |
36478998 |
|
2009 |
17 007 647 |
4 585 298 |
15012821 |
19468691 |
43200073 |
|
2010 |
21 815 517 |
4 653 528 |
16841826 |
23183420 |
51957908 |
|
2011 |
27 571 889 |
5 010 231 |
18459935 |
26456758 |
60892622 |
|
2012 |
30 346 958 |
5 473 161 |
19722218 |
28073181 |
64892025 |
|
2013 |
34 140 040 |
6 052 907 |
21189827 |
29454207 |
67395837 |
|
Note: Compiled by the
authors |
|||||
Estimate
the parameters of the regression equation in the LS method. As the dependent
variable is the size of GDP. Calculated by formulas z0, z1, z2 are independent
variables. Obtain a three-factor linear regression model:
![]()
The
regression equation is statistically significant and meaningful as all the
regression coefficients with variables.
Find
the coefficients of the original model according to the formulas:
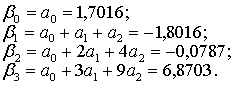
Thus,
the original model of distributed lag takes the following form:
![]()
Analysis
of the model shows that an increase in investment in fixed assets of 1 million
tenge will lead to an average GDP growth of 1,7016 millions tenge in the
current period.
When
investing in fixed capital in a year can be expected to decline in GDP by 0.1
million tenge, after two years at 0.17 million tenge.
Growth
of investment in fixed assets of 1 million tenge lead after three years to the
growth in GDP at 6.7 millions tenge.
We
calculate the contribution of each lag:
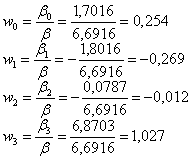
Consequently,
25.4% of the total increase in GDP caused by the growth of investment in fixed
assets, there is at the current time; -26.9% - a year; -1.2% - two years;
102.7% - in three years.
Average
lag model will be equal to:
![]() (years)
(years)
The
magnitude of the lag 2.79 years confirms that most of the effect of GDP growth
is manifested in three years.
Thus
we can say that the investment in fixed assets do have long-term positive
effect on the dynamics of the country's GDP, as one of the main indicators of
economic condition of the country. It
is interesting that in the first two years of their investment effect is
negative. However, the results allow us to assume that in the first two years
of the investment base of capital cannot be updated immediately, so the
investment does not demonstrate its effectiveness in the production process,
i.e. it is only partially transferred to the finished product. Naturally, this study can be expanded to accommodate other development
indicators of investment activity.
At
the macro level investment, and especially capital investment, are the
foundation for the development of the national economy and improve the
efficiency of social production, i.e. investment ultimately determine economic
growth.
References:
1. Марченко Г. Исследование
инвестиционного климата регионов России: проблемы и результаты / Г. Марченко,
О. Мачульская // Вопросы экономики. - 2011. - № 9.
2. Кобозев О.В. Анализ
подолов к оценке инвестиционной привлекательности регионов / О.В. Кобозев //
Экономика и управление. - 2010. - № 5 (66).
3. Тренев В., Лихачев А.
Повышение инвестиционной привлекательности региона // Информационные Ресурсы
России. - 2012.- № 5.
4. Гогуа М.В.
Финансирование инвестиций в инфраструктуру рекреационного комплекса: Автореф.
дисс. канд. эконом. наук. - Краснодар, 2011. - 25 с.
5. Оспанов М.Т., Мухамбетов
Т.И. Инвестиционный капитал и инвестиции: вопросы теории, практики привлечения
и использования. – Алматы, 2009.