Implementation of Lean Thinking to the Radiology Department
By Shayakhmet Umirzak,
Shimkent University, 2016
1. Introduction
The health care industry
is one of the world’s largest and fastest-growing industries in the world
recently. Healthcare management is a complex business that must continuously
balance the need for medical care together with an attention to the financial
constraints. Ageing population, technological investments, and operational
inefficiencies may cause cost increases in health care systems. One way to
improve this situation for the healthcare sector is to examine its processes
and to deliver care more efficiently and effectively within available budgets.
Although involving a
number of excellences and demonstrating outstanding advances in technology and
treatment, the healthcare sector is rife with inefficiencies and errors (Taner
et al., 2007).The related costs are largely under the control of healthcare
professionals (De Koning et al., 2006). Applying continuous improvement
philosophy and the techniques from lean management can provide a basis for
innovations as high quality healthcare service with lower costs (Brandao de
Souza, 2009).
This study demonstrates
how to apply lean philosophy in a teaching medical hospital, particularly in
the radiology department, with regards to the patient waiting time and cost of
printing the MR images. The study also expects to increase access to hospital
services and reduce costs while improving the quality of patient care.
Keywords: 5S, Kaizen, Lean Hospital, Lean Healthcare Applications
2. Lean Thinking
Lean is a
customer-centric methodology focused on continuously identifying improvement
opportunities by eliminating “non-value added” (or wasteful) activities and
creating value. Lean thinking puts the expectations of patients at the center
of the procedures for improving the hospital efficiency; getting an appointment quickly, understanding the consequences of their treatment, knowing how long they will stay in hospital,
being able to choose their meals, etc.
These basic patient requirements are no longer unmet due to operational
constraints but are incentives for changing the organization of the hospital.
3. Implementation of Lean
Thinking to the Radiology Department
Founded in 1996, the
medical university hospital has over 20,000 students and 810 academic staff
operates under the motto of ‘A world
university’. Having over 15 years of experience in medical education in Ankara,
than it has been moved and opened several branches in Istanbul. Along with the medical faculty, the
radiology department serves patients 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. Screening
devices used to set diagnosis can be connected to each other with the help of
digital radiology and archiving system at the radiology department. The
screening results are saved in the computer and can be sent online to another
centre.
This study emphasized
the improvement of the system performance by using lean management tools adding
value to the service rendered, reducing costs and increasing the healthcare
revenue in the hospital. Processes
within the system of the patients admitted to the radiology department was
transferred to a time function map, bottlenecks and unnecessary costs are
identified and measured,activities to achieve the goal of kaizen has been planned. Then PDCA cycle have been utilized
to identify the root cause of our study.
Time Function Analysis
While making the value-stream map value added time and
waste should be separated from each other. Non-value added time of the system
are named as waste and will be eliminated from the system. Net hours worked are calculated by
dividing the patient demand. The following is how we proceeded to calculate the
Net Working Time.
Healthcare
institutions are working 7/24. Therefore, total operation time is
calculated over 24 hours.
Total Run Time = 24Hours / day x 60 minutes / hour =
1440 Minute = 86400 seconds / day
Net Working Time = 24
hours / day = 1140 minutes / day = 86400 seconds / day is calculated.
The results shows that
the patient time in the department have been reduced from 22,75min to 13,75min
as indicated on the map.
Tact Time
The tact time is a term
used for the rate of just equal Production quantities sold . Tact time = /. It
is compared to the cycle time. Cycle time is a reflection of the production:
this is the unit of time required to produce 1 piece to the customer. TC = /.
It is used in this study to determine the time spent by a patient before and
after lean tool implementation in radiology department.
The total number of
patients admitted to MRI, CT and X-ray in Department of Radiology is 53 523
persons as given in Table 4.
Radiology department provides services 365 working
days in a year. Accordingly, the tact time is calculated as follows.
Daily demand = 53 523/365 = 146,7≈147 person /
day
Takt Time = Daily Working Time / Daily Demand
Takt Time = 86400 seconds / 147 = 587.8 seconds /
person. So, for a patient MR to CT or X-ray takes average 9.8 minutes.
Table 1. Radiology
department cycle time before lean thinking
|
|
X-RAY |
MR |
CT |
|
Image Printing |
10 minutes |
10 minutes |
10 minutes |
|
Report hours |
4 hours |
4 hours |
4 hours |
Table 2. Radiology
department cycle time after lean thinking
|
|
X-RAY |
MR |
CT |
|
Report |
1 hours |
4 hours |
4 hours |
PCDA Cycle
 It is an iterative four-step management method used for the control and
continuous improvement of processes and products. Therefore it is useful to our study since the aim of kaizen is to
eliminate waste and keep it improving. The plan–do–check–act cycle (Figure 1)
is a four–step model. Just as a circle has no end, the PDCA cycle should be
repeated again and again for continuous improvement.
It is an iterative four-step management method used for the control and
continuous improvement of processes and products. Therefore it is useful to our study since the aim of kaizen is to
eliminate waste and keep it improving. The plan–do–check–act cycle (Figure 1)
is a four–step model. Just as a circle has no end, the PDCA cycle should be
repeated again and again for continuous improvement.
Figure.2 PDCA cycle
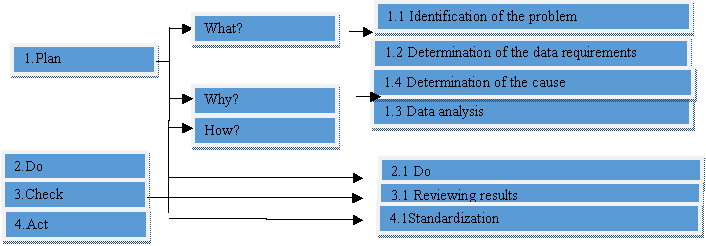
PLAN
The planing importance layed on the
requirement to educate the radiology department’s physicians, employees on the
cause of switching to the digital system and adopting lean management method.
In planing process three questions were asked to help us implement the lean
management tool: What, why and how? The
answers leads us to the followings:
July 2014 - July 2015 data
|
|
NUMBER |
UNIT PRICE |
COST |
|
|
LOGO
CD |
15400 |
3,05
(unit) |
8442,68 (unit) |
|
|
The
CD CUP LOGO |
16475 |
0,15
|
2471,25 |
|
|
BIG
BAG X-RAY |
23841 |
1,05
|
25033,05 |
|
|
X-RAY
PURSE SMALL |
10995 |
0,70
|
7696,5 |
|
|
TOTAL
43643,23 |
||||
|
FILM
+ MACHINE FEE |
148147,70 |
|||
|
TOTAL |
191790,93 |
|||
It shows the total cost
of both films and machines fromJuly
2014 - July 2015.
Determination of the
cause
The PCDA cycle help us to determine the root
cause of waste in the department. Some of these causes are mentioned in the
following table:
|
1.
Patient
complaints (patients have to carry X-rays results with them) |
|
2.
Patients
forget have to print again the film that is why patients must pay a fee for
it |
|
3.
waste
of time staff who prints (workload again) |
|
4.
Delays
being experienced in the treatment |
|
5.
Archive
storage space shortage (forgotten films are stored 1 month) |
|
6.
Loss
of prestige, environment and state hospitals already have passed this system
of hospitals) |
|
7.
Have
increased the cost of the film |
|
8.
Business
inserting the film in the present operation leads to loss of time in service. |
|
9. Lack of
connection between different departments |
Do stage:
After detecting the causes of waste in the radiology
department, some steps have been put forward to correct them. Kaizen have been implemented in the department process, from patient’s
admission to the issue of the CDs. Therefore some measures are taken:
§
When pictures doesn’t fit on CDs
then the department can use DVDs.
(films shot on the same day at the same CDs)
§
Keeping CDs According to the
shooting
§
Tomography is recorded on the DVD.
§
Patients who applied again will be
given CDs
§
Designing of paperboard CD
Check:
In this area plan is made to test the efficacy and
efficiency of our implemented Kaizen method.
For improvement results must be reviewed:
o
MR, CT writing on CDs 08/07/2015
o
Getting lost in the floor, CDs
should be in CD container files
o
The plaza is not used; print of CDs
is slow, missing image, difficulties in guiding patients
o
The fail probabilities in Plaza
o
The determined image of a doctor can
be which detects or visual may have difficulties
o
Films print request from the outside
(another hospital external filming, and then getting the patient treatment)
o
CD printing by patients requests,
Storage increased of X-ray CD printing.
o
We will continue through the PACS
o
MR Tomography devices can benefit
their own CDs.
o
The launch of the draft work of the
files (for the patient's final report and CD storage)
o
Printing Machine Company gets back.
DSA will have own room.
o
The first CD robot is not working
properly.
Before
lean implementation, the following table shows cost of performance
July 2014 - July 2015 data
|
|
NUMBER |
UNIT PRICE |
COST |
|
|
LOGO
CD |
15400 |
$0,18(3,05TL
KUR) |
$2772/
8442,68 TL |
|
|
The
CD CUP LOGO |
16475 |
0,15
TL |
2471,25 |
|
|
BIG
BAG X-RAY |
23841 |
1,05
TL |
25033,05 |
|
|
X-RAY
PURSE SMALL |
10995 |
0,70
TL |
7696,5 |
|
|
43643,23 |
||||
|
FILM
+ MACHINE FEE |
148147,70 |
|||
|
TOTAL |
191790,93 |
|||
After Lean Implementation
August 2015-August 2016 (number and unit price is calculated from the
maximum value)
|
|
NUMBER |
UNIT PRICE |
COST |
|
LOGO
CD |
40000 |
$0,14(3,05
KUR) |
$5600/
17080 TL |
|
BIG
BAG X-RAY |
1000 |
1,05
TL |
1050 |
|
POCKET
REPORT FILE |
35000 |
0,5
TL |
17500 |
|
35630 |
|||
|
EARNINGS |
156160,93 |
||
·
FILM PRINTING MACHINERY Removed
·
SMALL X-RAY BAG deprecated
·
DIGITAL PRINTING FAIR USE CD with CD
were REDUCED COST
·
CD CUP COST lifted
4. Conclusion and Future
Work
The radiology department
is one of the most highly congested departments in the hospital services, and
faces a great pressure, compared to the other departments in the hospitals.
Delays in the activities of this department would result in difficulties in
scheduling services at specialty units and decrease patients satisfaction. This
study addressed the cost and time reduction through lean thinking. The objective
of this research was to study the scope of lean thinking and in particular to
explore its successful deployment in the radiology department of a medical
university hospital.
The
study presented here was restricted to the objective of studying the impact of
lean thinking on the cost and time wastage of the patients in radiology
department only. The study was limited within only radiology department.
However, a careful observation of the results led to the conclusion that there
could be further scope of improvement in managing the image printing time and
its cost. Utilizing advantages of information technology could be effective for
further improvements.
References
1.
BozenaP. (2010) , “The current state
of Lean implementation in health care: literature review”
2.
Christopher S. Kim, David A.
Spahlinger, Jeanne M. Kin, John E. Billi. (2006), “Lean Health Care: What Can
Hospitals Learn from a World-Class Automaker?”
3.
Gopala K. N. murthy, AnandG.(2014),
“Lean Thinking in Healthcare Sector: Experience from an Indian Hospital”,
Indian Institute of Management Kozhikode, Kerala, India
4.
Rajeev C. M. Potash, A. Singh, and
J.Kalra. (2012)“Lean and queuing integration for the transformation of health
care processes”, Royal University Hospital, Saskatoon, Canada
5.
Janet H. Sanders, and Tedd Karr
V.(2015), “Improving ED specimen TAT using Lean Six Sigma”, East Carolina
University, Greenville, North Carolina, USA
6.
John S. Toussaint and Leonard L.
Berry. (2014), “The Promise of Lean in Health Care”
7.
Joseph C. Chen, ChaitanyaThota.
(2012),“Implementing Lean Methodologies in Healthcare Systems - A Case Study”, Bradley University Peoria, IL 61625, U.S.A
8.
Michael B. , and Anne R.(2007),“Lean
as a learning system in a hospital ward”, Hopital Nord 92,
Villeneuve-la-Garenne, France